|
Quickly go to:
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
In this article:
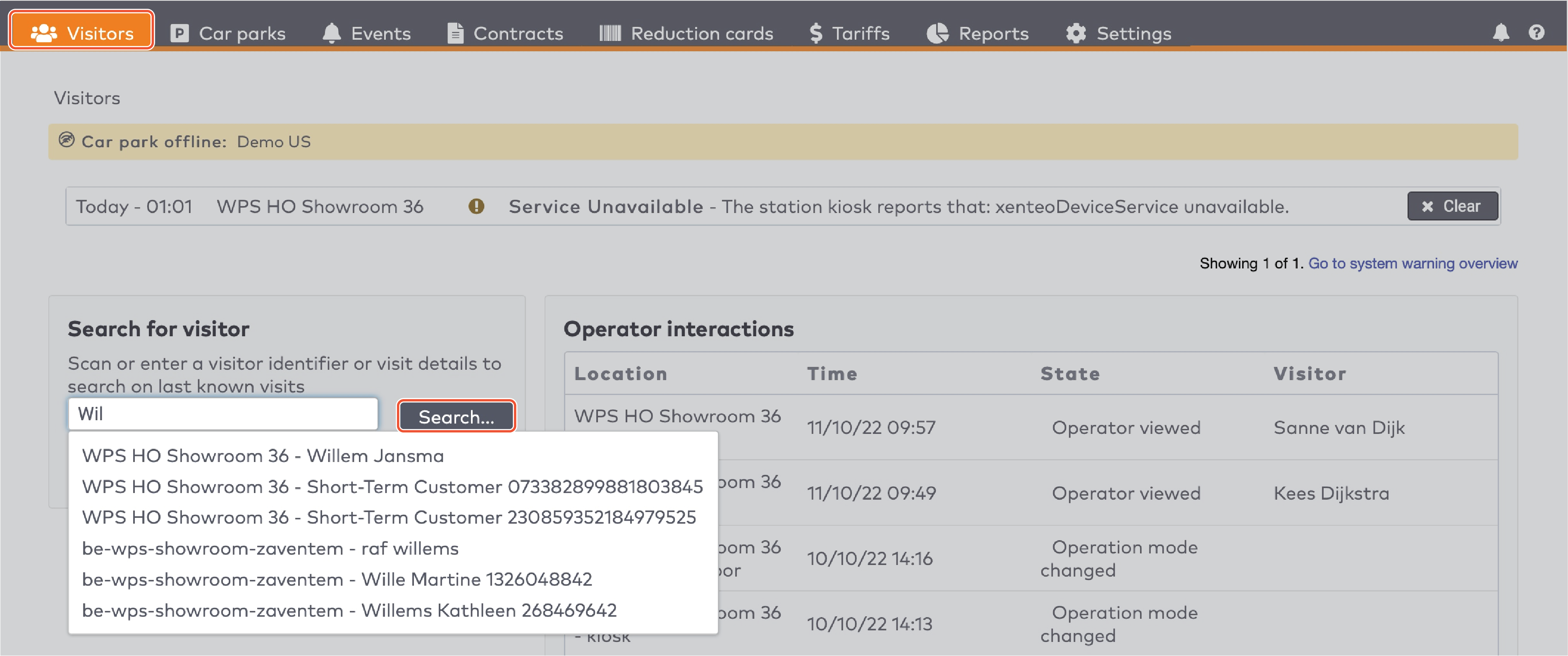
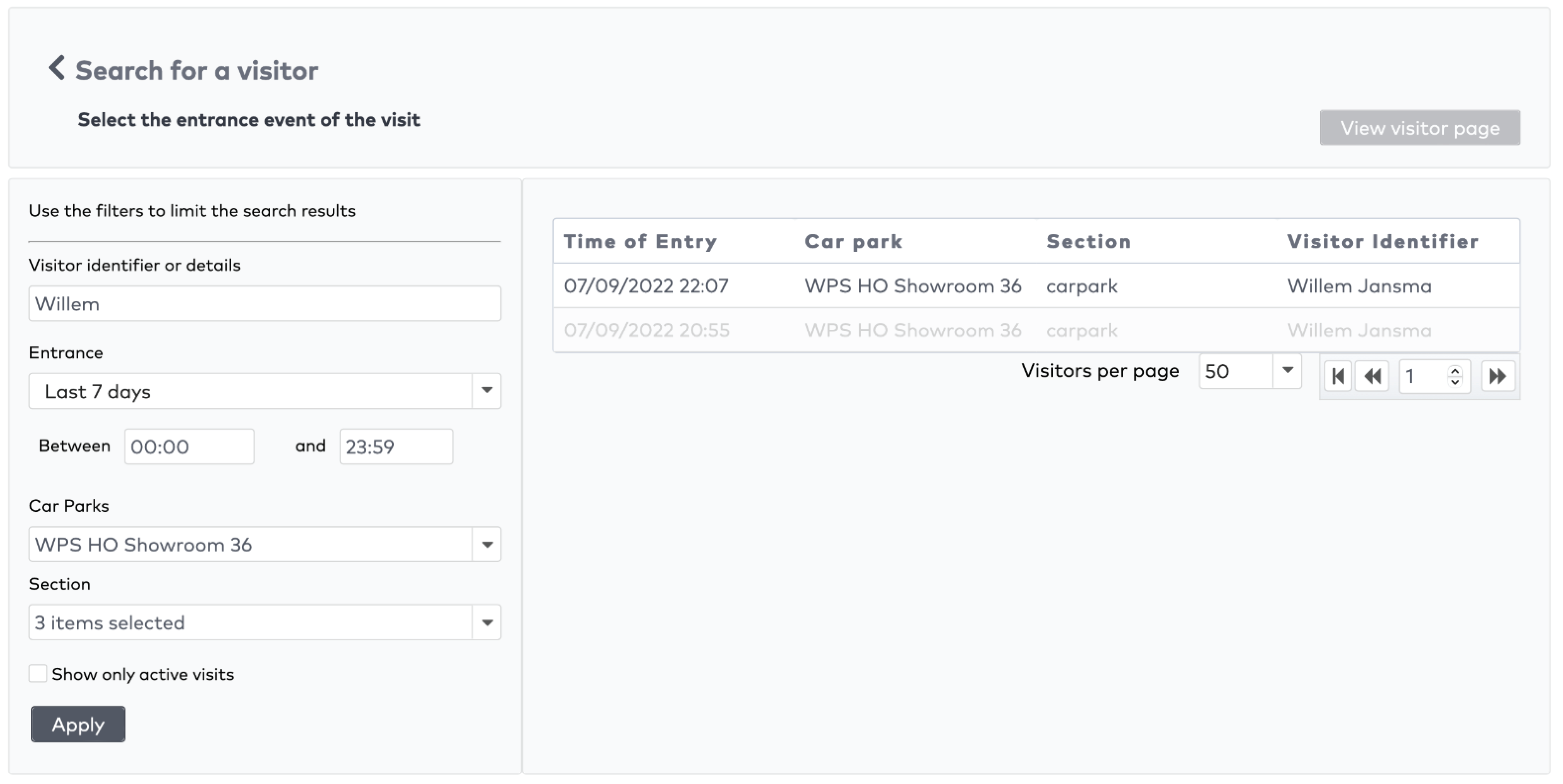
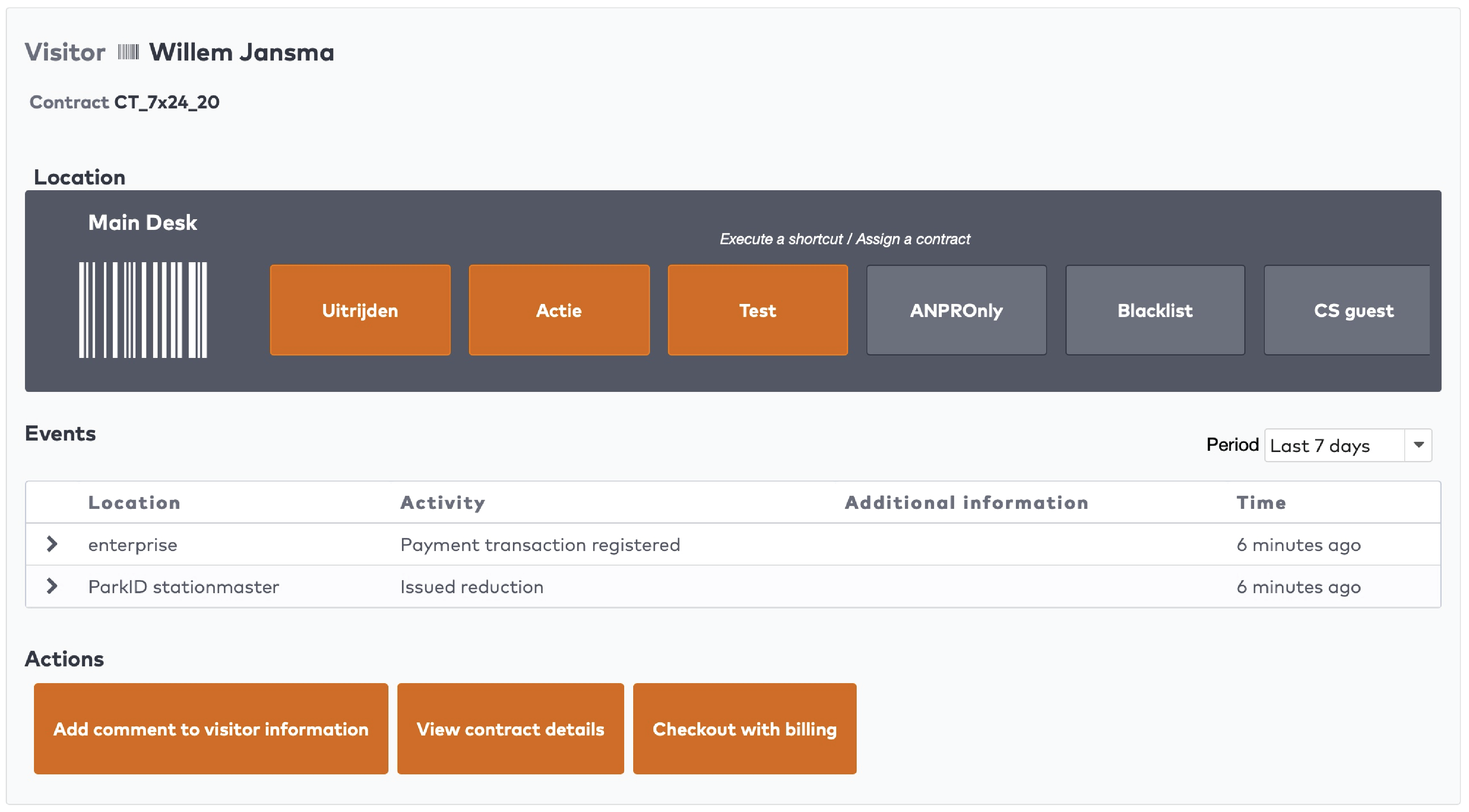
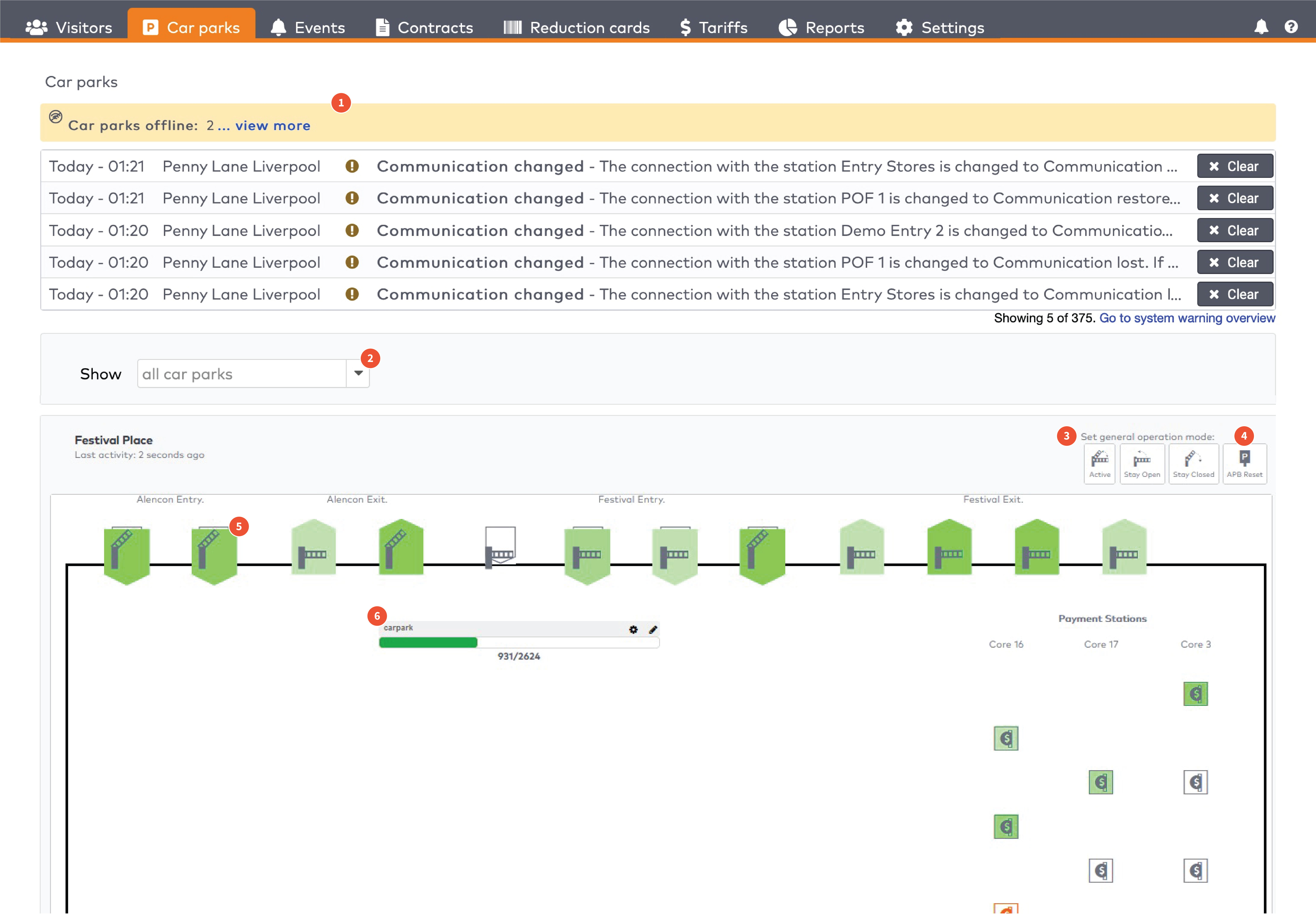
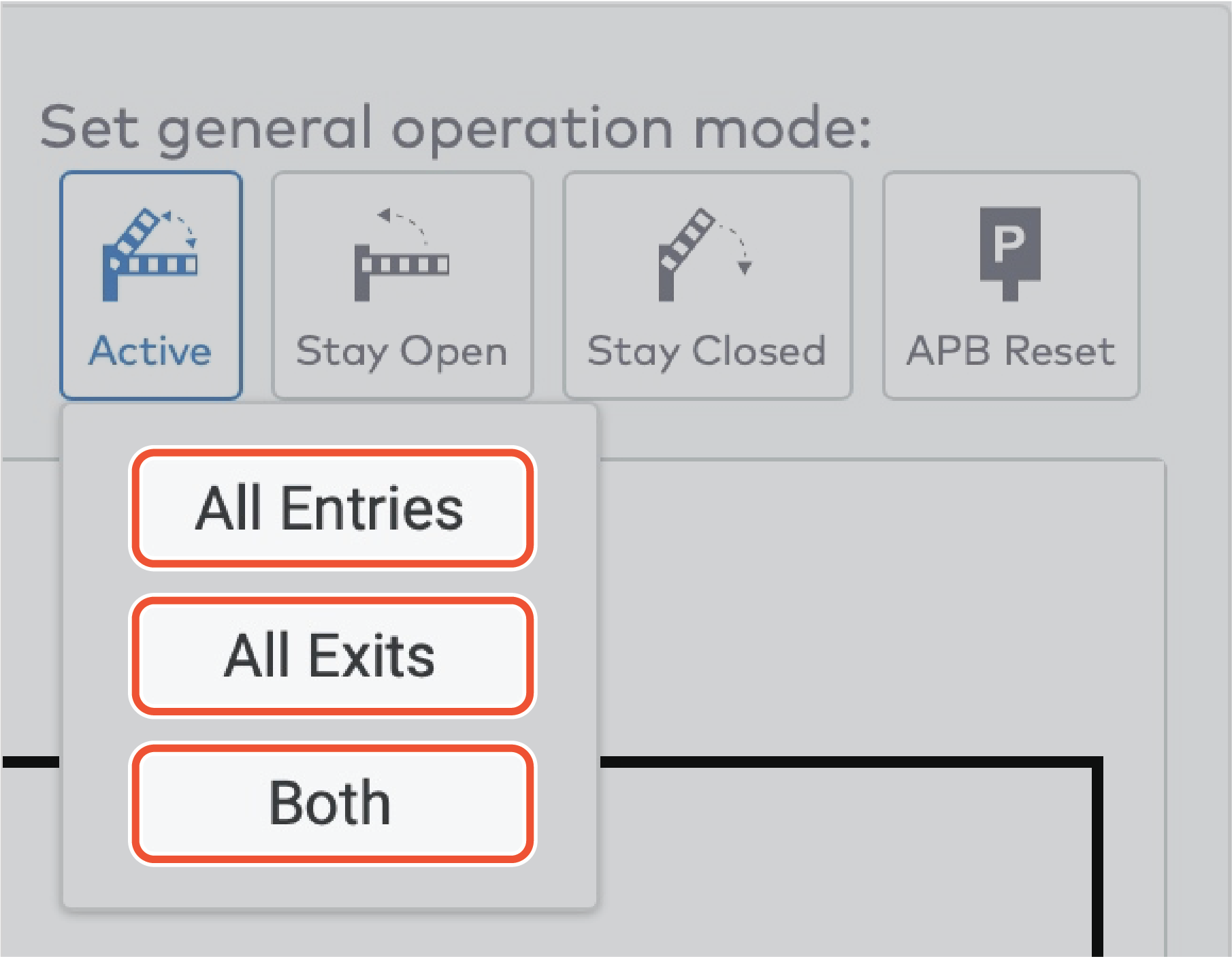
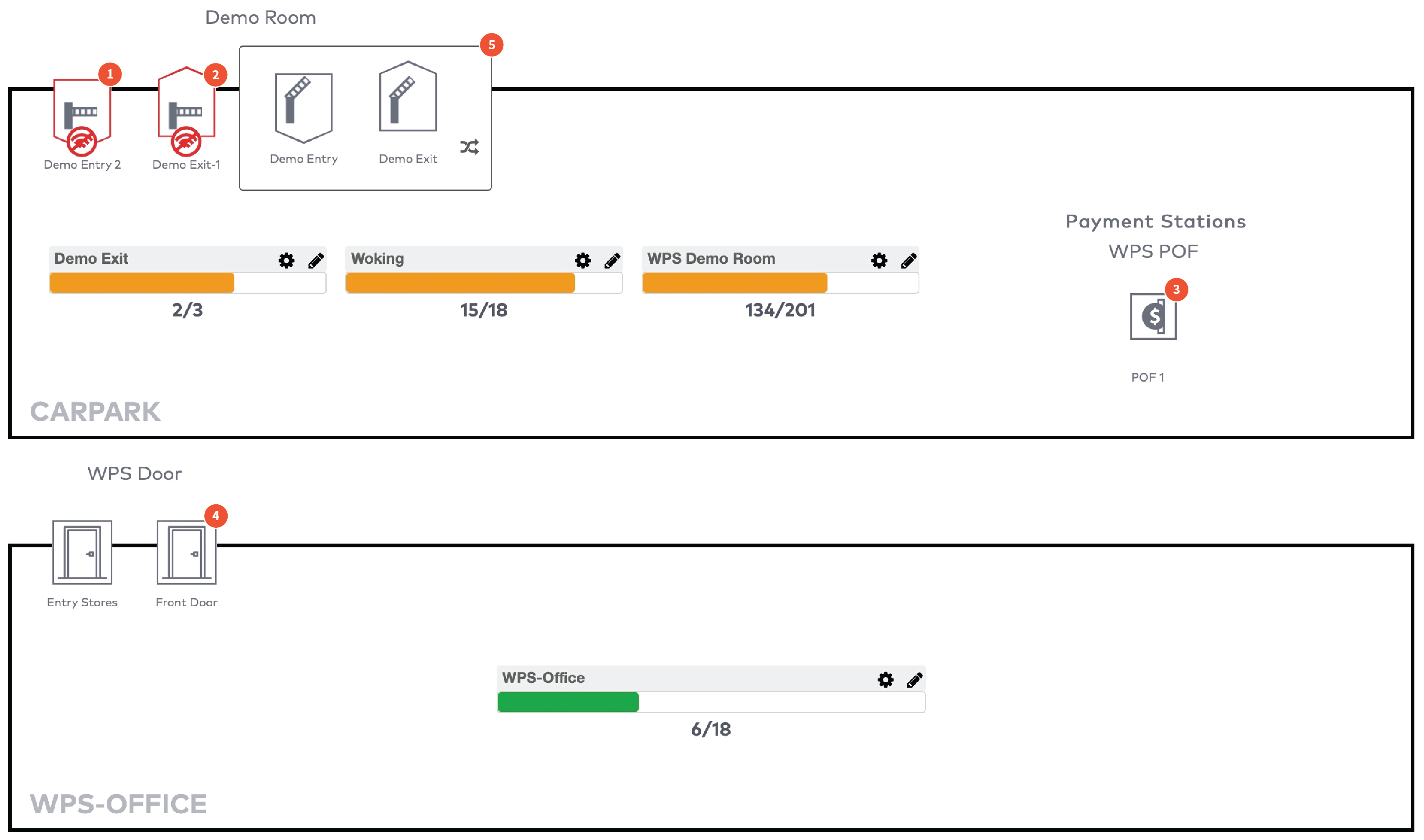
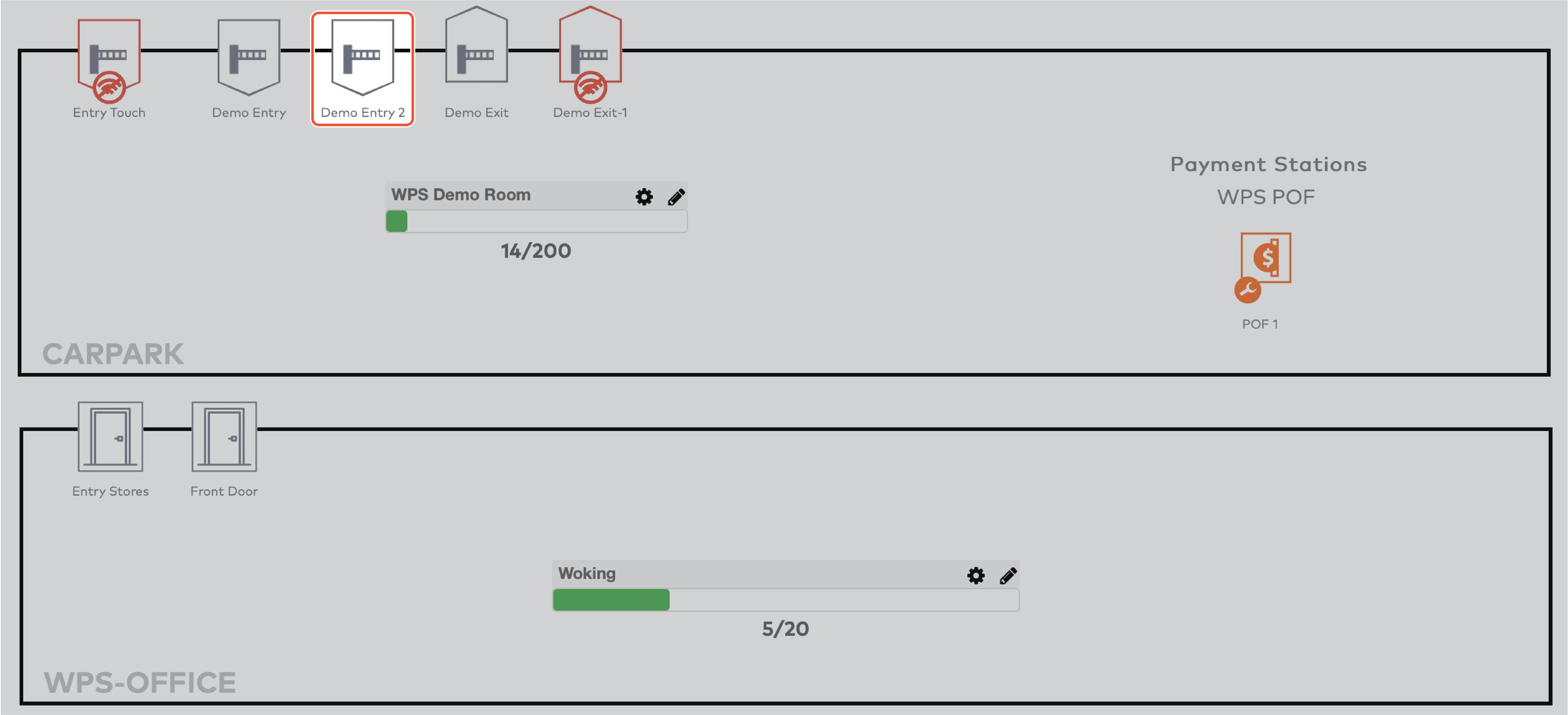
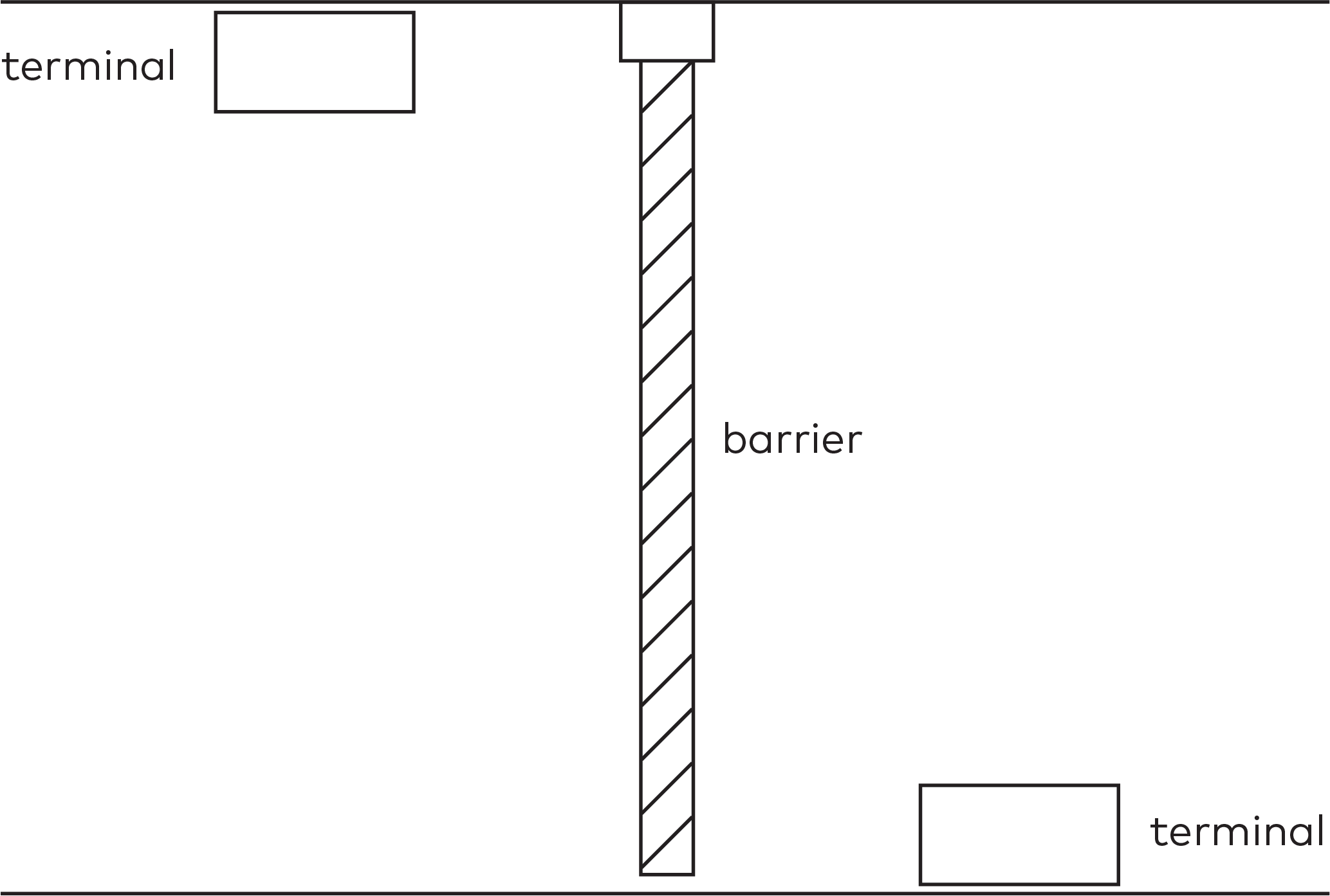
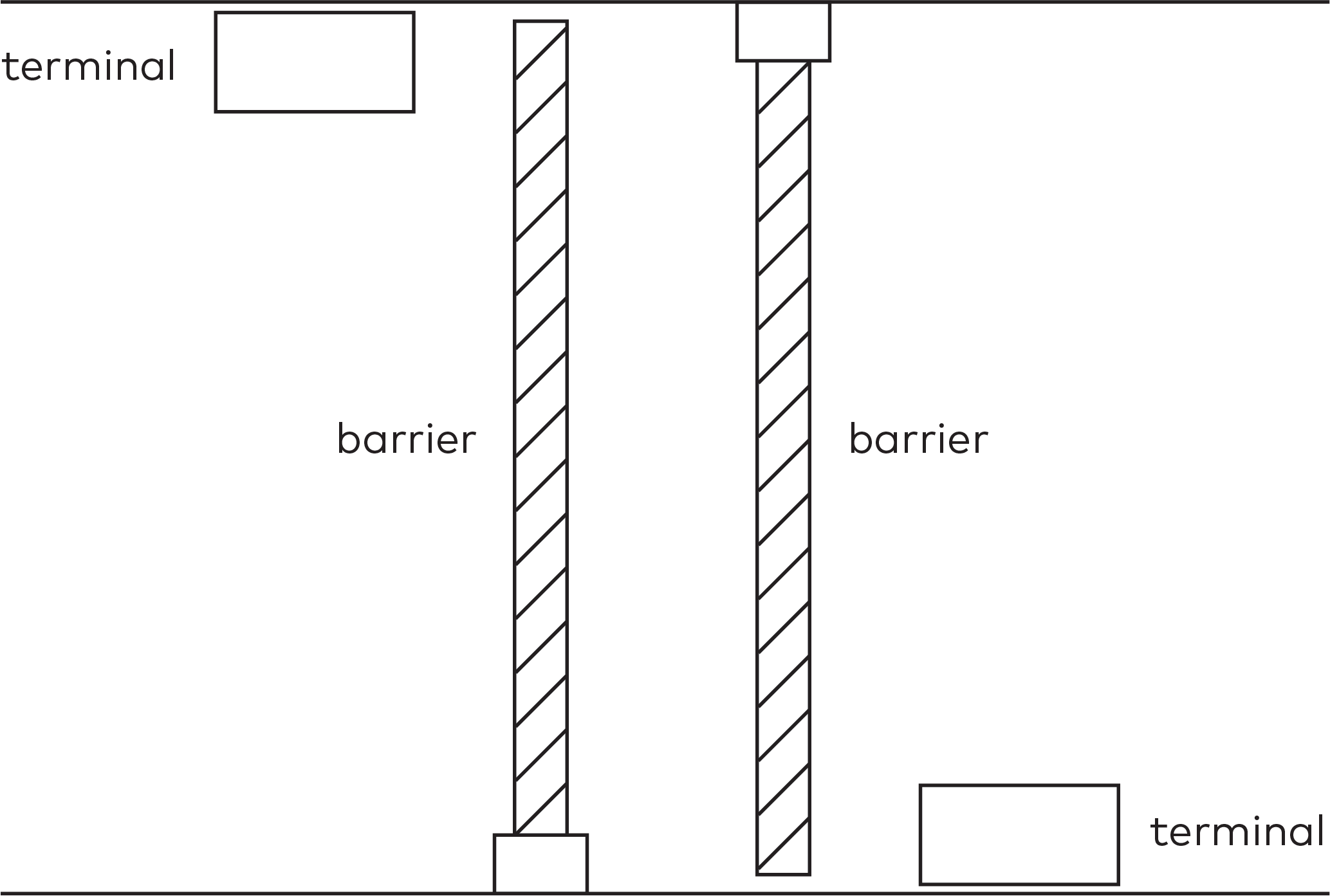
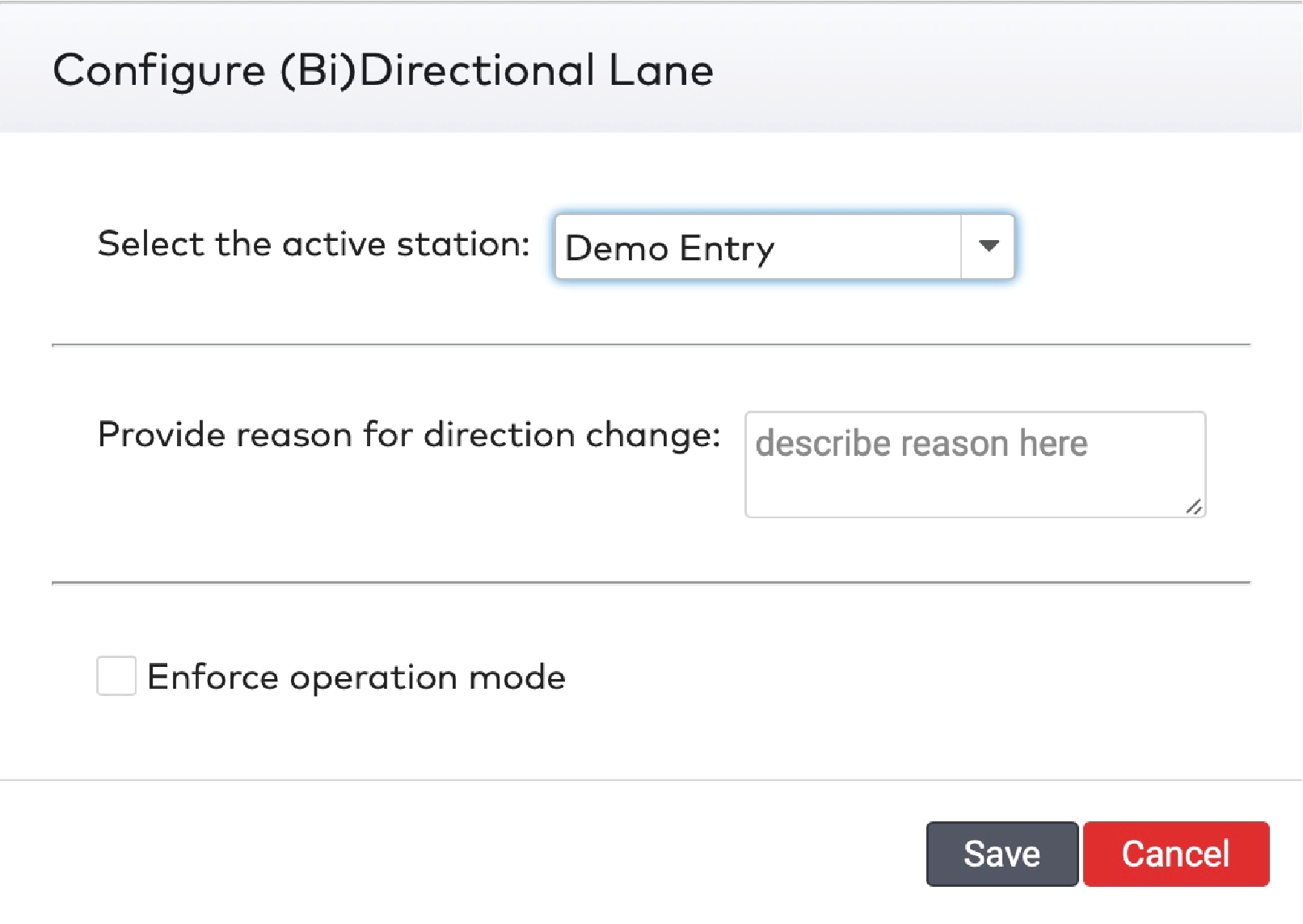
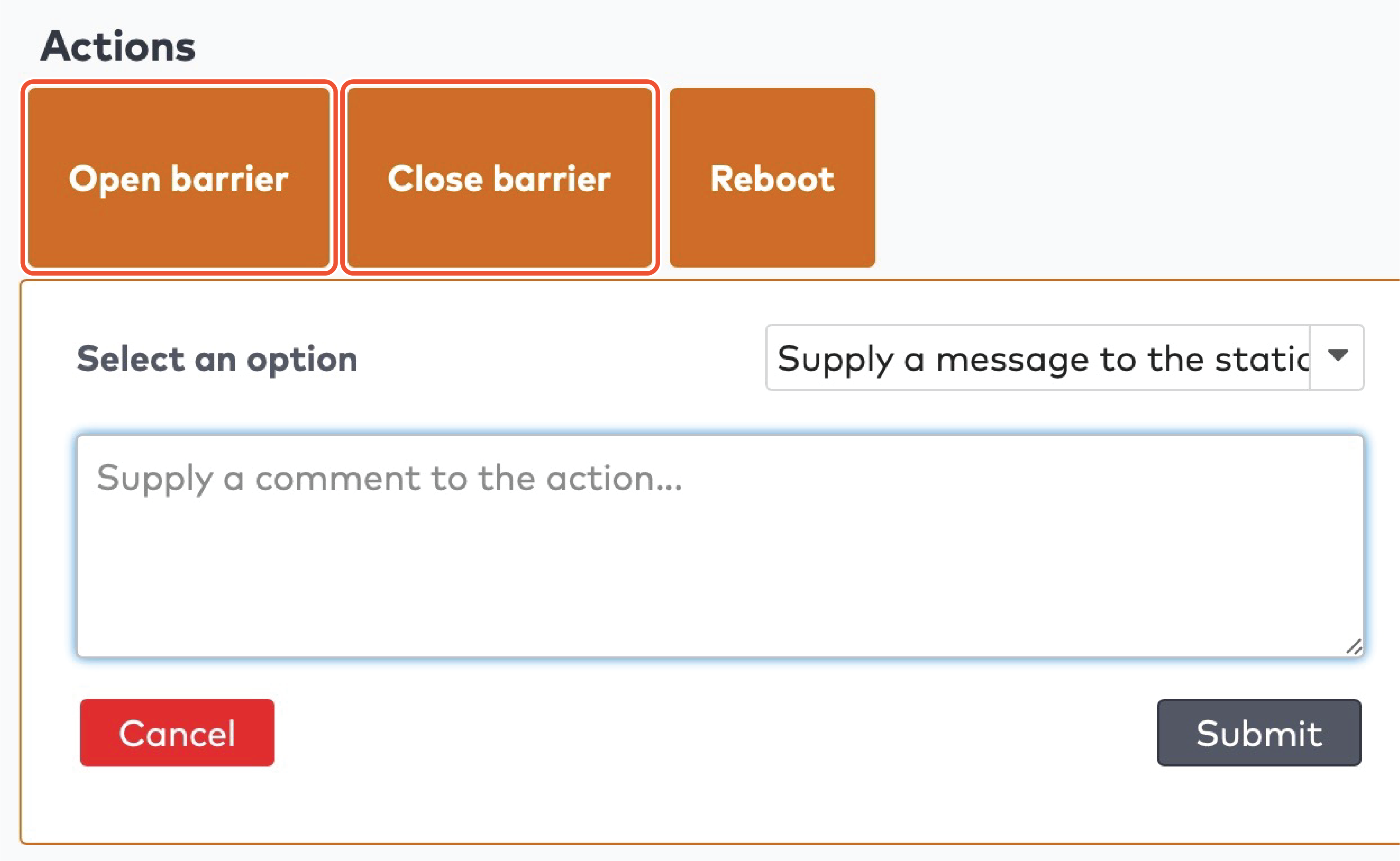
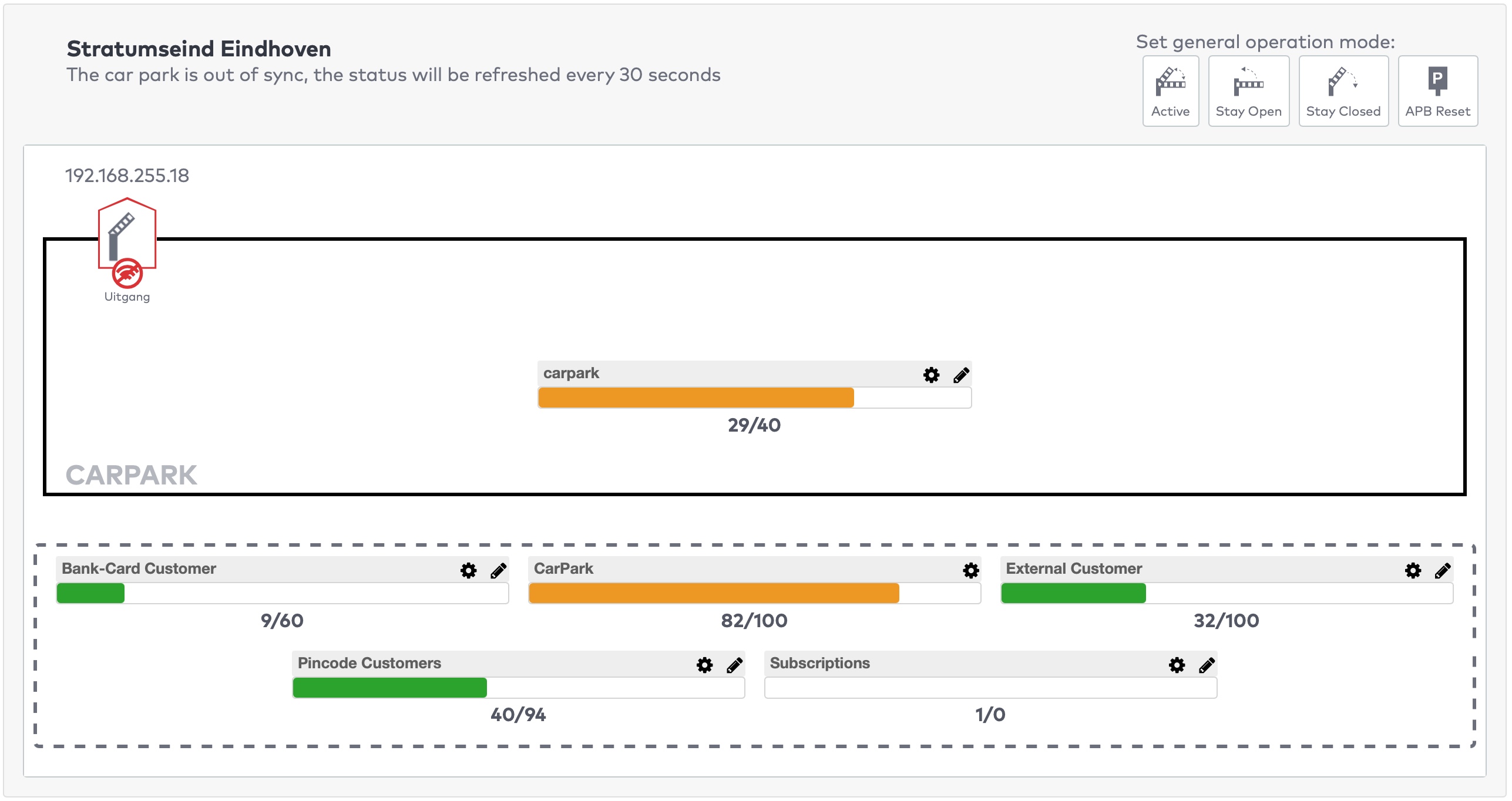
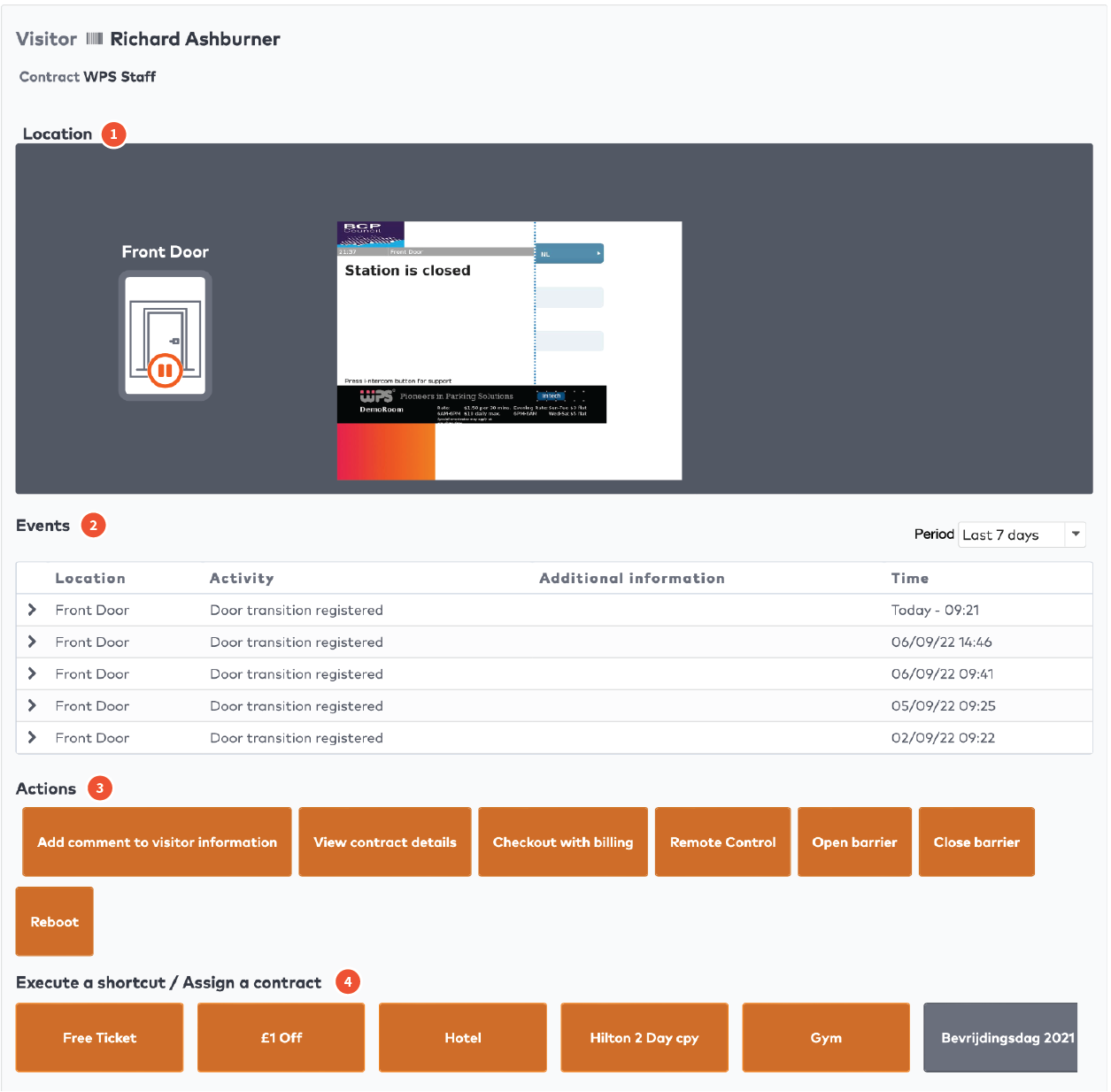
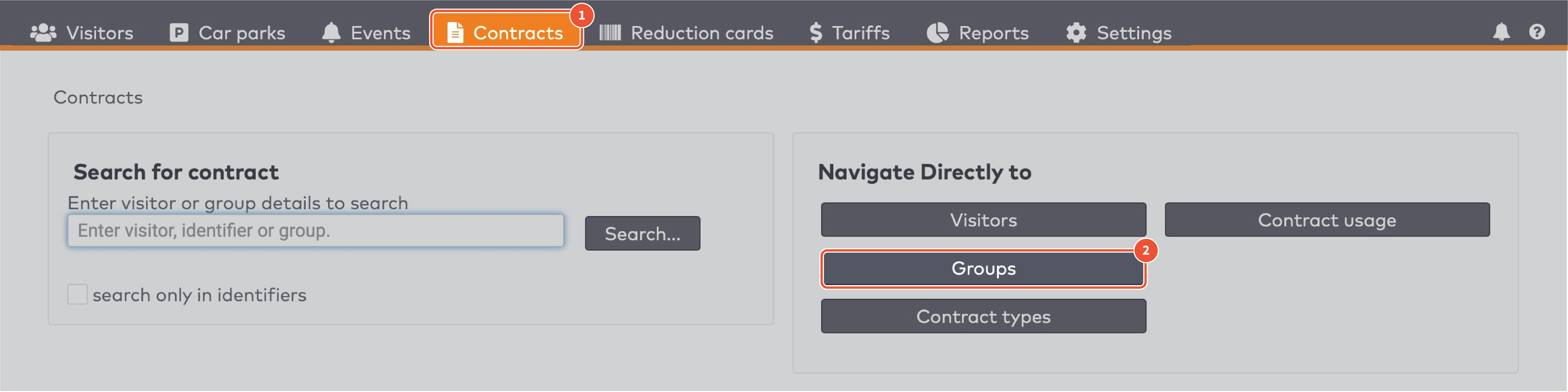
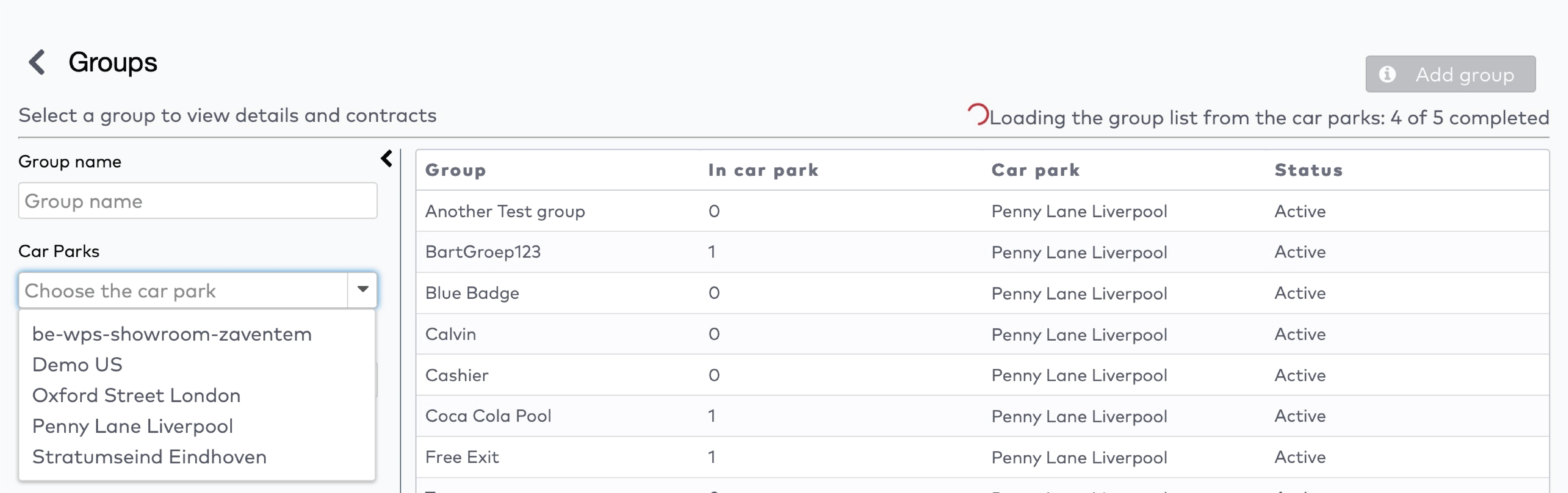
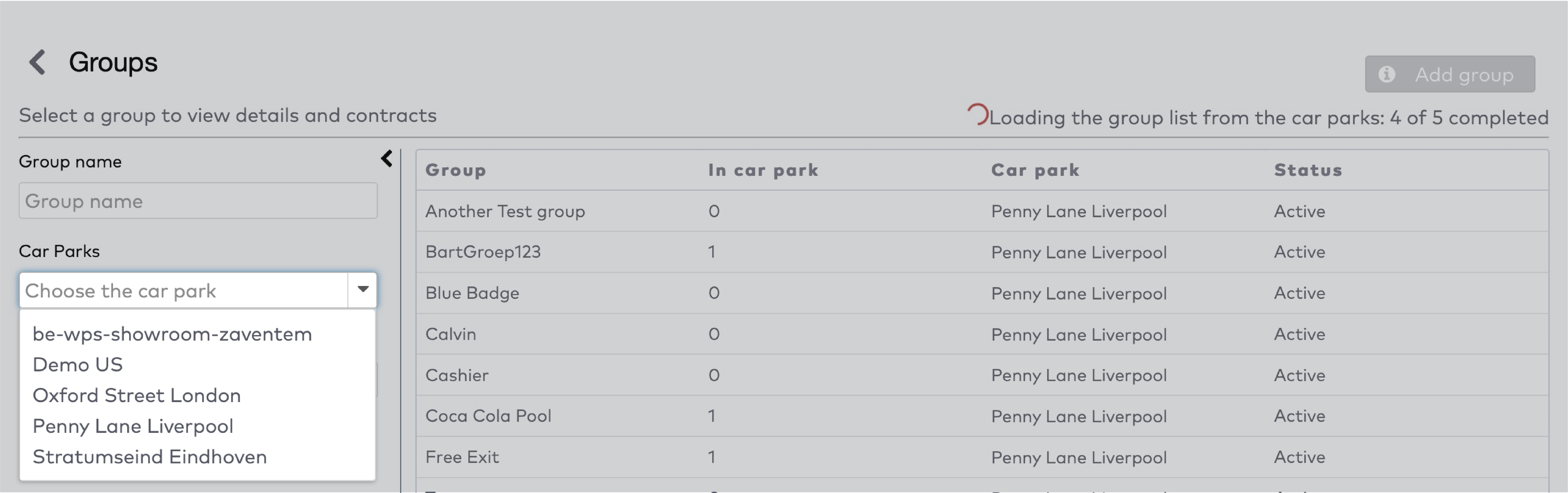
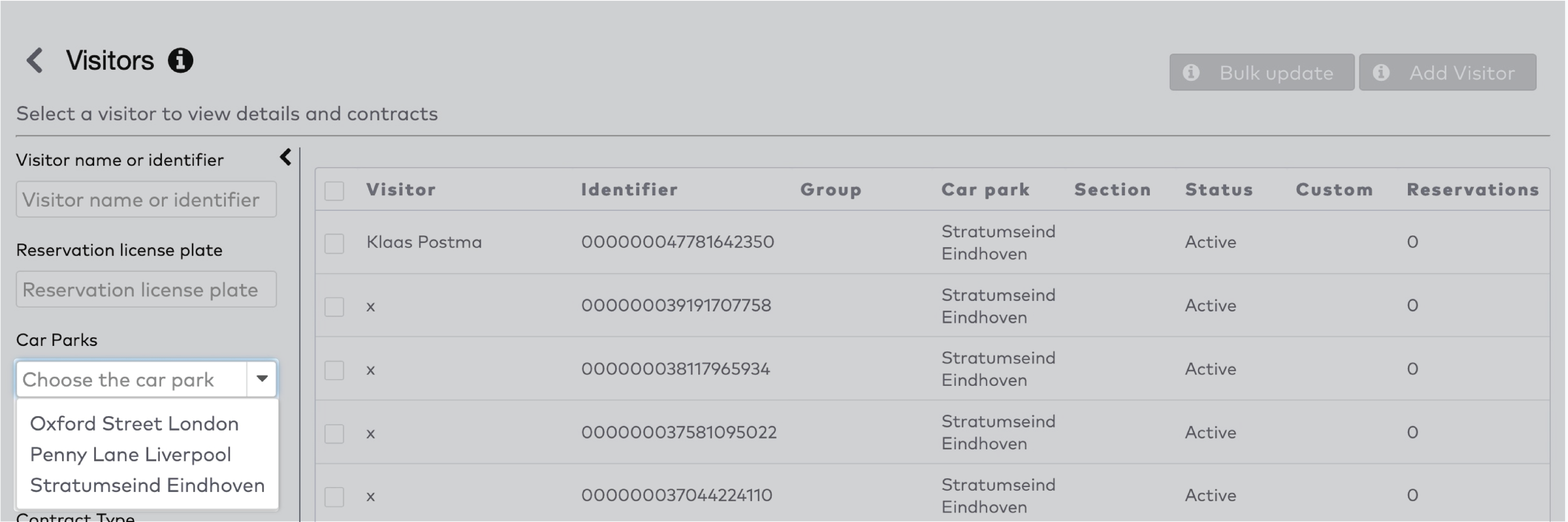
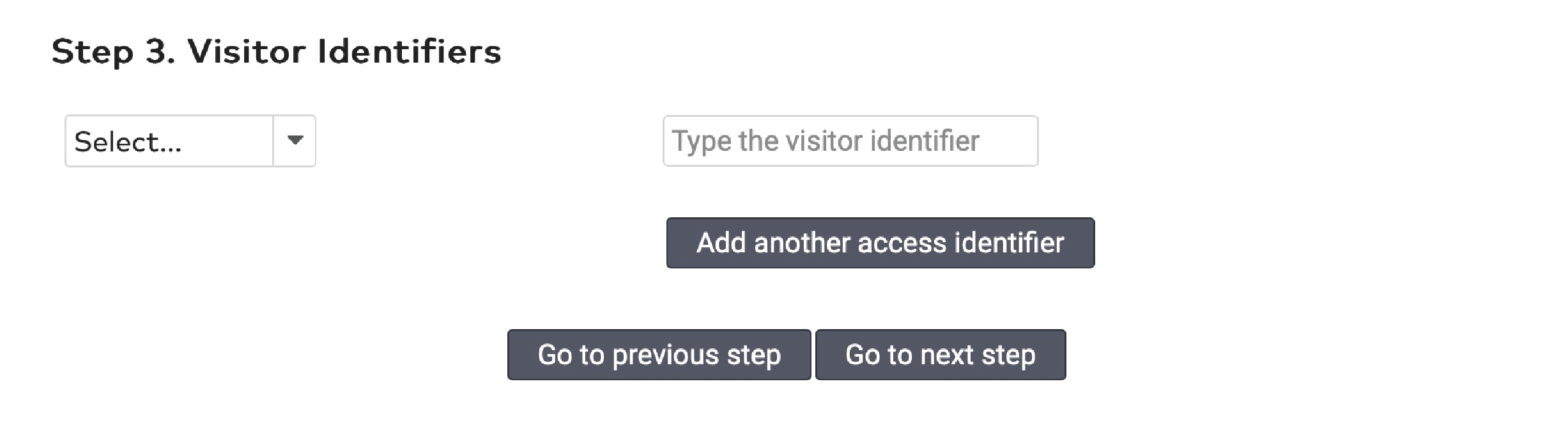
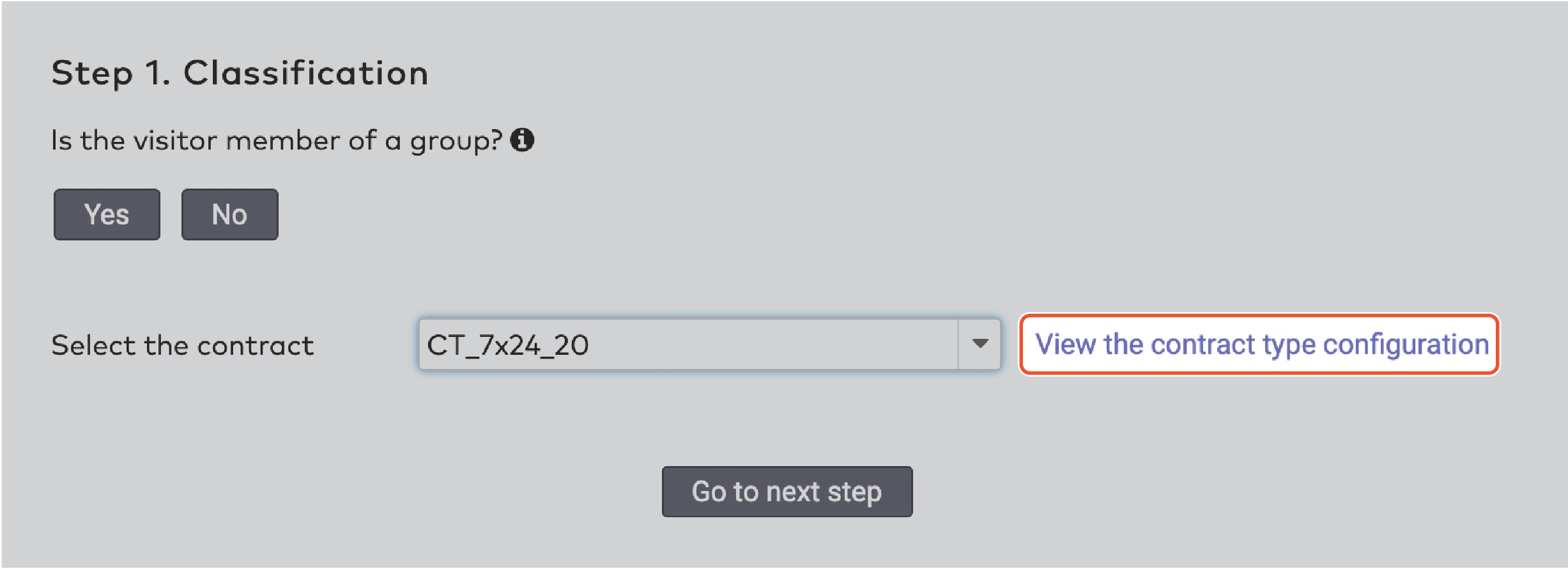
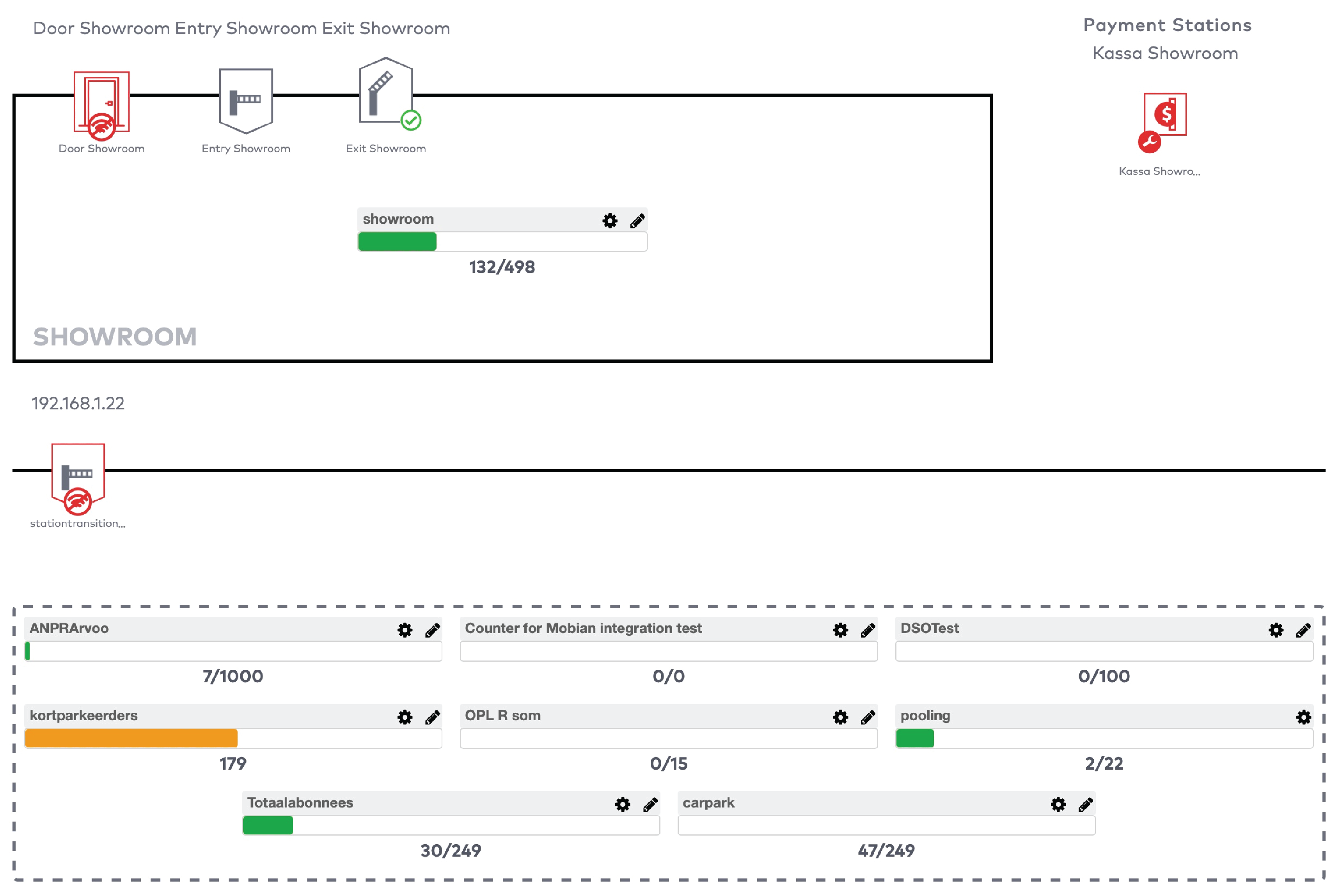
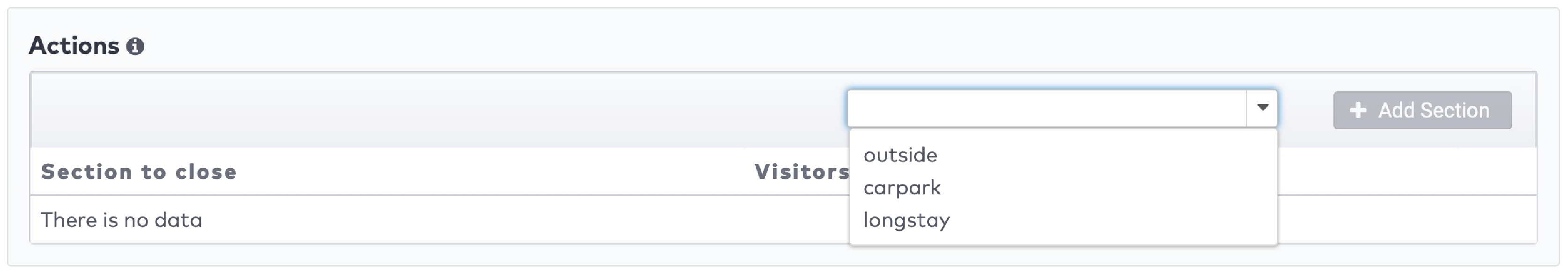
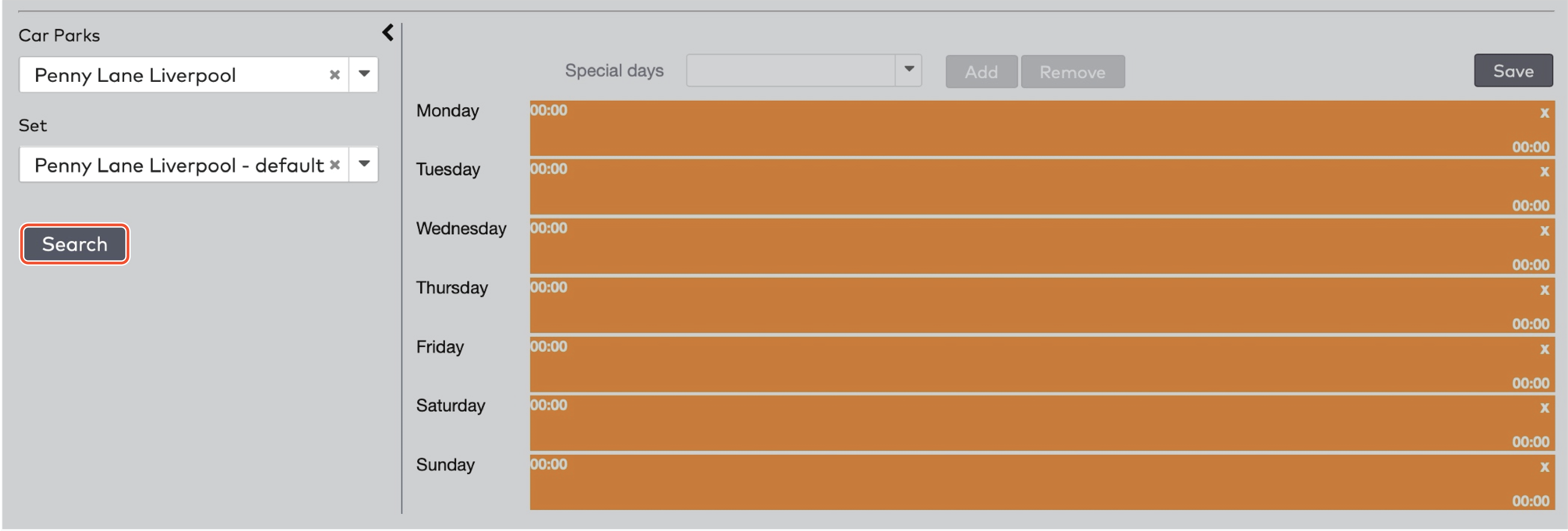
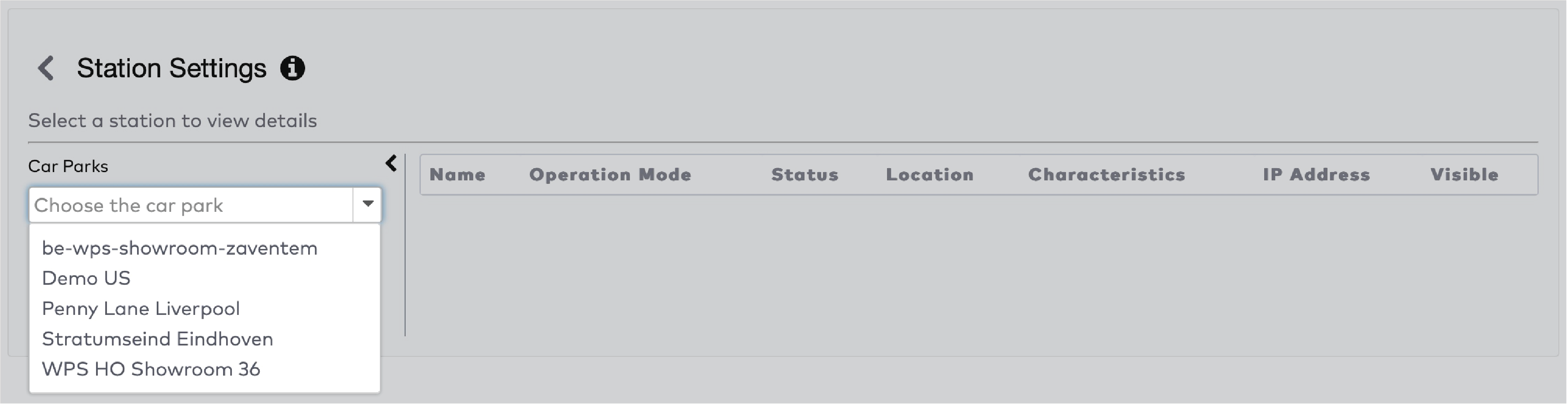
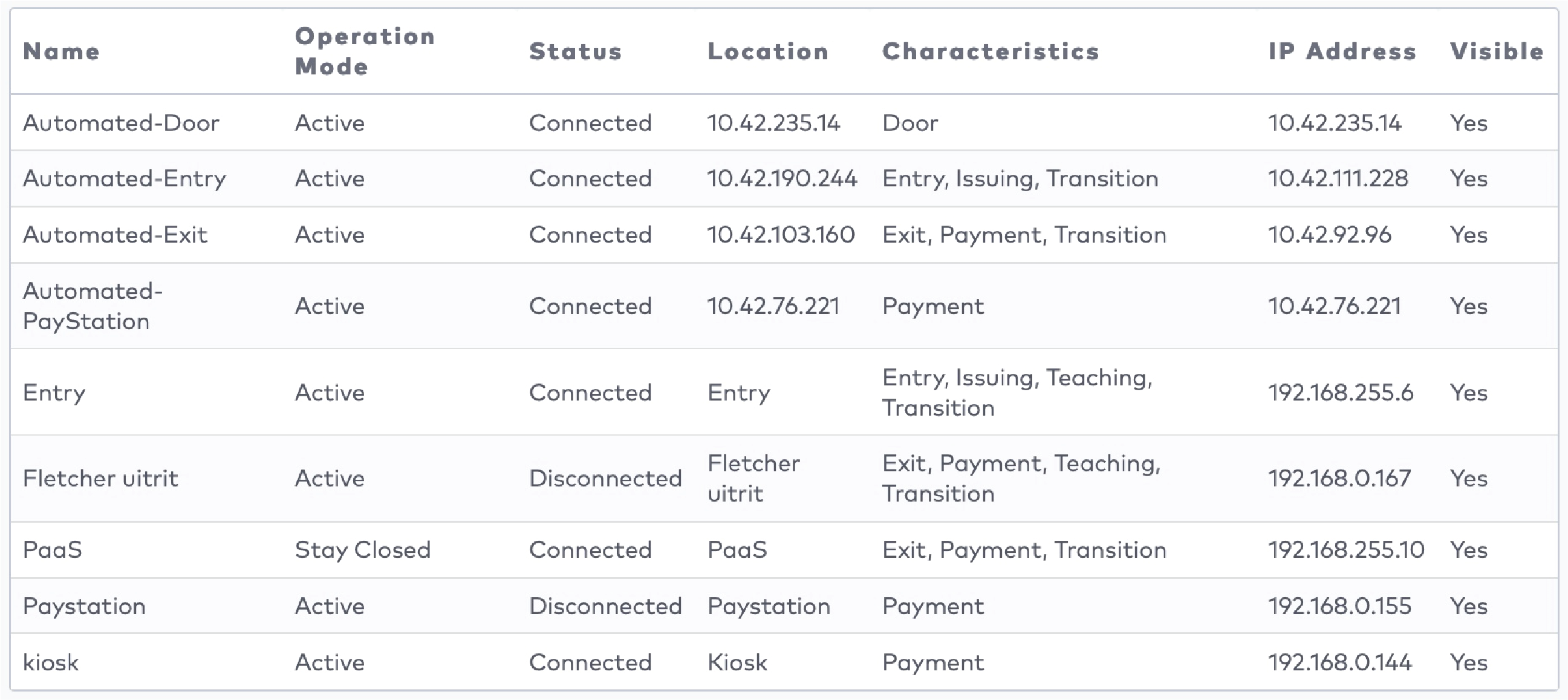
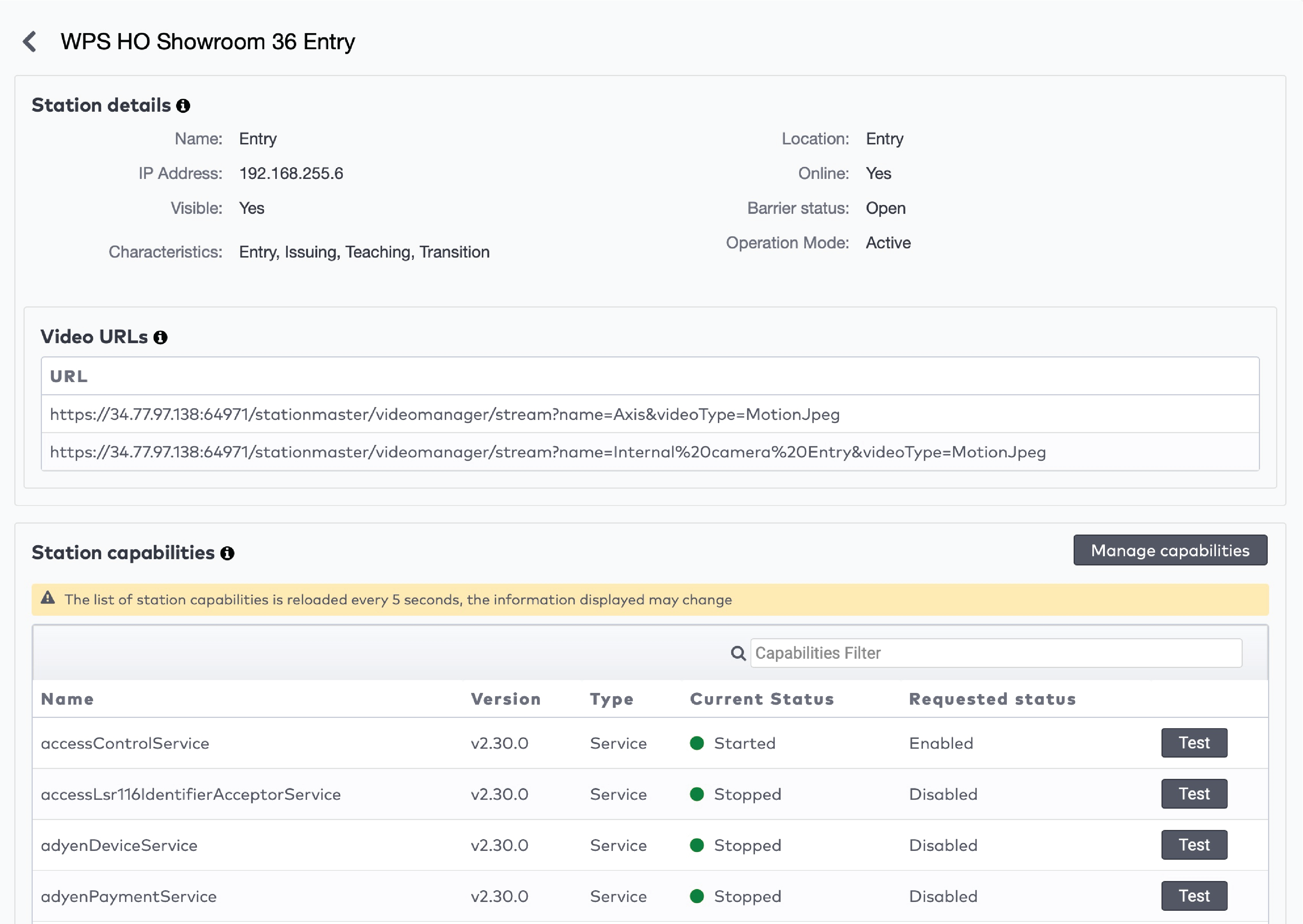
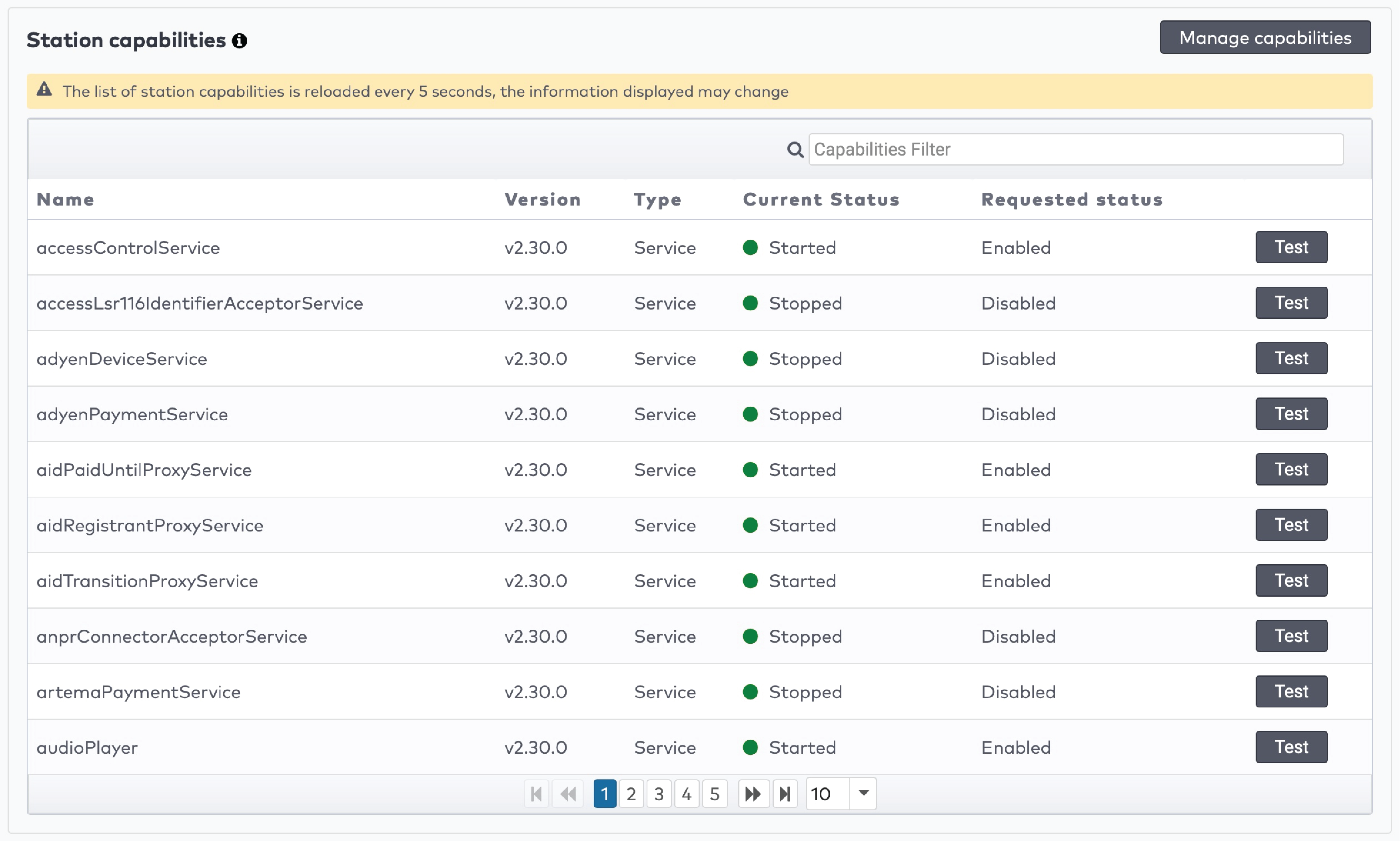
Operate the individual stations. Stations are grouped by section in the car park (5)
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
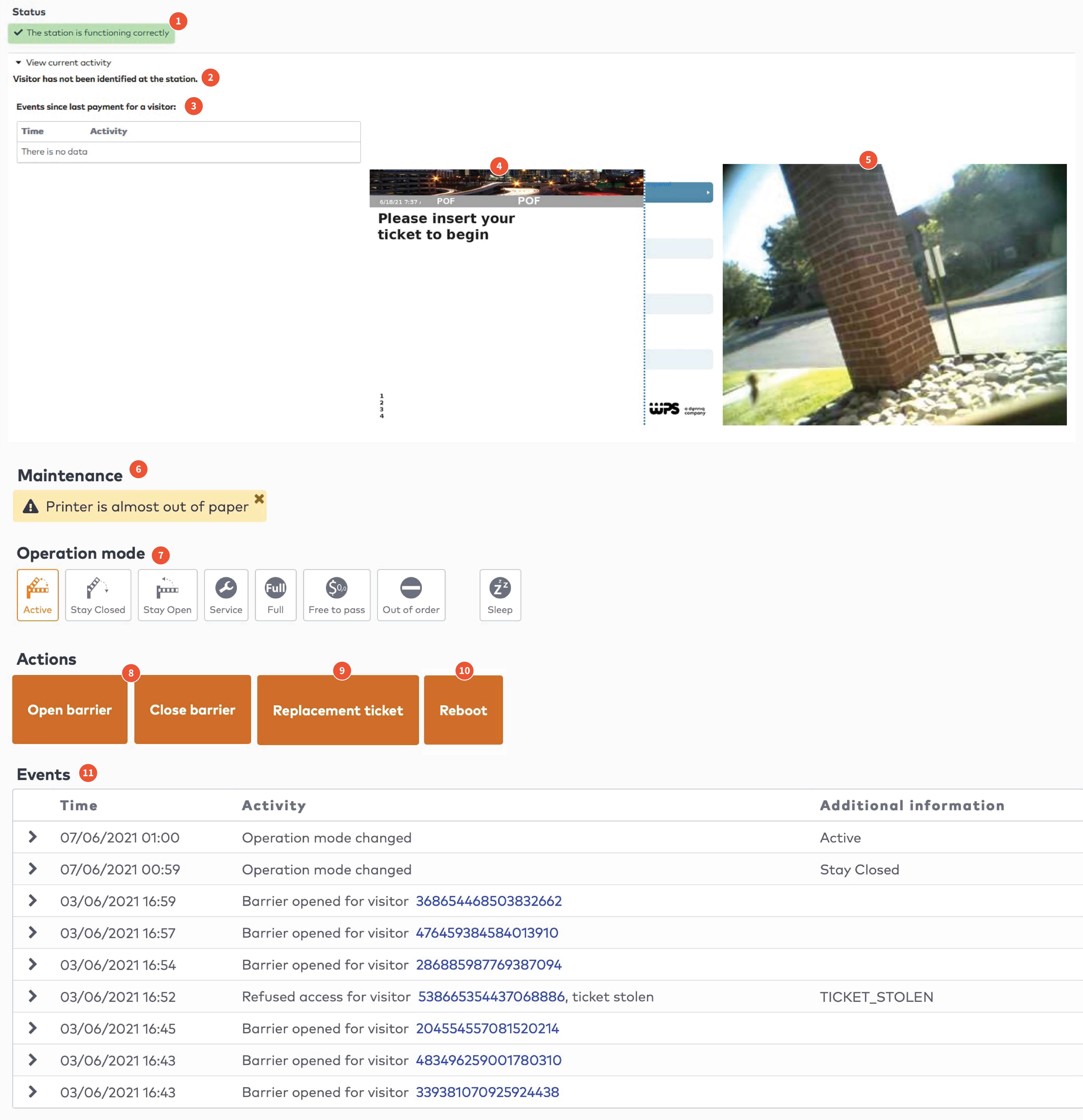
The station is active and operating normally.
|
|
The operation mode of this station is set to Stay closed. Visitors cannot pass.
|

|
The operation mode of this station is set to Stay open. Visitors can freely enter or exit.
|

|
The operation mode of this station is set to Service. The station is in maintenance mode. The station does not accept visitors.
|

|
The operation mode of this station is set to Full. The barrier only opens for visitors who are allowed to access car parks when they are full. For example, staff, service personnel, or other people who need to be able to access the car park at all times.
|

|
The operation mode of this station is set to Free to pass. Accepting visitors without checking their validity, clearance or schedule.
|

|
The operation mode of this station is set to Out of order. The station is out of order and the barrier is closed.
|
|
The station is offline and the status is unknown.
|

|
The operation mode of the station is enforced. Any schedules for this station are overridden.
|
|
|

|
|
Operation mode
|
Entry station
|
Exit station
|
Payment station
|
Door
|
|
Active. The station is operating normally.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Stay closed. The station is always closed. Visitors cannot pass.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Stay open. The station is always open. Visitors can freely enter or exit.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Service. The station is in maintenance mode. The station does not accept visitors.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Full. The barrier only opens for visitors who are allowed to access car parks when they are full. For example, staff, service personnel, or other people who need to be able to access the car park at all times.
|
X
|
|||
|
Free to pass. Accepting visitors without checking their validity, clearance or schedule.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Out of order. The station is out of order and the barrier is closed.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
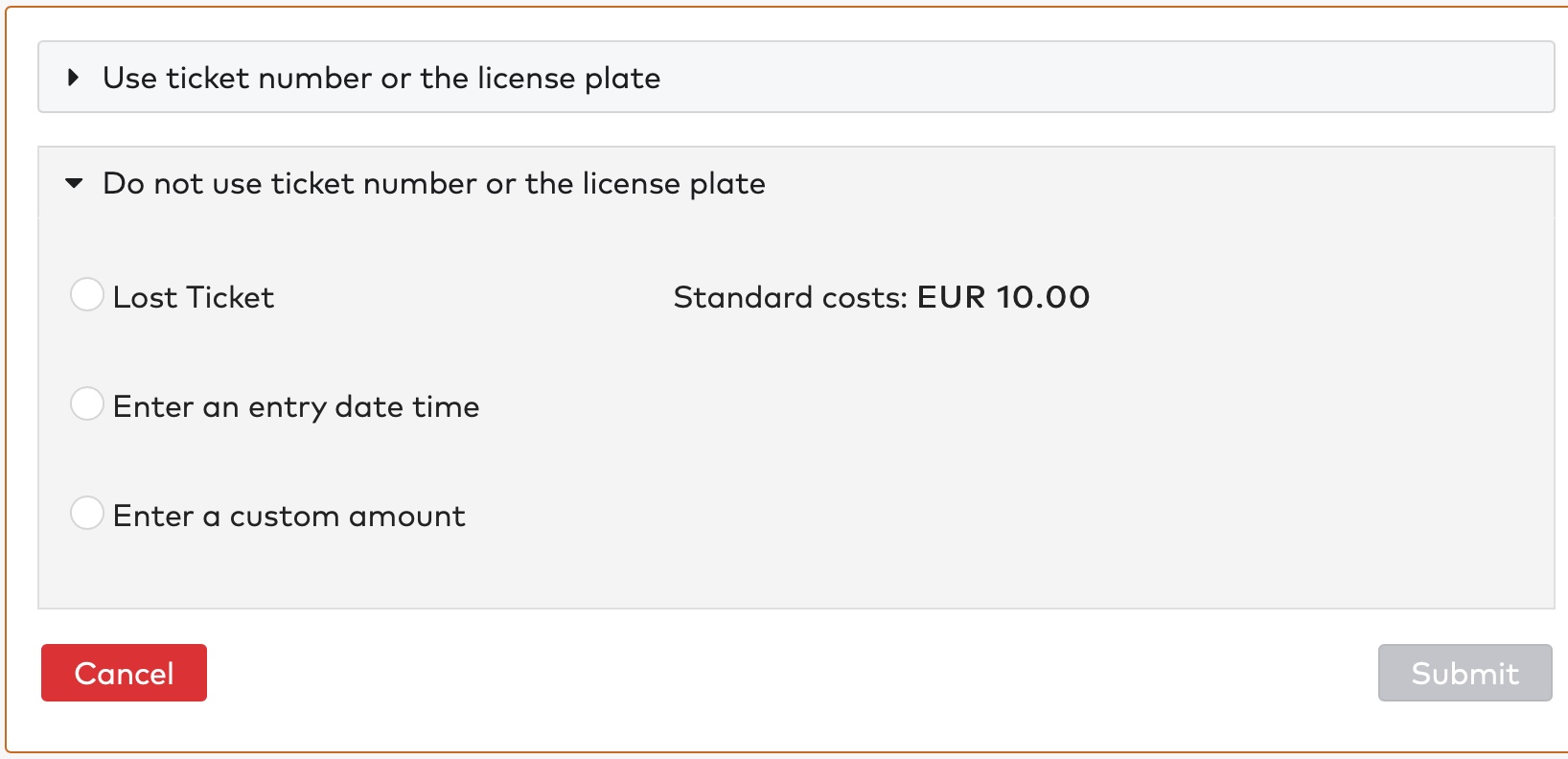
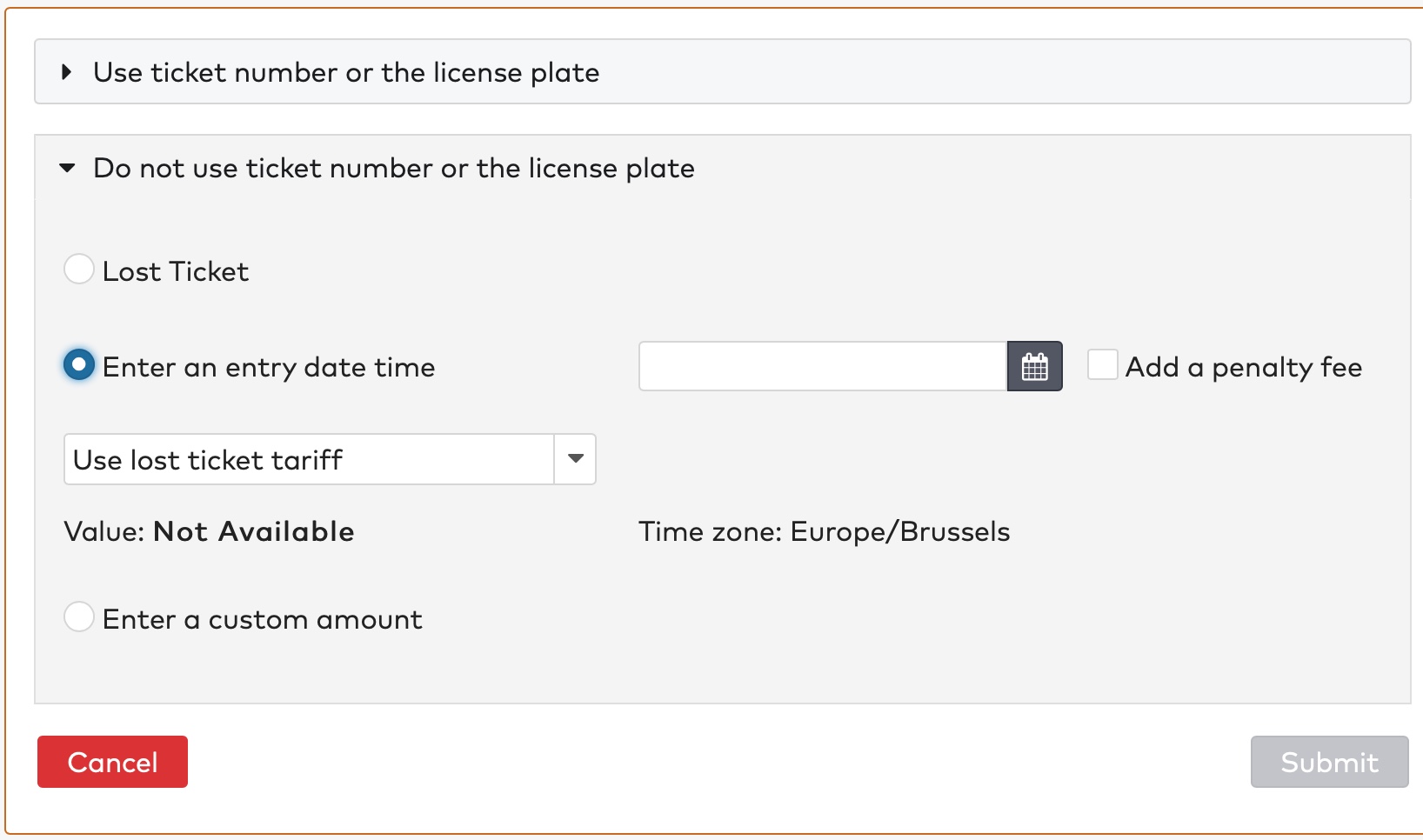
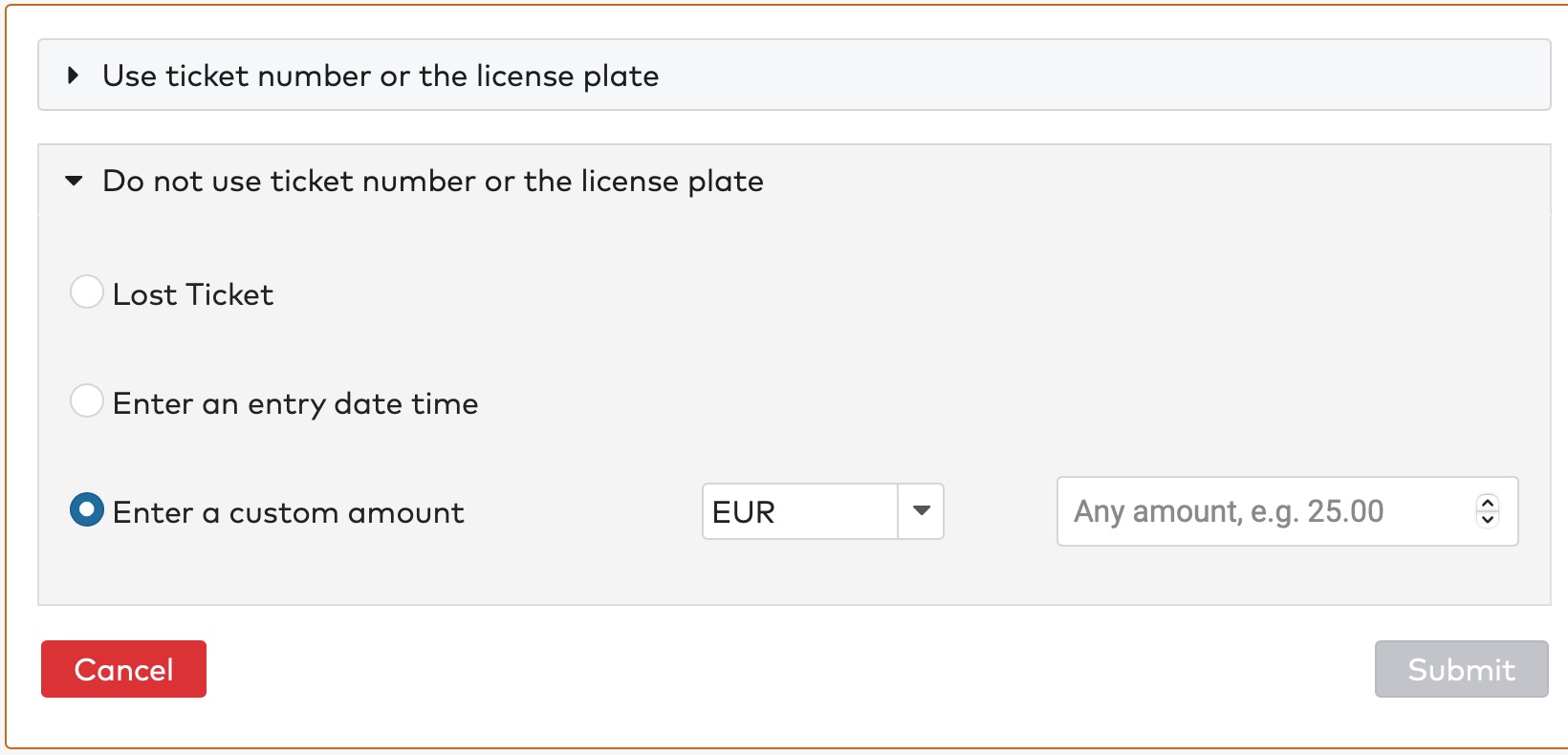
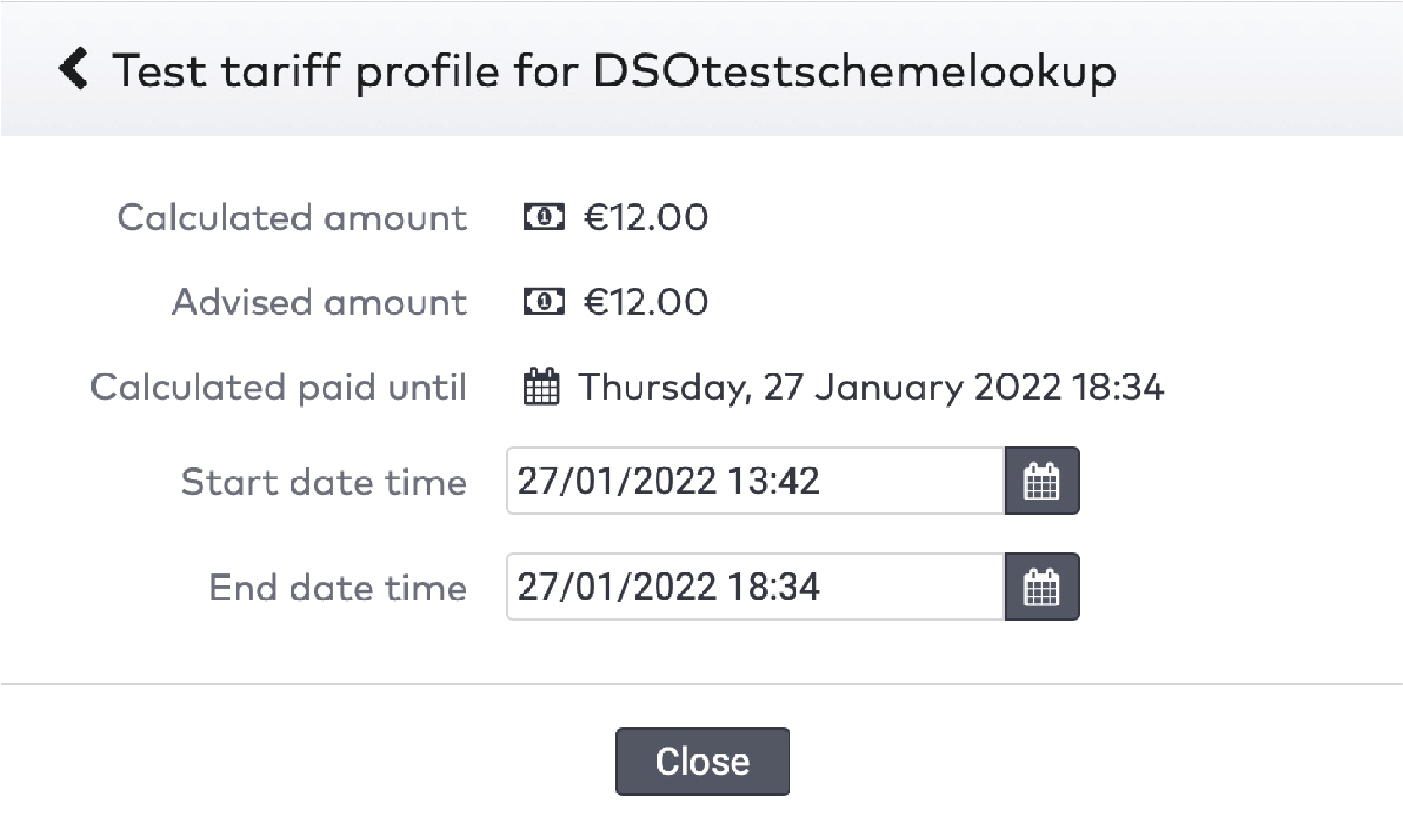
 to enter the entry date and time.
to enter the entry date and time.
|
|
|
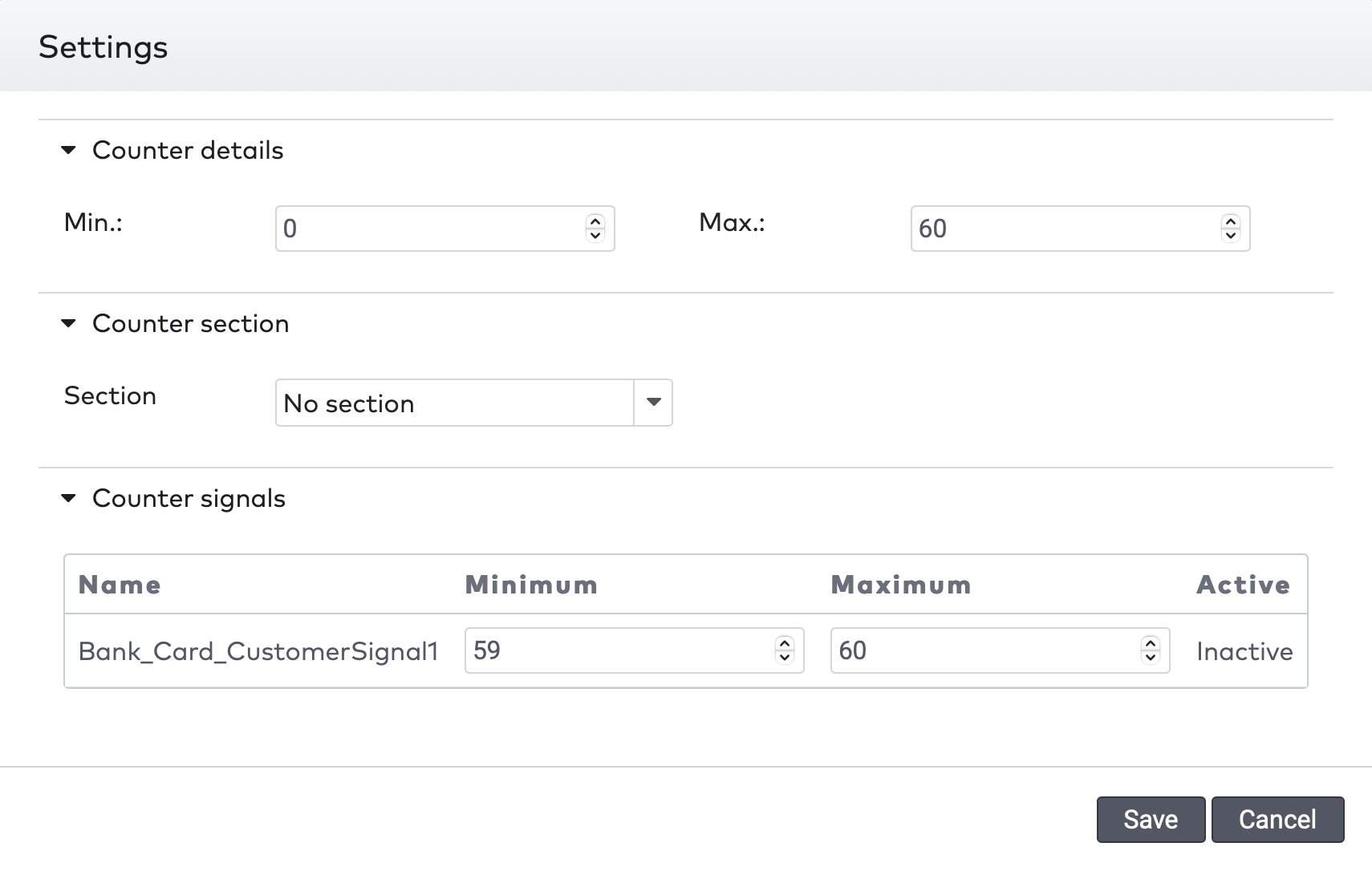
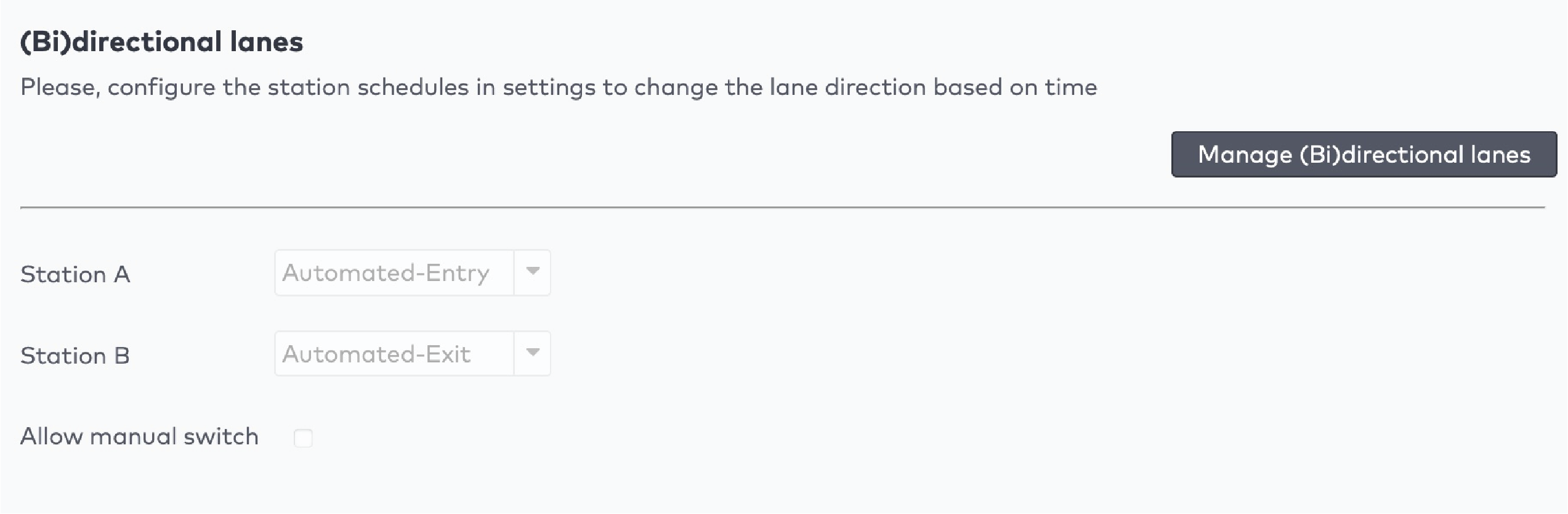
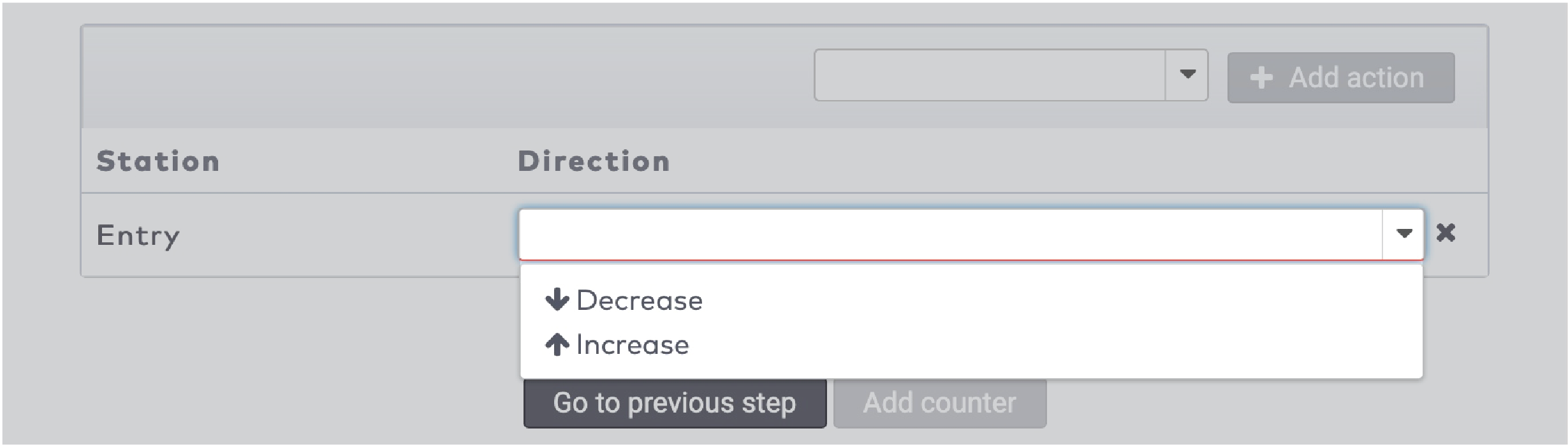
 next to the counter you want to adjust.
next to the counter you want to adjust.
 to discard any changes.
to discard any changes.

|
 next to the counter you want to adjust.
next to the counter you want to adjust.
|
|
|
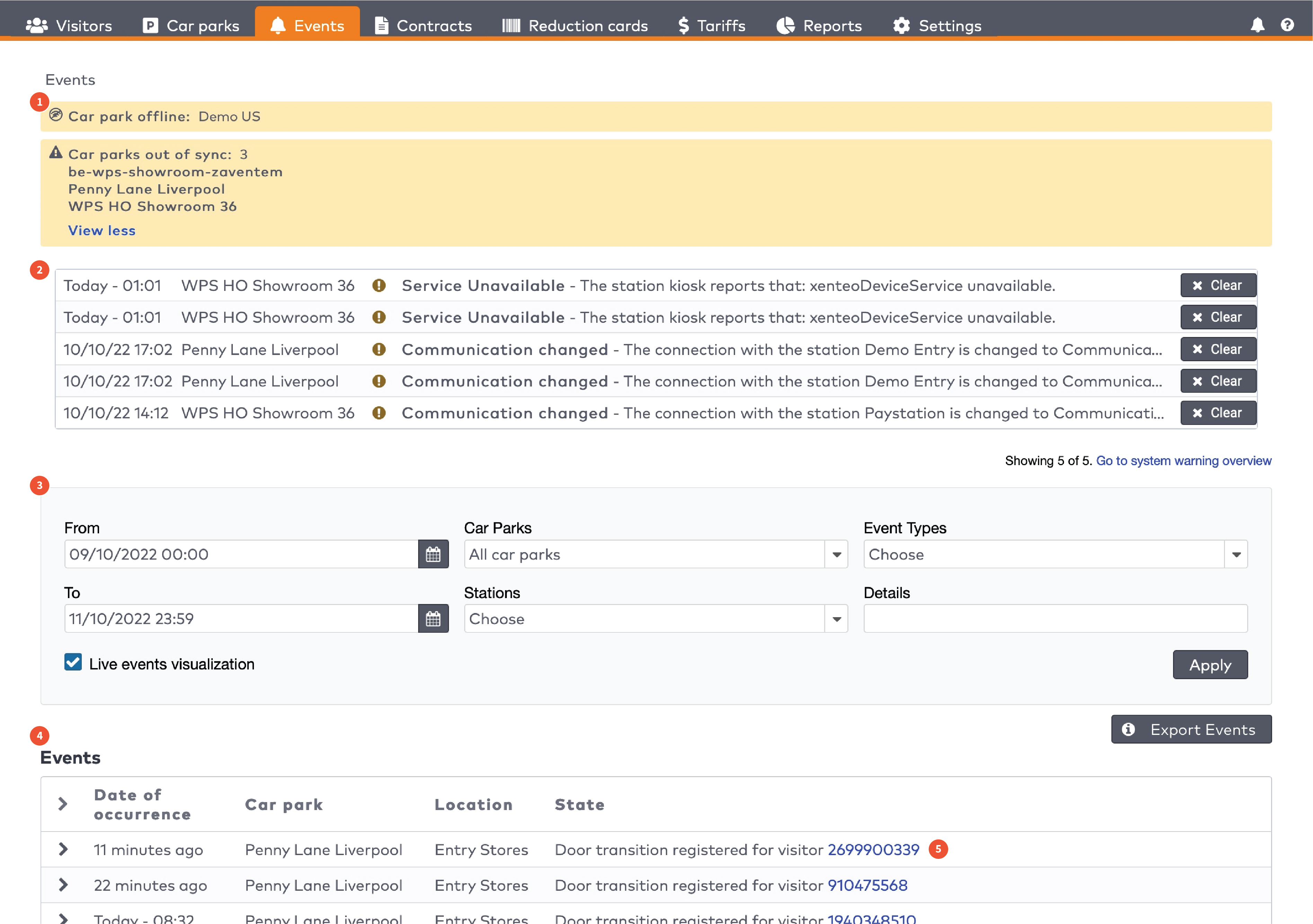
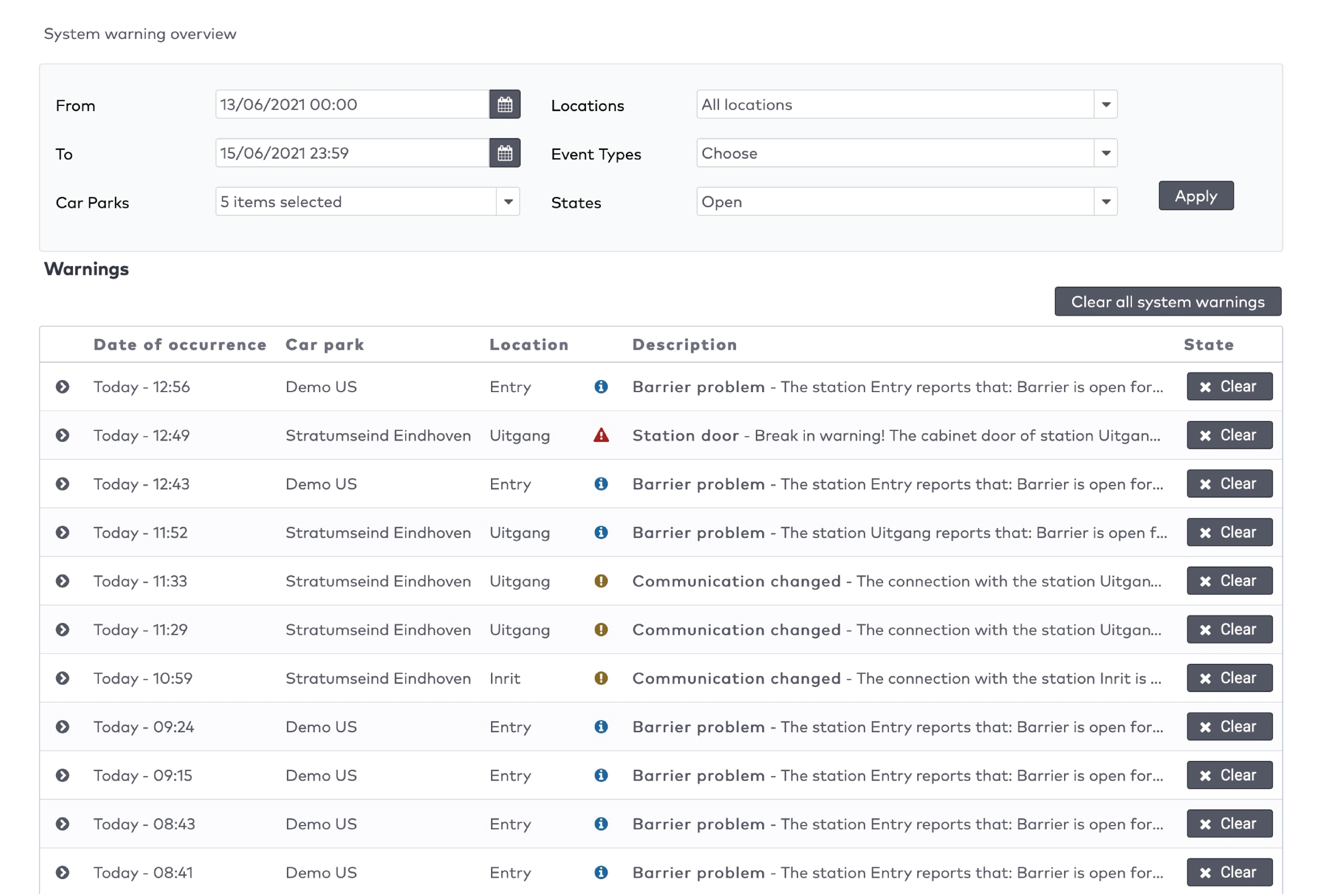
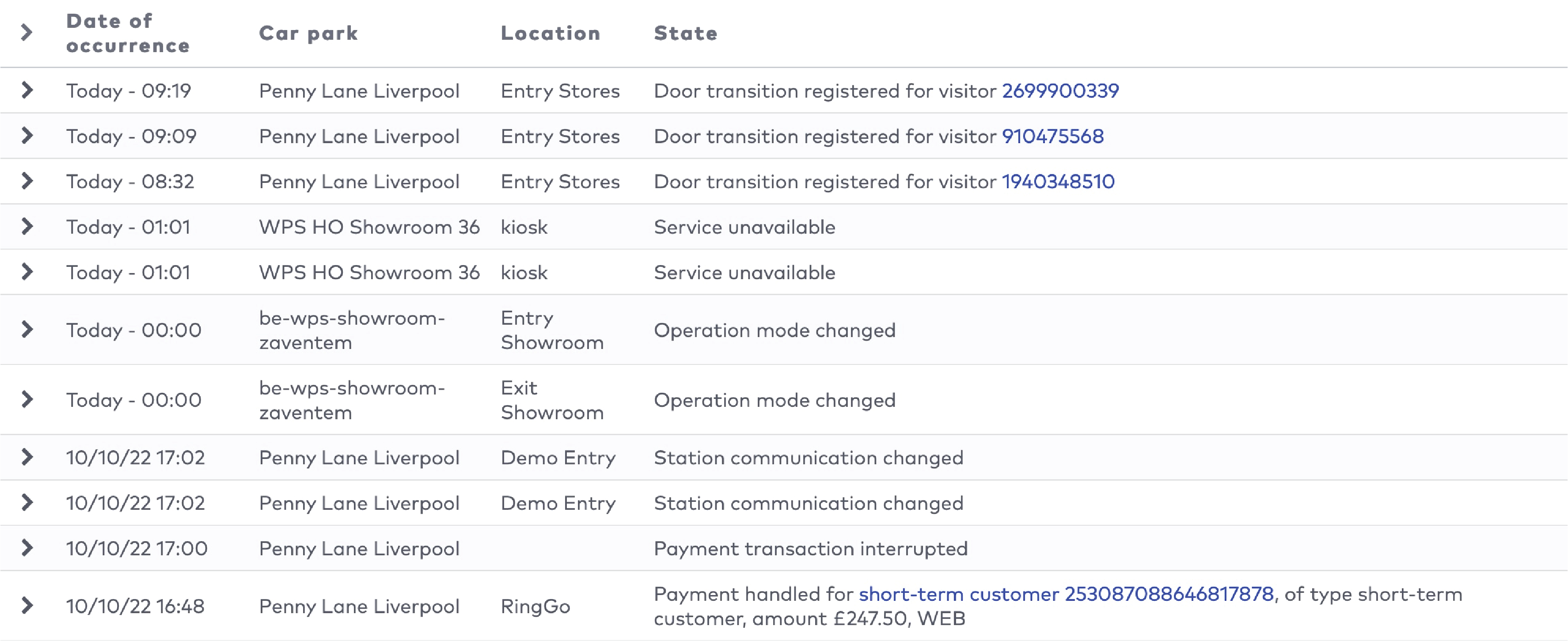
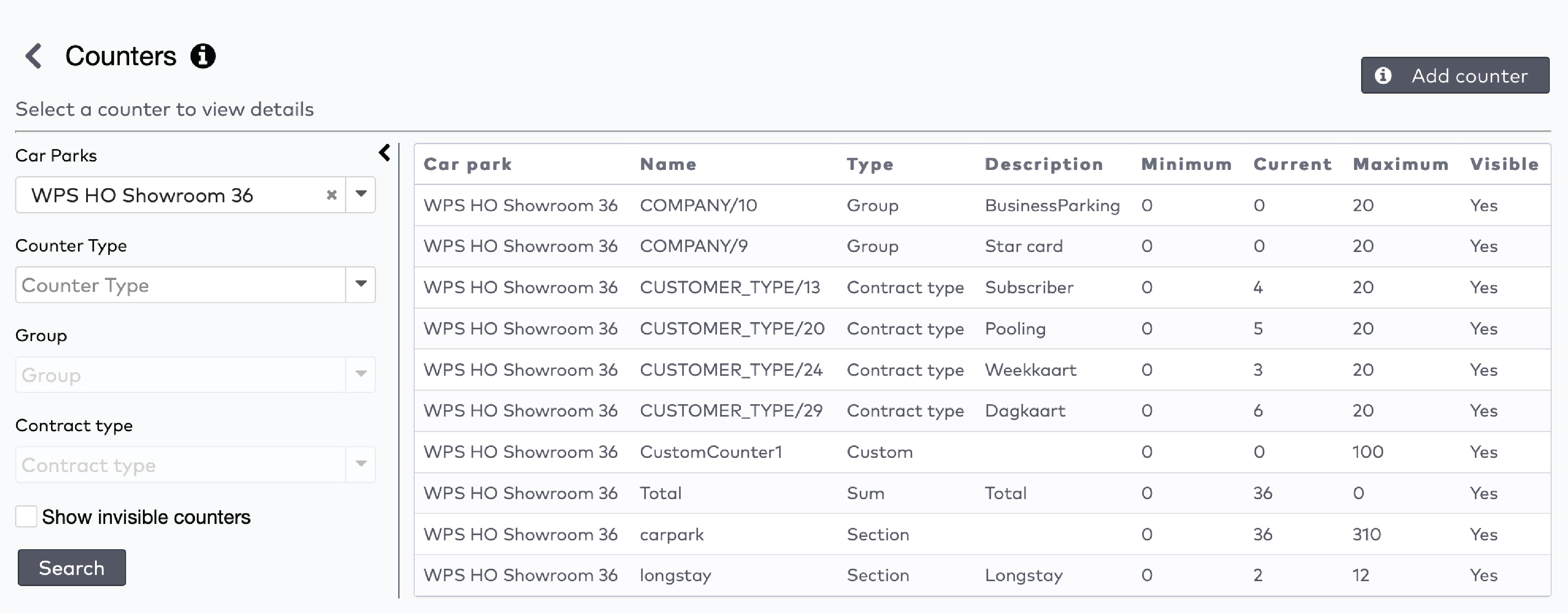
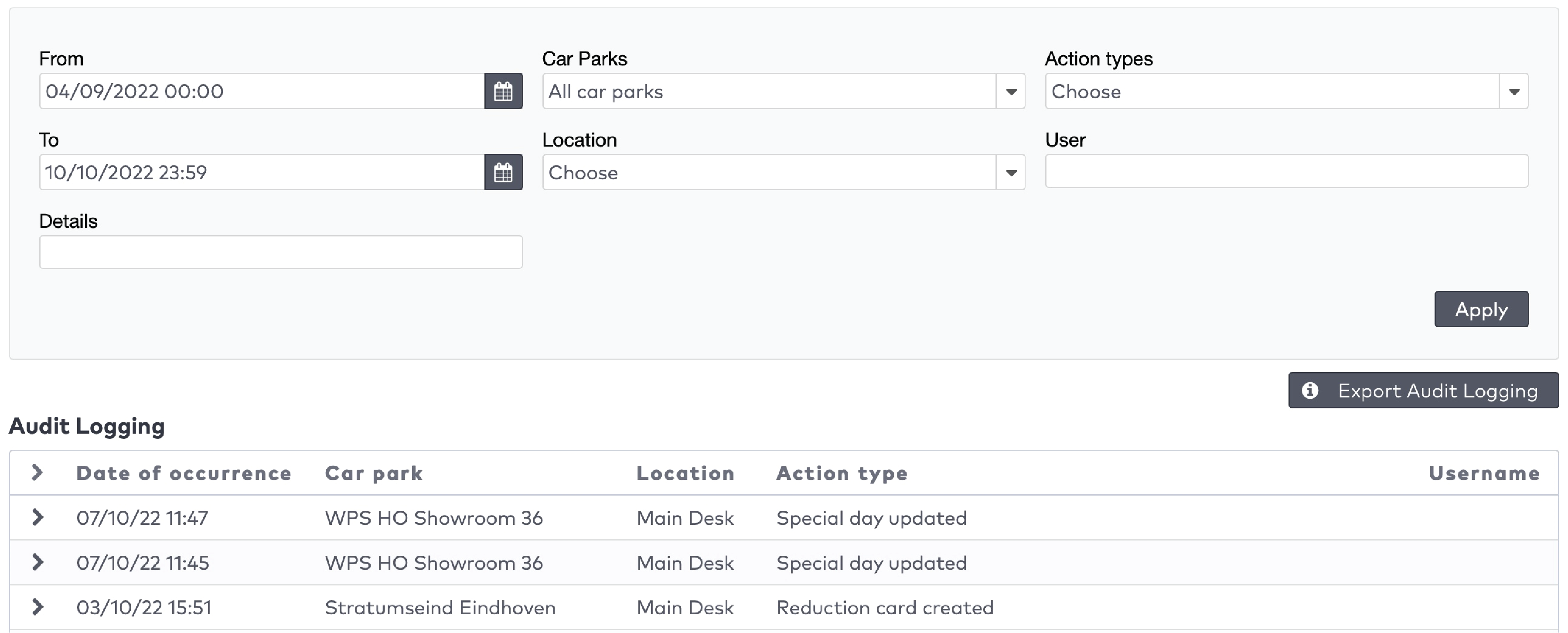
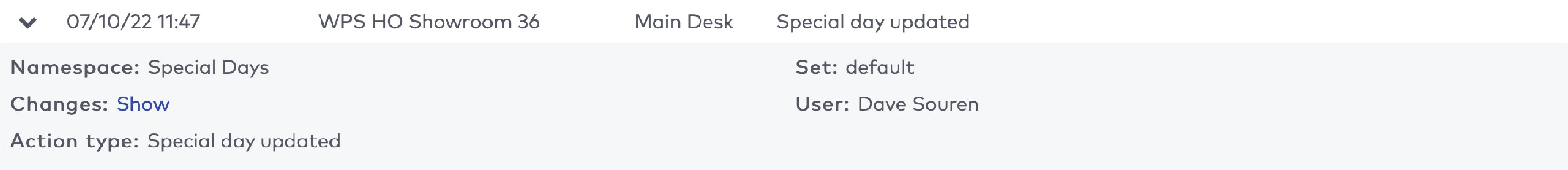
The five most recent system warnings (2)
|

|

|
|
 in the menu bar.
in the menu bar.

|
|

|
Critical warning
A very important message to the user about an unexpected system behavior or state which can have major effects on the system performance, user experience or visitor experience.
|

|
Warning
An important message to the user about an unexpected system behavior or state
|

|
User action requests
A message to trigger the user to take action
|
|
|
 next to it:
next to it:

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
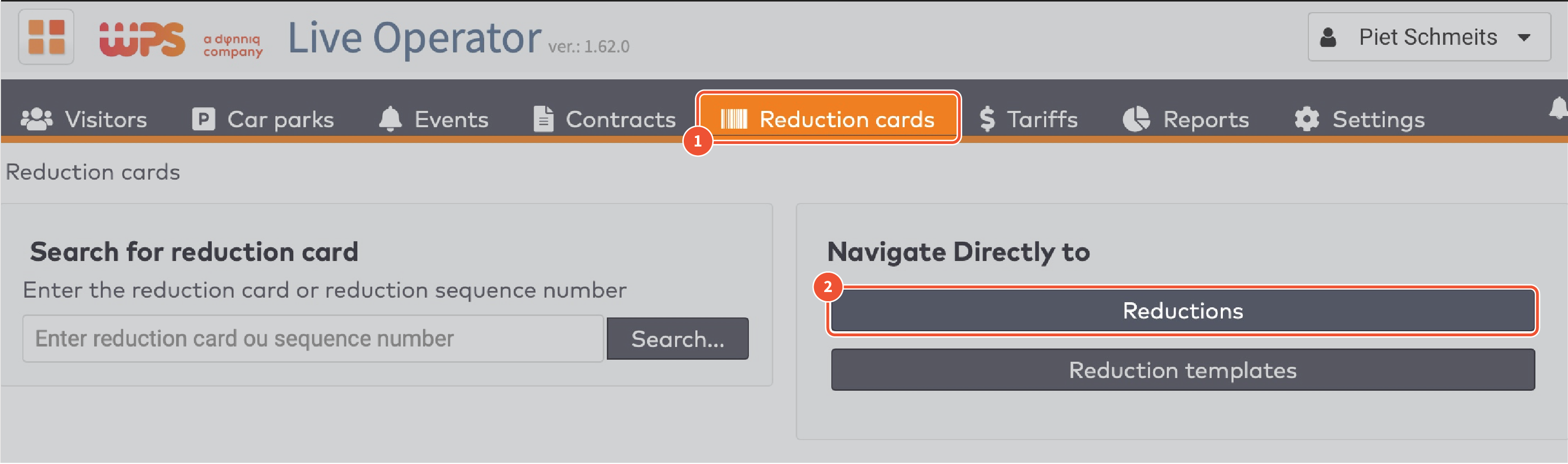
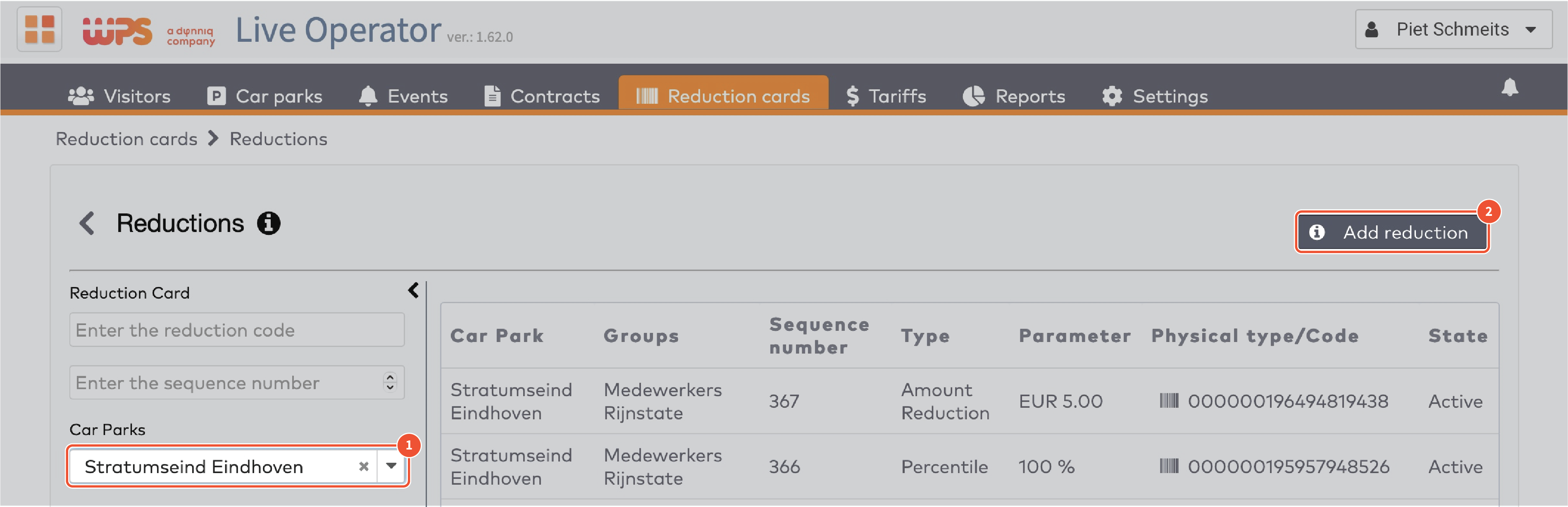
Example reduction card with bar code.
|
Example reduction card with QR code.
|
|
|

|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
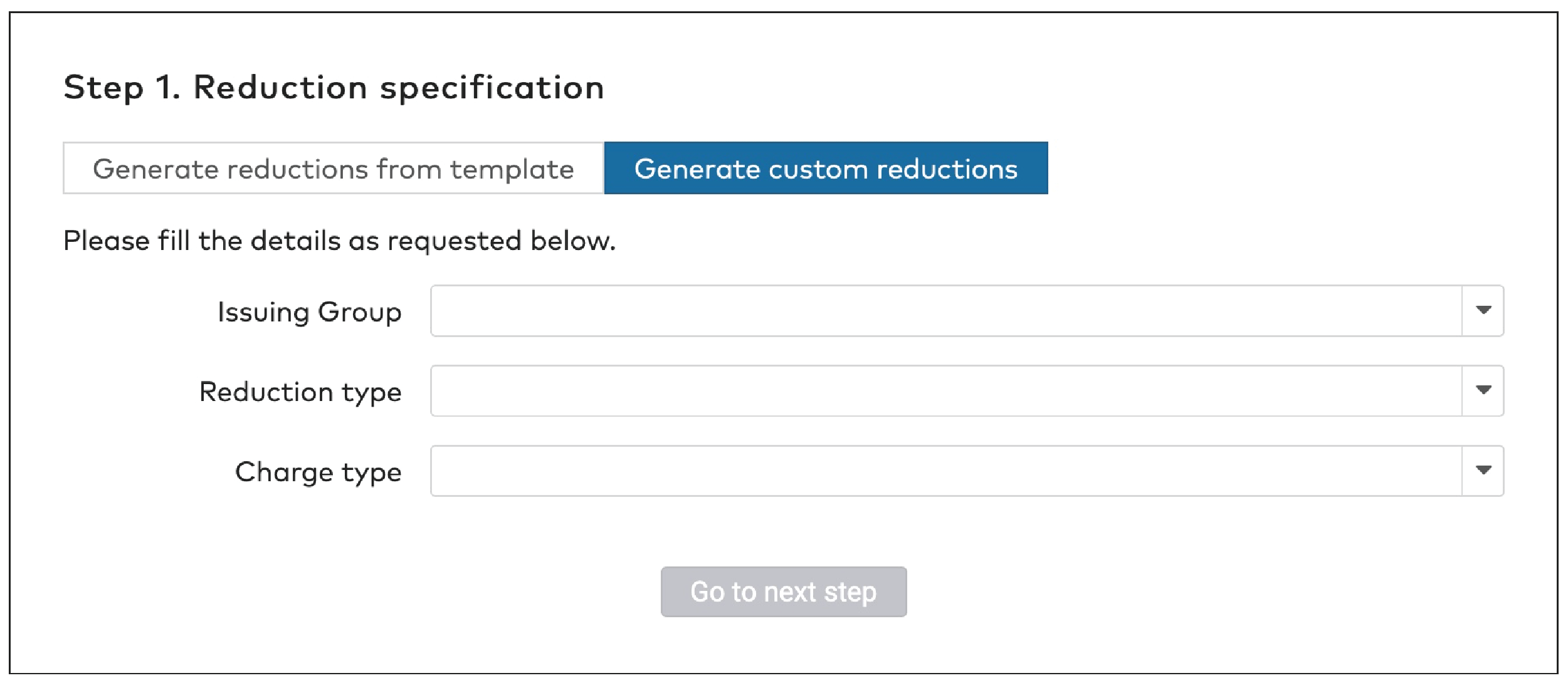
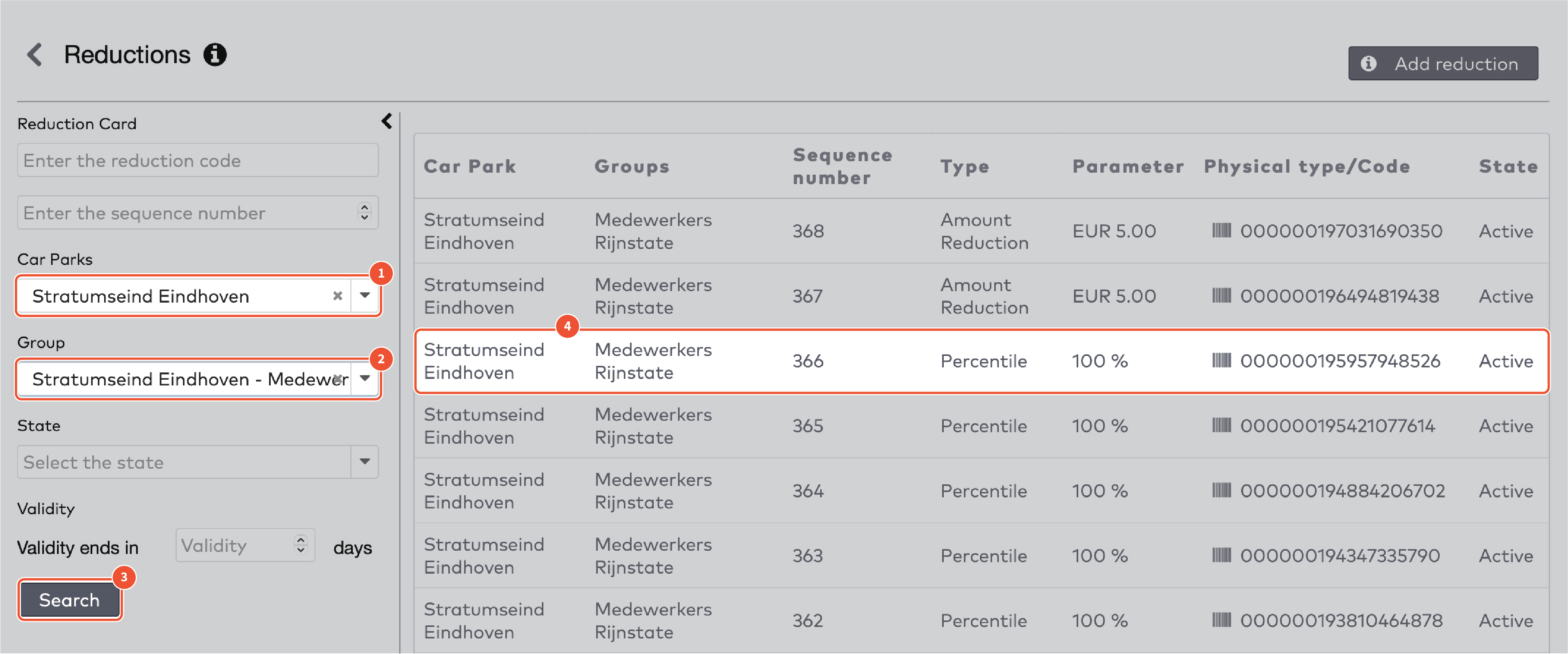
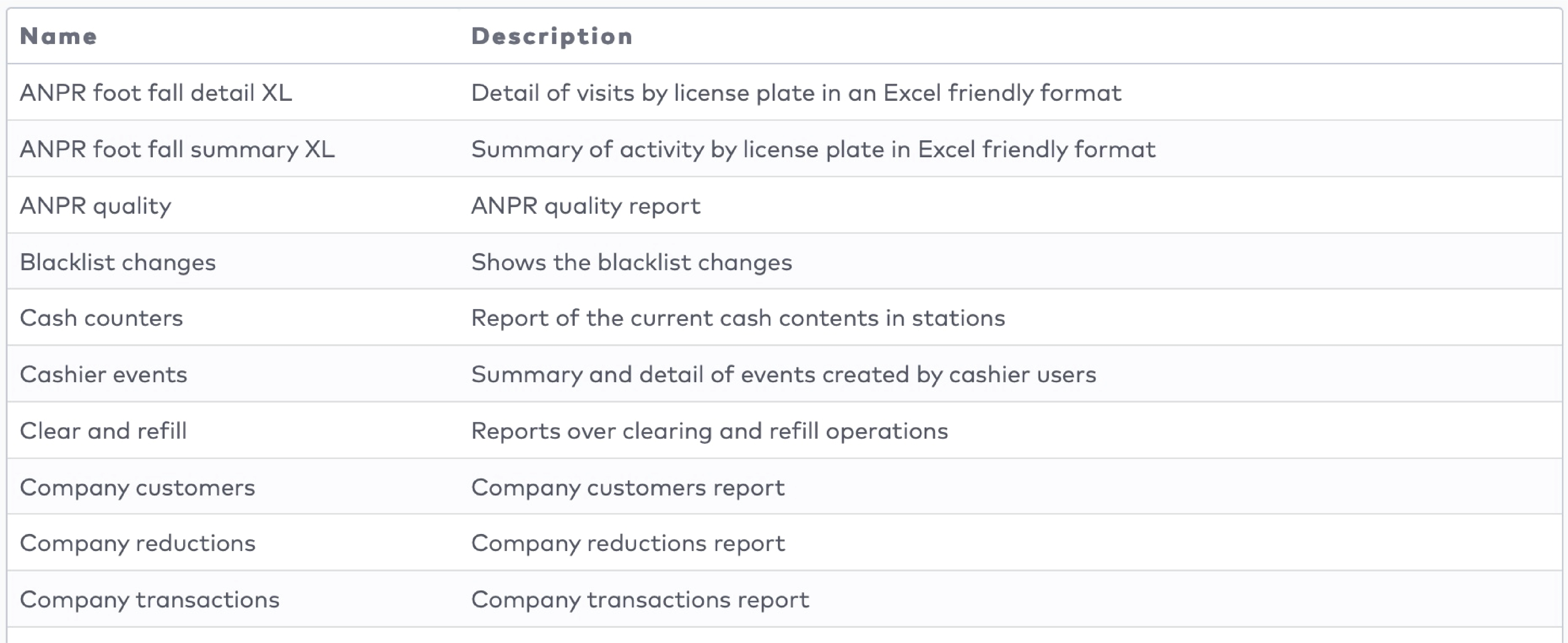
Reduction type
|
|
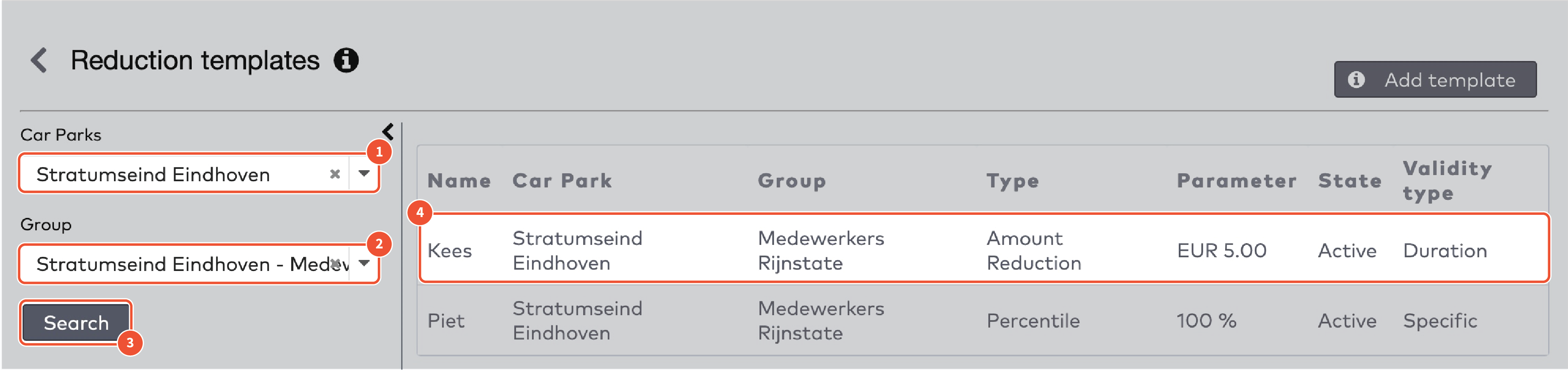
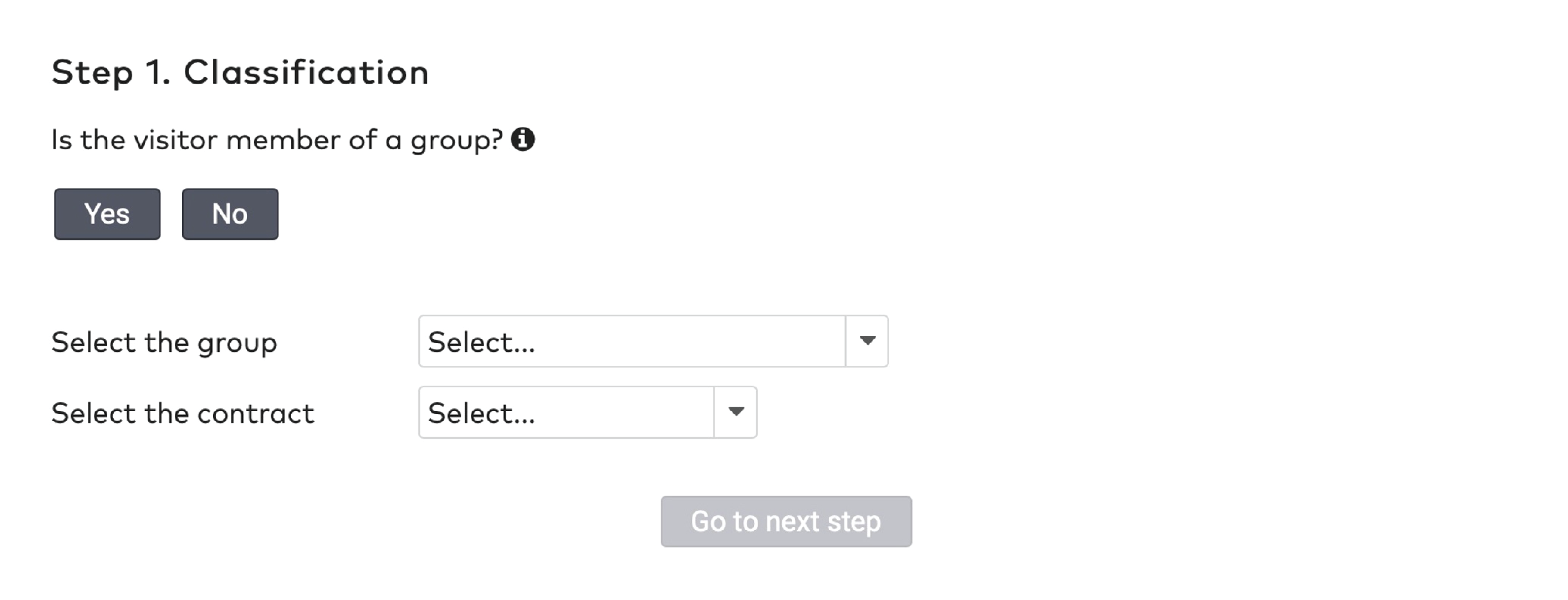
There are five reduction types:
Amount reduction
Fixed time
Percentile
Sales amount
Tariff switch
Amount reduction
A fixed amount is subtracted from the amount due.
For example: a visitor who has to pay €10 and has a reduction card with a fixed amount of €6 pays €4.
Fill in the Amount reduction.
Select the applicable currency from the dropdown menu.

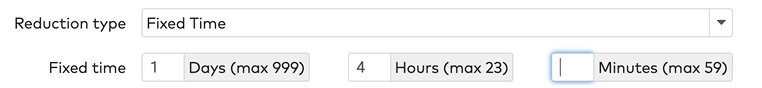
Fixed time
A fixed amount of time is subtracted from the total parking time.
For example, a visitor who has parked for 1,5 hours and has a reduction card with a fixed time of two hours gets a free exit.
Fill in the number of Days, Hours and Minutes in the respective fields.

Percentile
The amount due is reduced by a set percentage of the original sum.
For example: a visitor who has to pay €10 and has a reduction card of 50% pays €5.
Fill in the Percentile in whole numbers, without decimals.
Fill in a maximum reduction amount, if applicable.
For example, if the maximum reduction amount is €10, a visitor who has to pay €50 and has a reduction card of 50% gets the maximum reduction of €10 and pays €40.

Sales Amount
The amount due is replaced by a set amount.
For example: a visitor who has to pay €10 and has a reduction card with a sales amount of €3 pays €3.
Fill in the Sales Amount in whole numbers, without decimals.

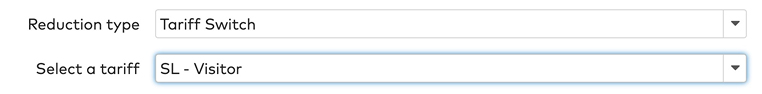
Tariff switch
The tariff applied to the parking time is changed.
For example: a visitor who has parked 4 hours during the day for €2,50/hour and has a tariff switch reduction card set to the more favorable night rate of €2/hour pays €8.
Select a Tariff from the dropdown menu.

|
|
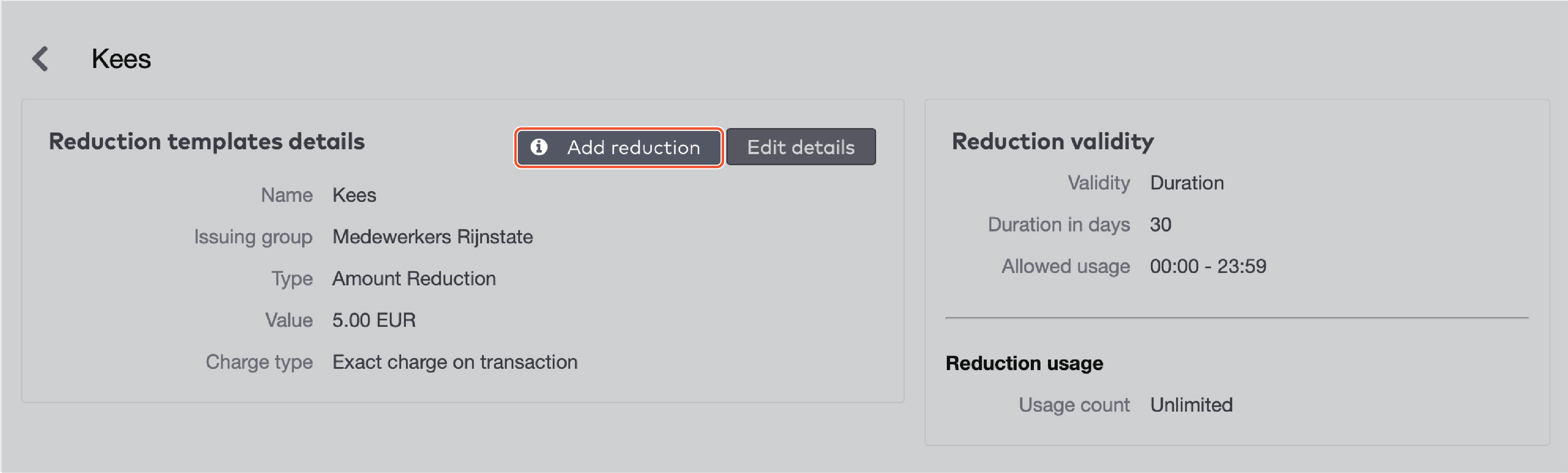
Charge type
|
|
Reduction cards are paid for by the issuing group. You can charge the group
When the cards are created (charge on issue). All cards are paid for, regardless whether they are used or not.
When the cards are actually used (charge on transaction). Unused cards will not be charged.
If you charge the group when the cards are actually used, you can either
Set a fixed amount per card (fixed charge on transaction) regardless of the actual value of the reduction. For example, you could create a set of reduction cards with a percentile reduction of 50% and sell them for €2,50 each.
Charge the exact reduction amount (exact charge on transaction).
When you have made your choice:
Select the Charge type from the dropdown menu.

Fill in the Charge amount, if applicable.

Select a currency from the dropdown menu.
Click Go to next step.
|
|
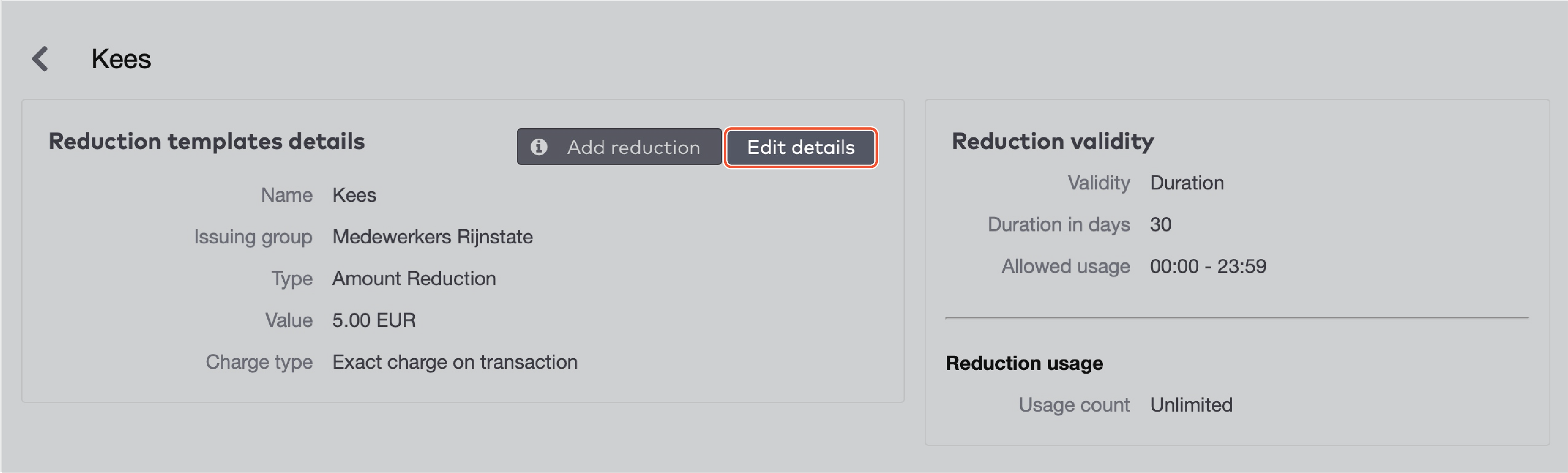
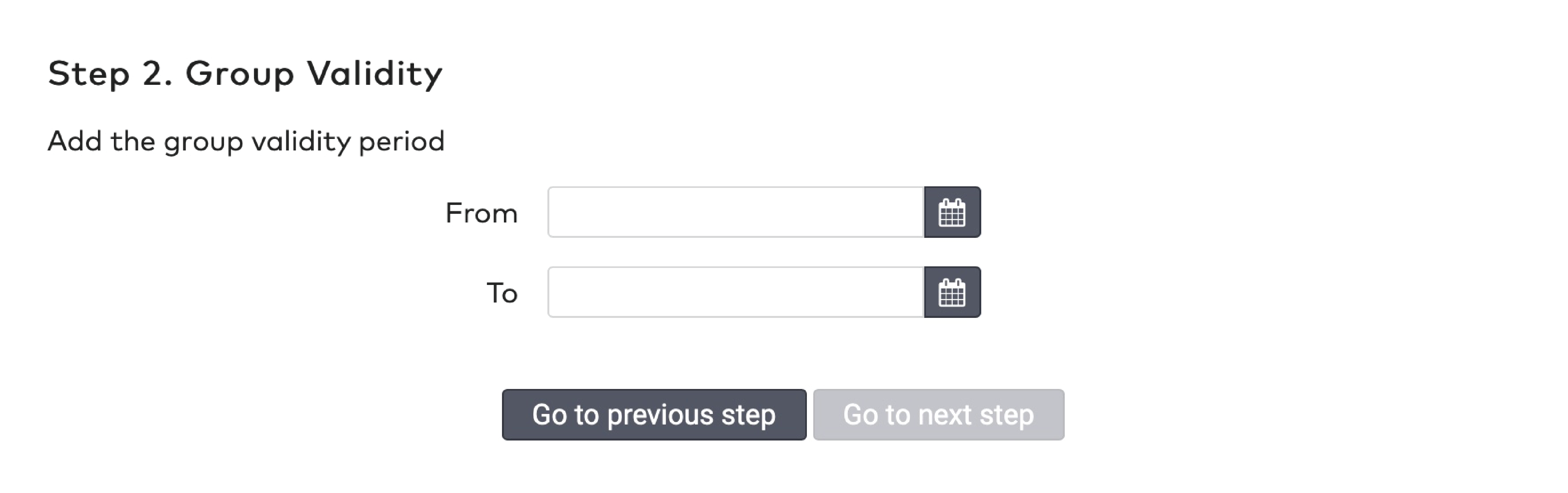
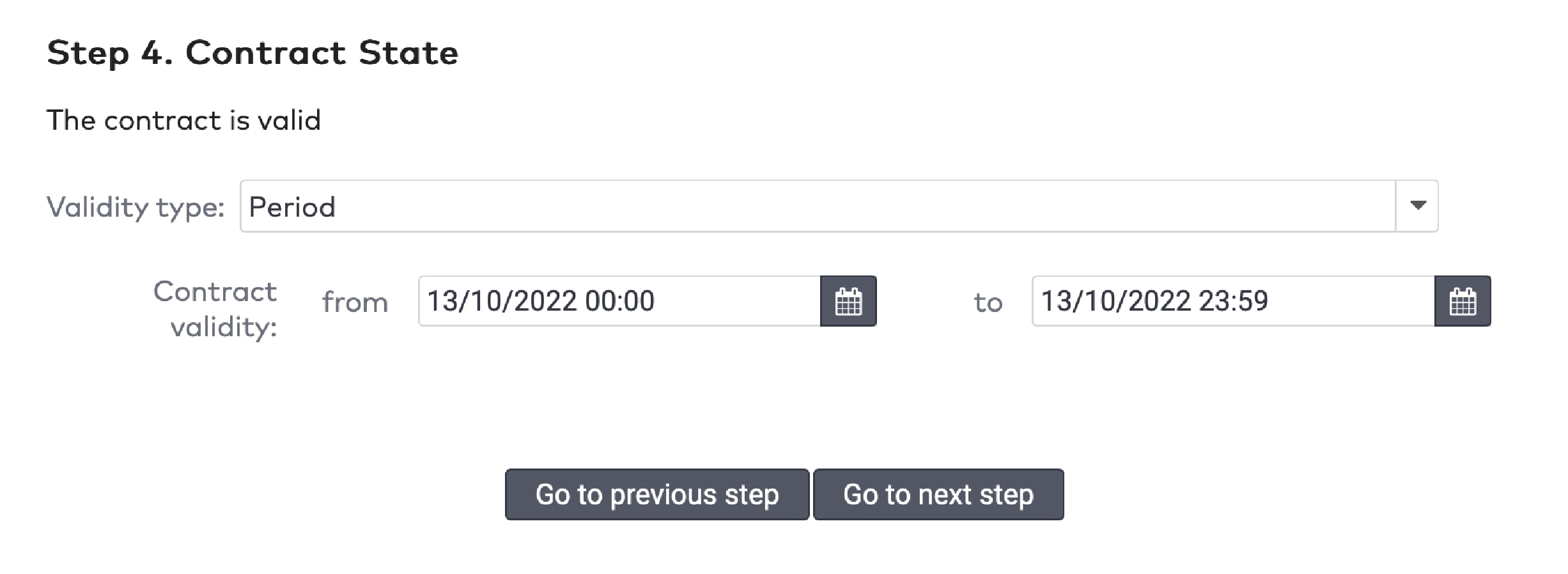
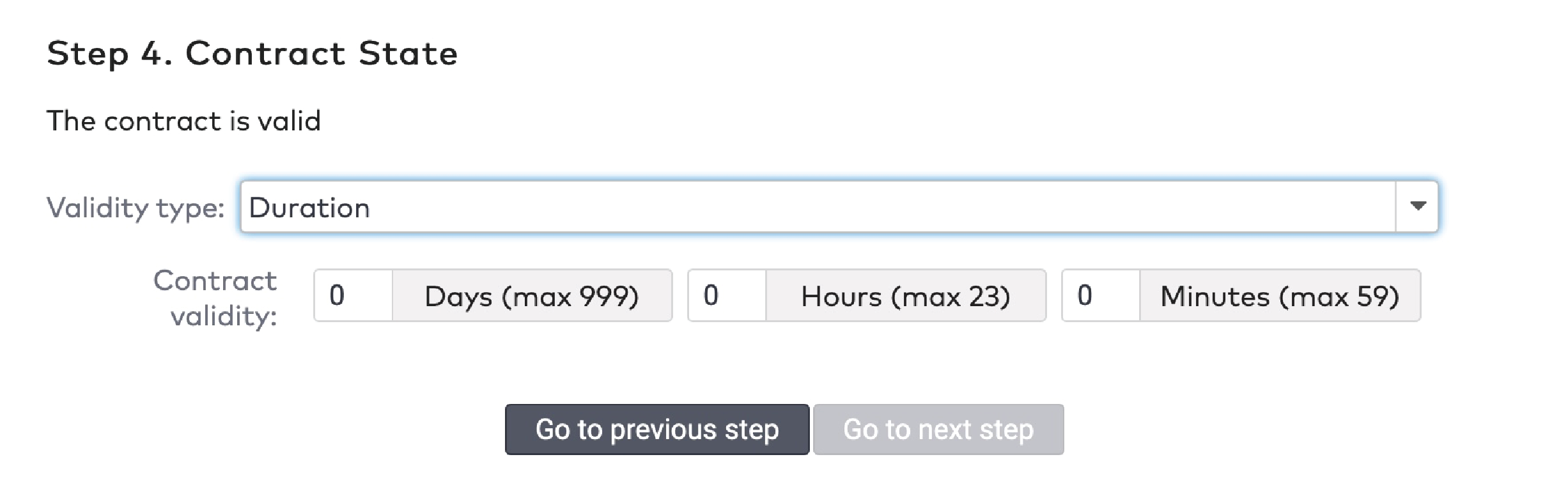
Validity
|
|
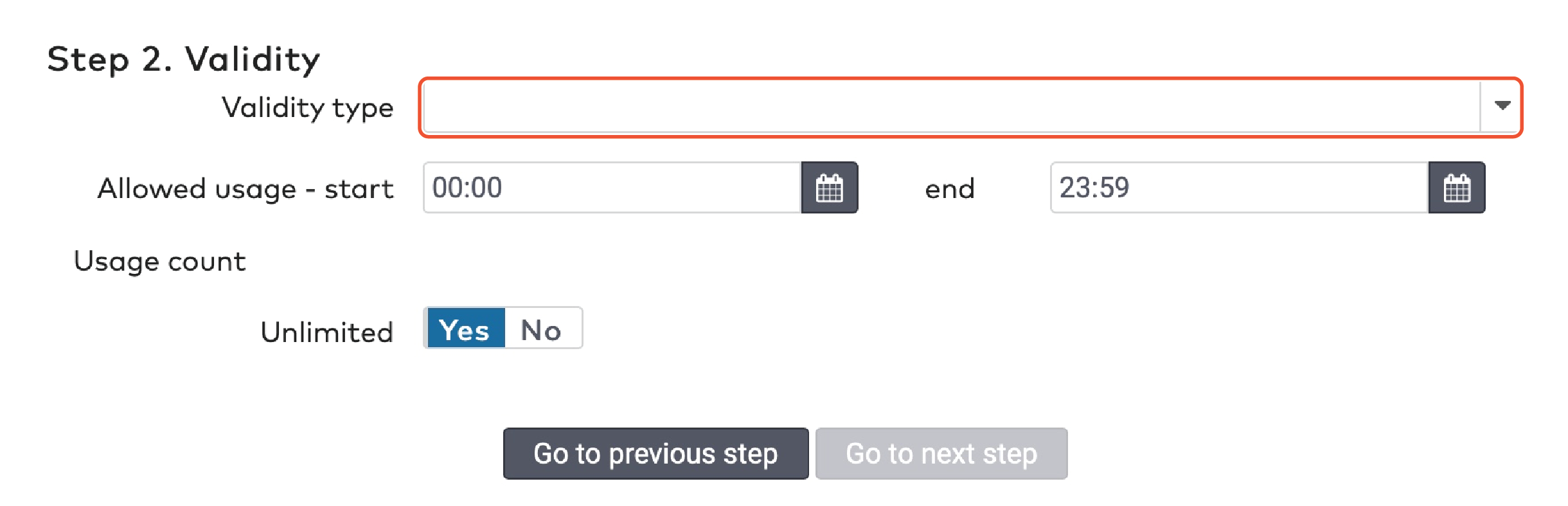
Reduction cards have a limited validity. You have to specify a date range in which the reduction card can be used. Additionally, you can set a time window in which it can be used. Between 9.00 AM and 6.00 PM, for example.

Select a Validity type from the dropdown menu. This can be a duration in days from the creation date, or a specific date range.
If you selected Duration, fill in the Duration in days.

If you selected Specific, pick a start date and an end date.

To set the time window in which the reduction can be applied:
Fill in a start and end time in the Allowed usage field.

You can set reduction cards to be used once, multiple times or unlimited times. Under Usage count
Set Unlimited to Yes if you want the cards to have no limit of usage.
Set Unlimited to No if you do want to limit the usage of the cards. Fill in the maximum Number of uses.

Click Go to next step.
|

|

|
|
|
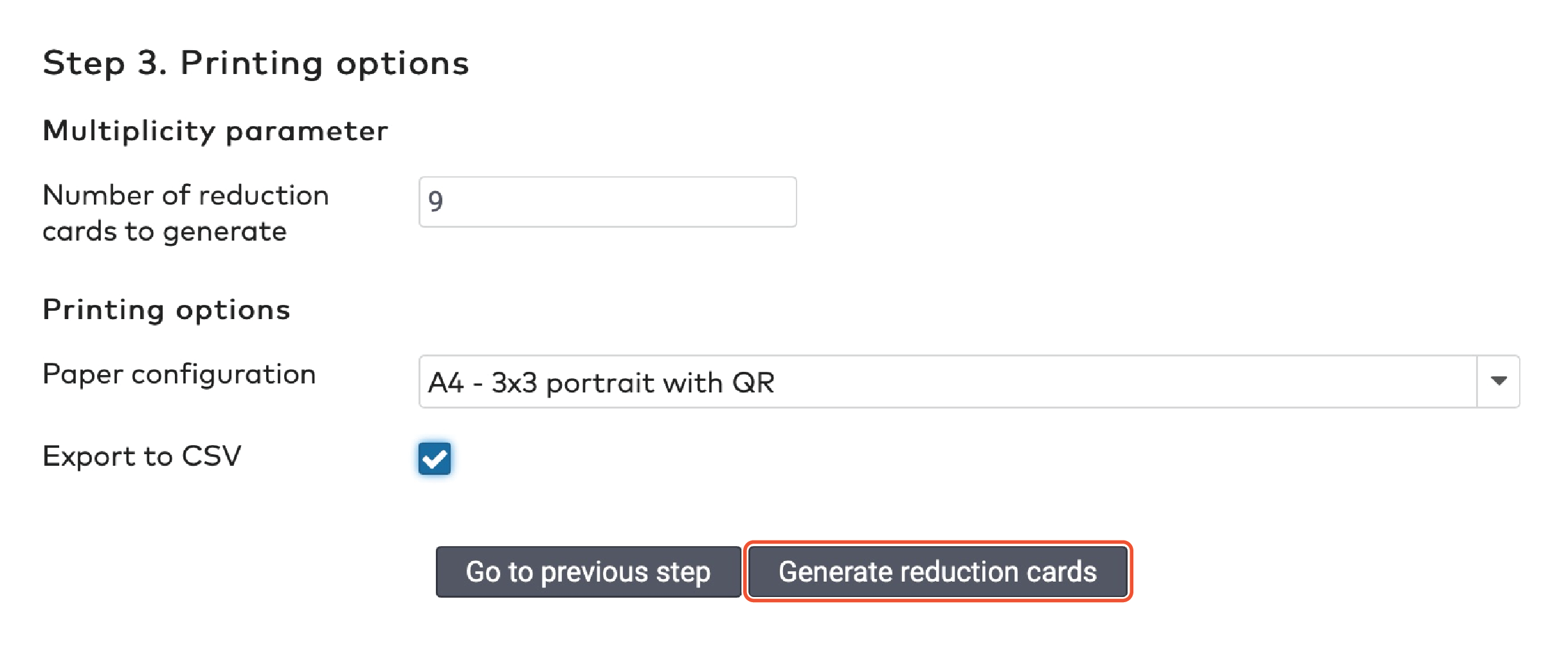
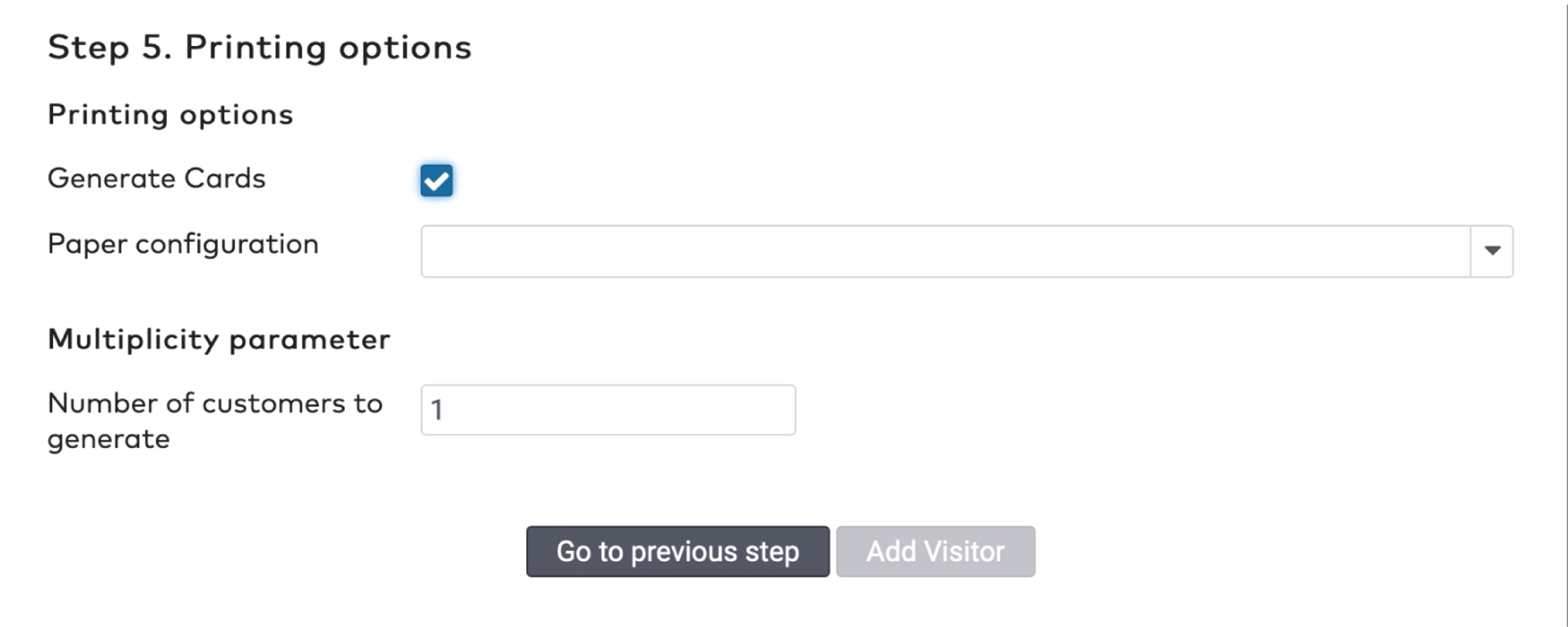
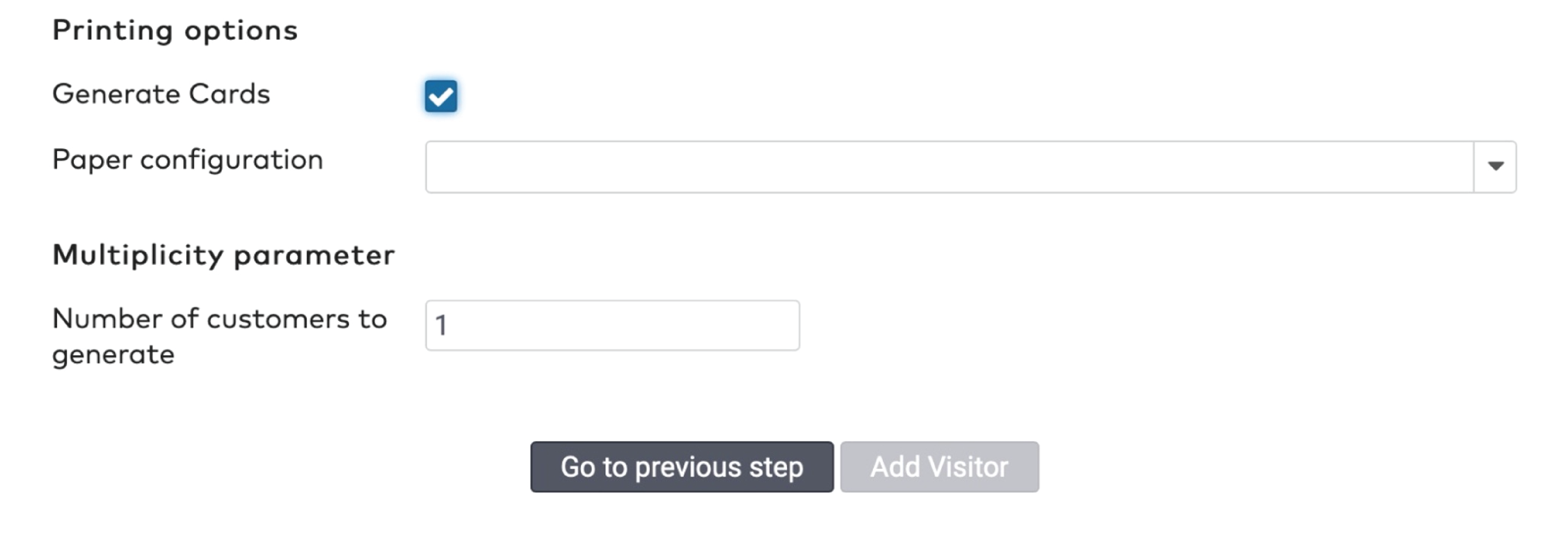
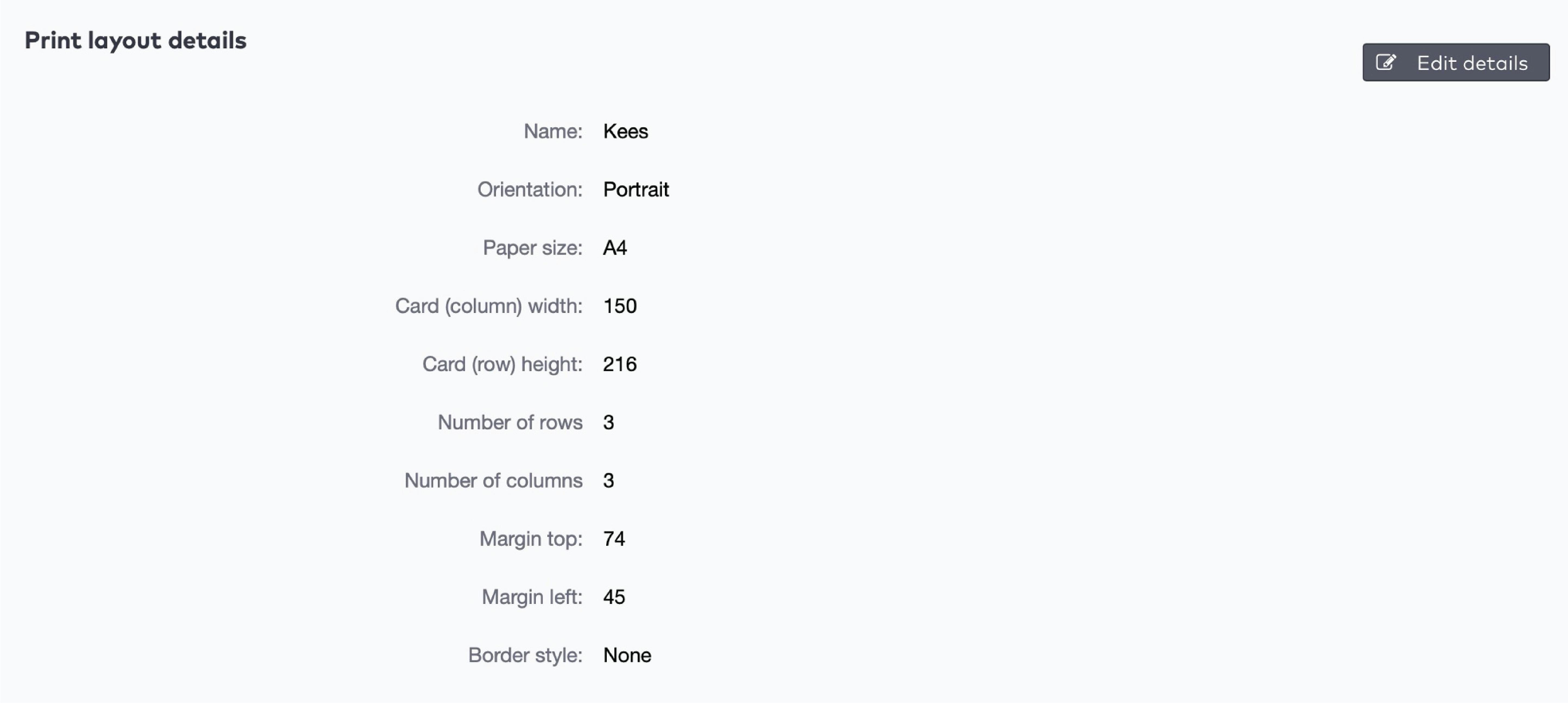
Printing options
|
|
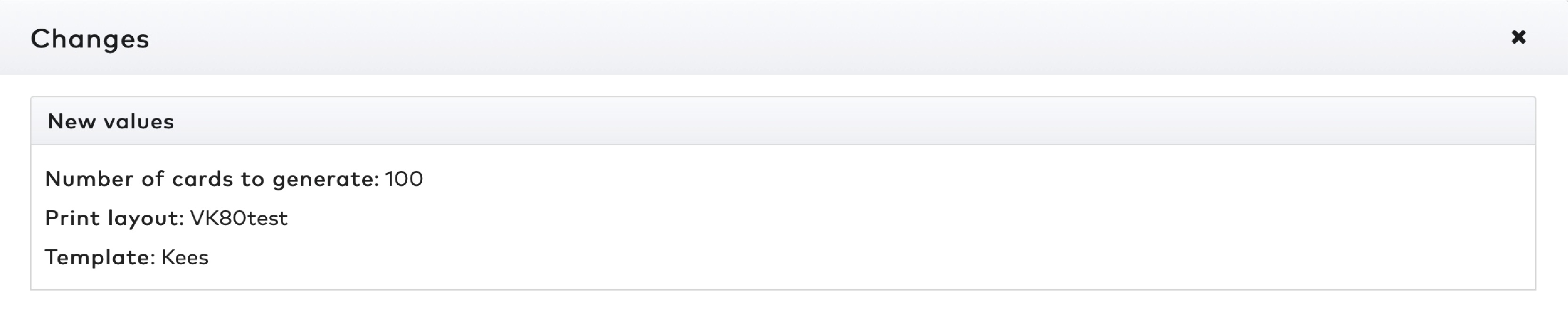
Set the Number of reduction cards to generate. The maximum number of cards is 9.999.
Select the appropriate Paper configuration.
Tick Export to CSV if you want to save the sequence numbers and bar code numbers to a separate file.
|

|
|
|
|
Printing options
|
|
Set the Number of reduction cards to generate. The maximum number of cards is 9.999.
Select the appropriate Paper configuration.
Tick Export to CSV if you want to save the sequence numbers and bar code numbers to a separate file.
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
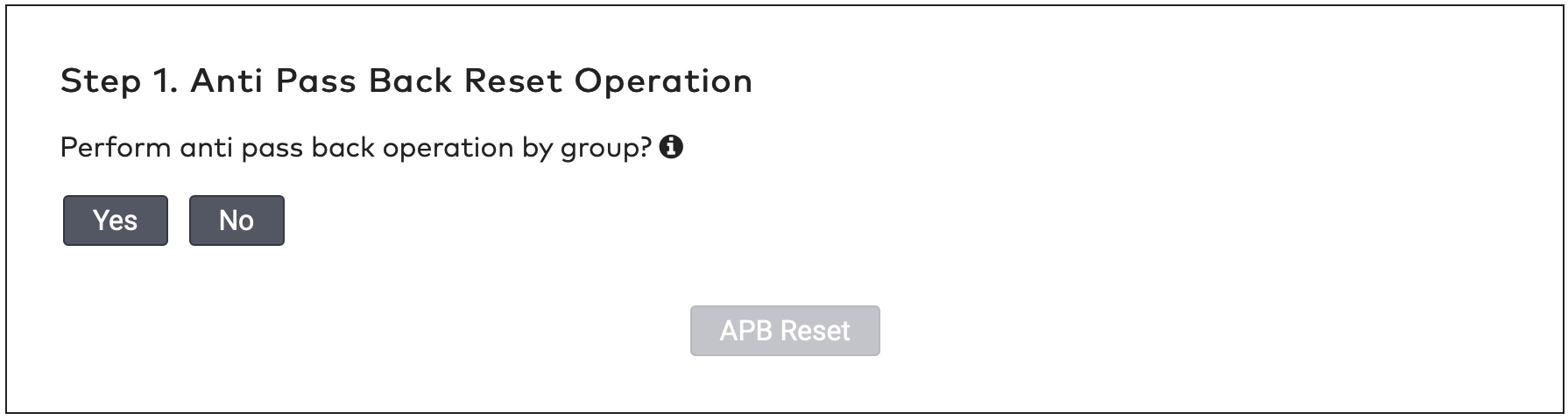
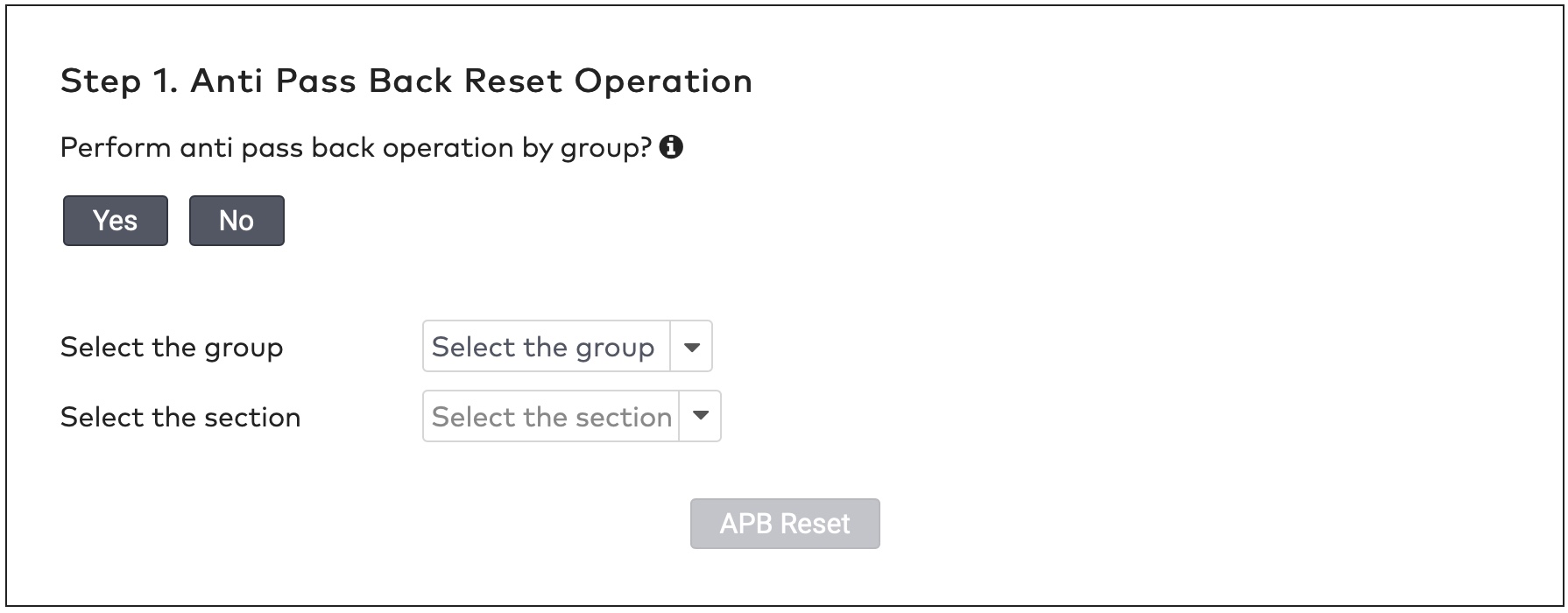
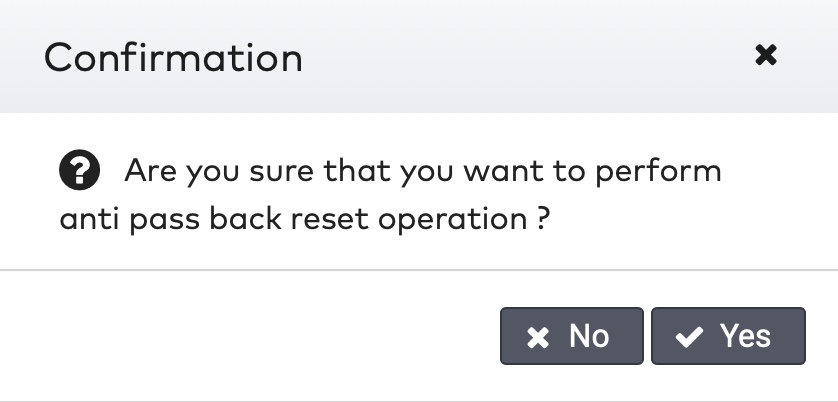
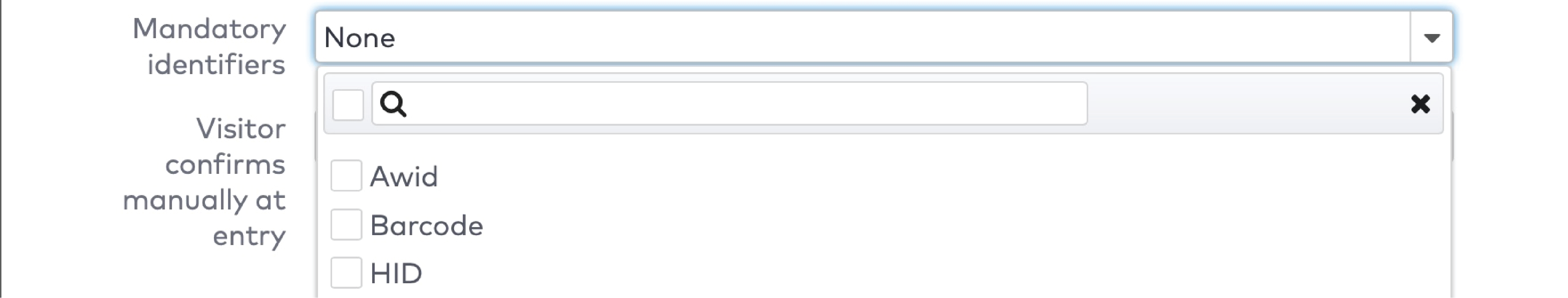
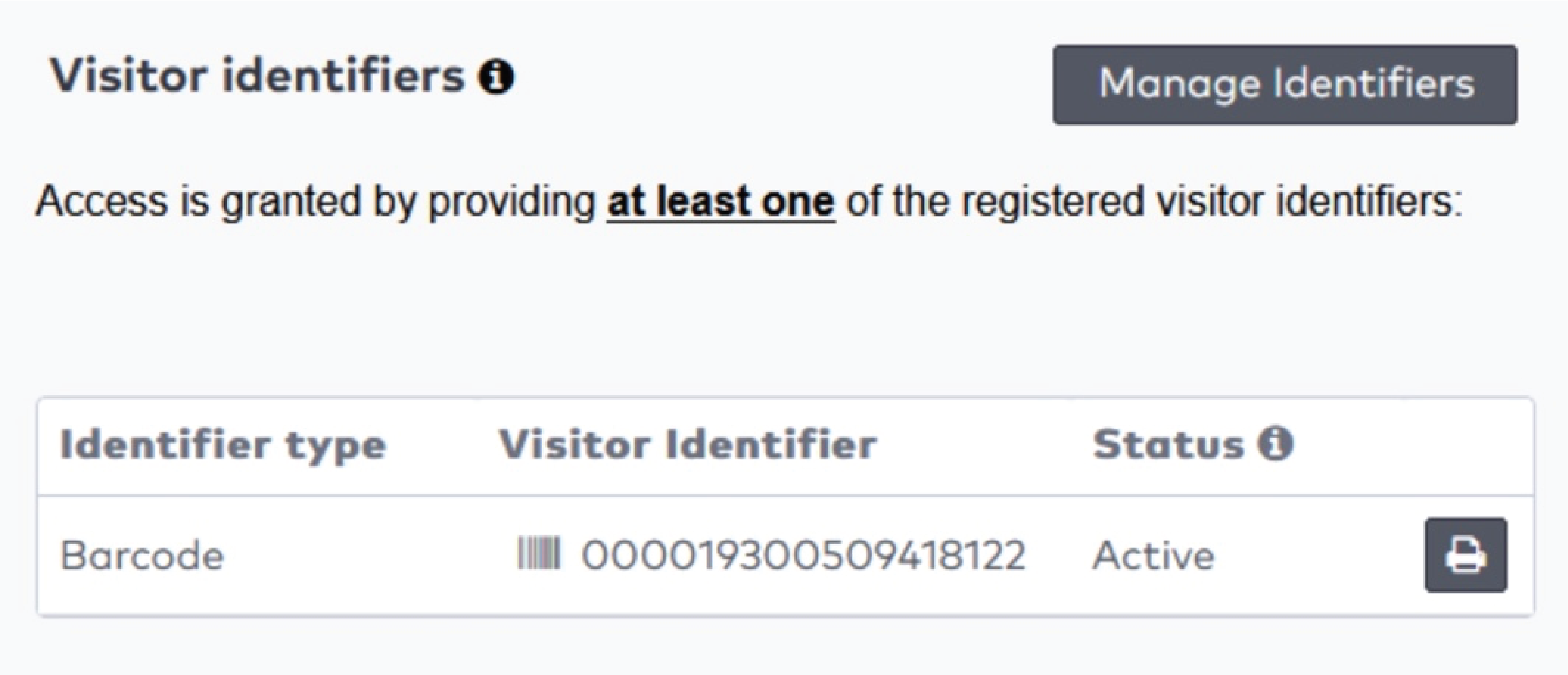
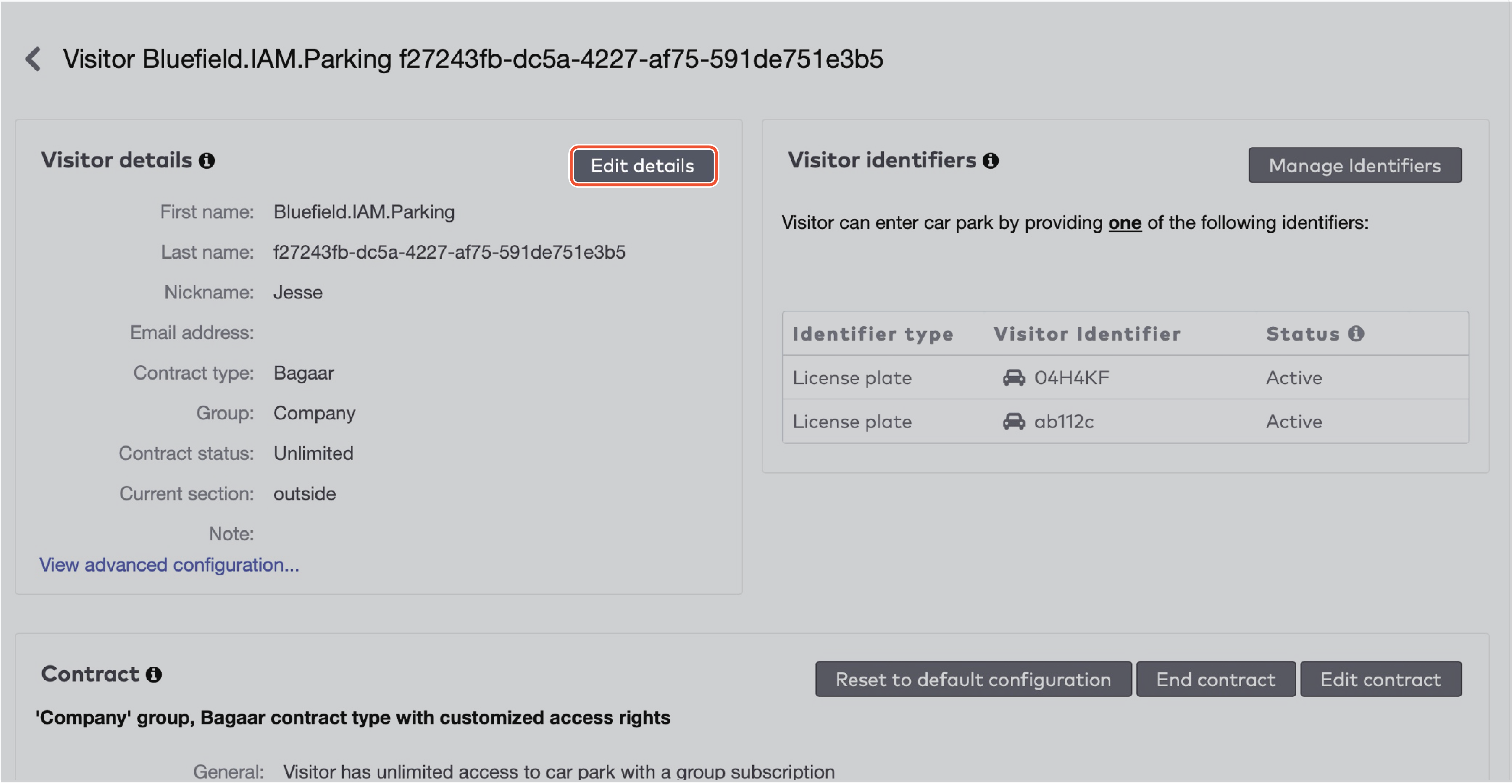
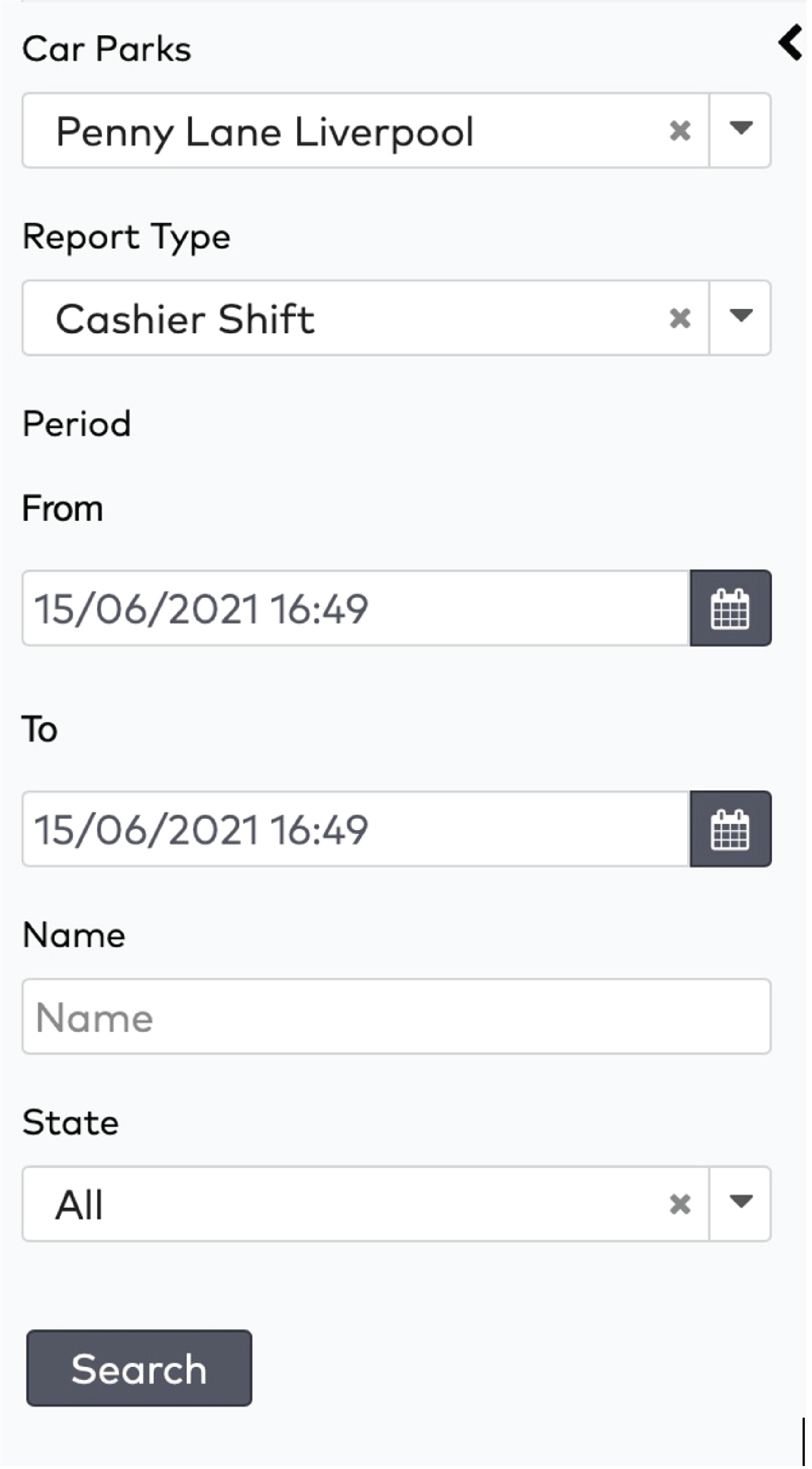
ParkID detects misuse of visitor identifiers. This is called anti-pass back. For example: when the same visitor identifier is used by two or more visitors at the same time.
|

|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|

|
|

|
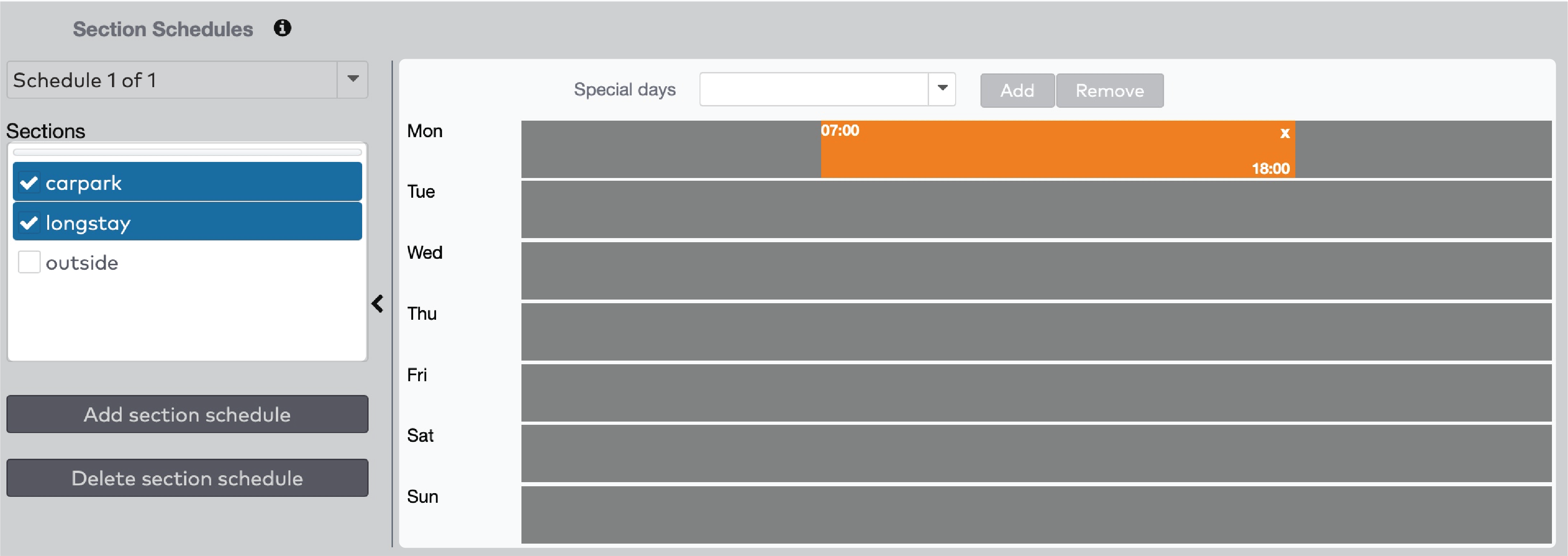
 to remove the orange bar.
to remove the orange bar.

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
With Pooling you can limit the number of visitors from a group. There are three types of pooling:
1.
Visitors are denied access when the maximum amount of visitors is reached.
2.
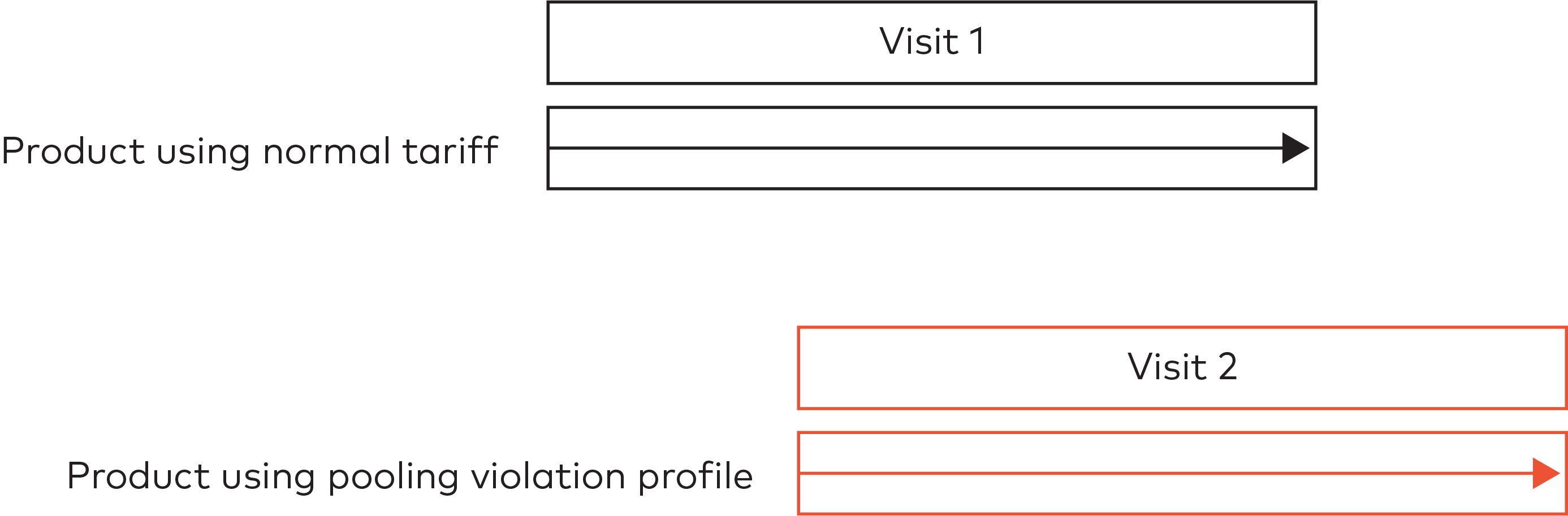
Visitors are charged the entire parking time as a pooling violation.
For example: a visitor (visit 1) enters the car park while making use of the pool. Visit 1 is charged with the normal tariff configured for the group. When visit 2 arrives, the pool is full. Visit 2 is charged a different tariff the entire time.
3.
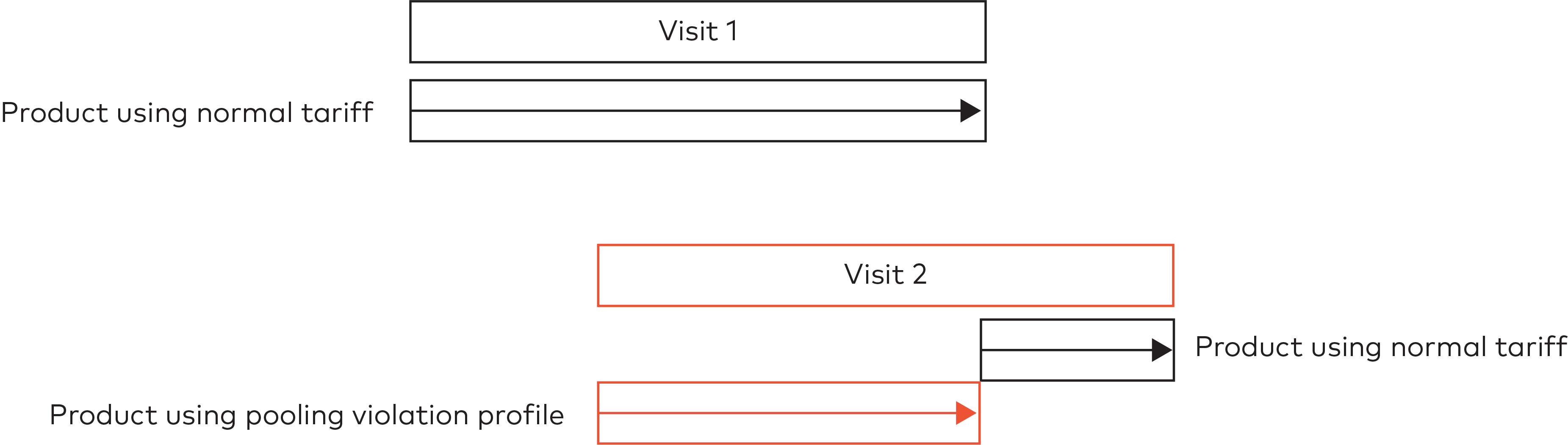
Visitors are charged only the parking time under pooling violation.
For example: a visitor (visit 1) enters the car park while making use of the pool. Visit 1 is charged with the normal tariff configured for the group. When visit 2 arrives, the pool is full. Visit 2 is charged a different tariff. When visit 1 leaves, a spot becomes available in the pool. Visit 2 is charged the normal tariff from that moment onwards.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
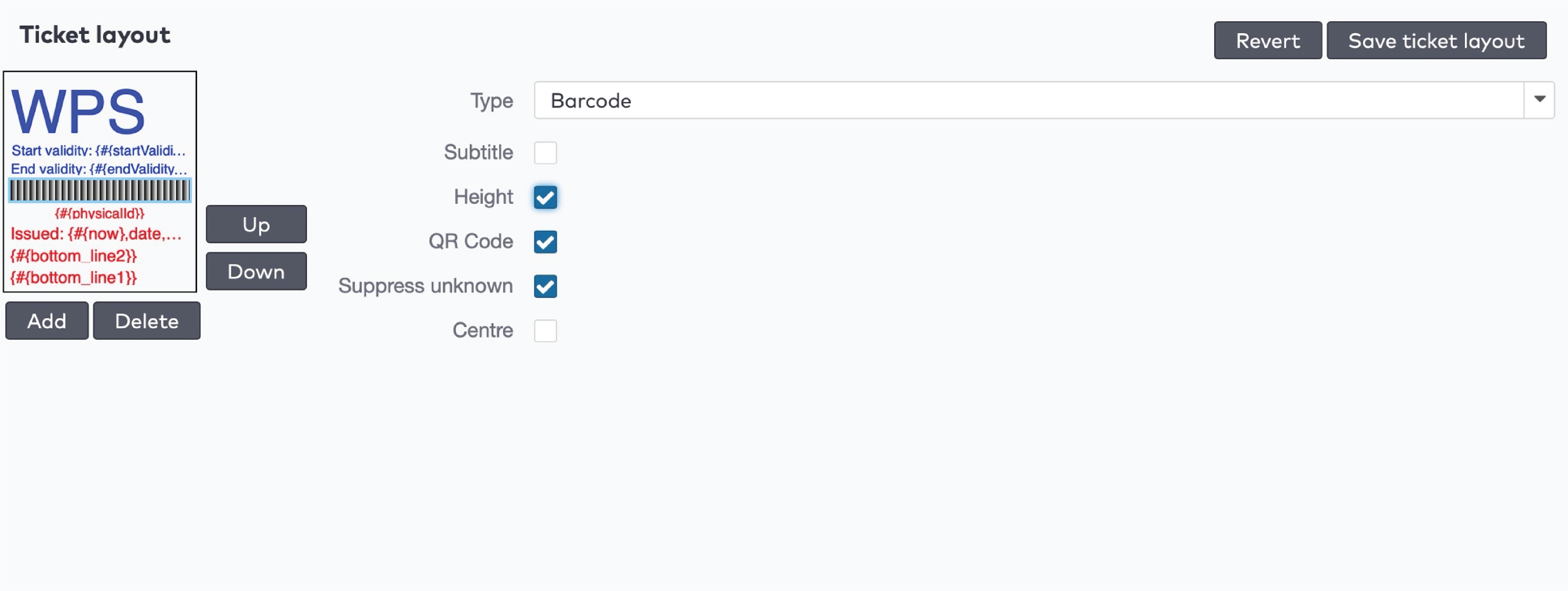
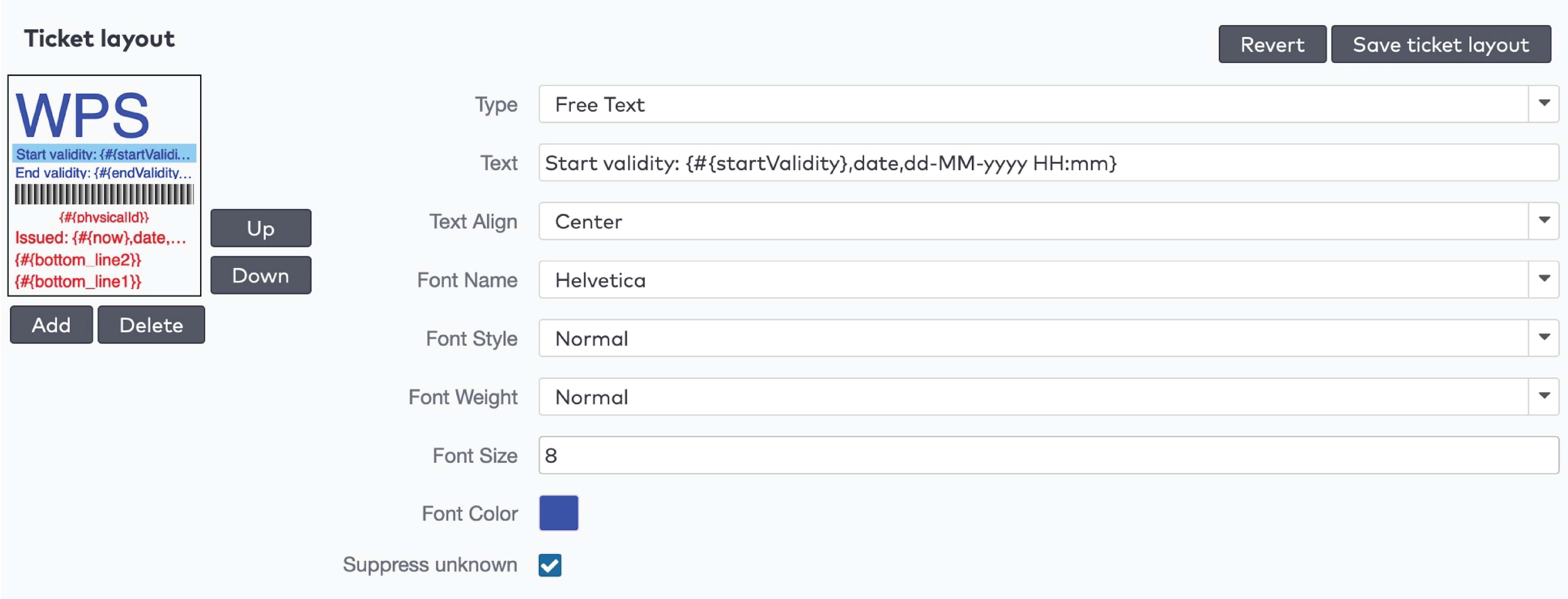
 to print the barcode.
to print the barcode.
|

|

|
|
|
|

|

|
 to print the barcode.
to print the barcode.

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
 to print the barcode.
to print the barcode.

|

|

|
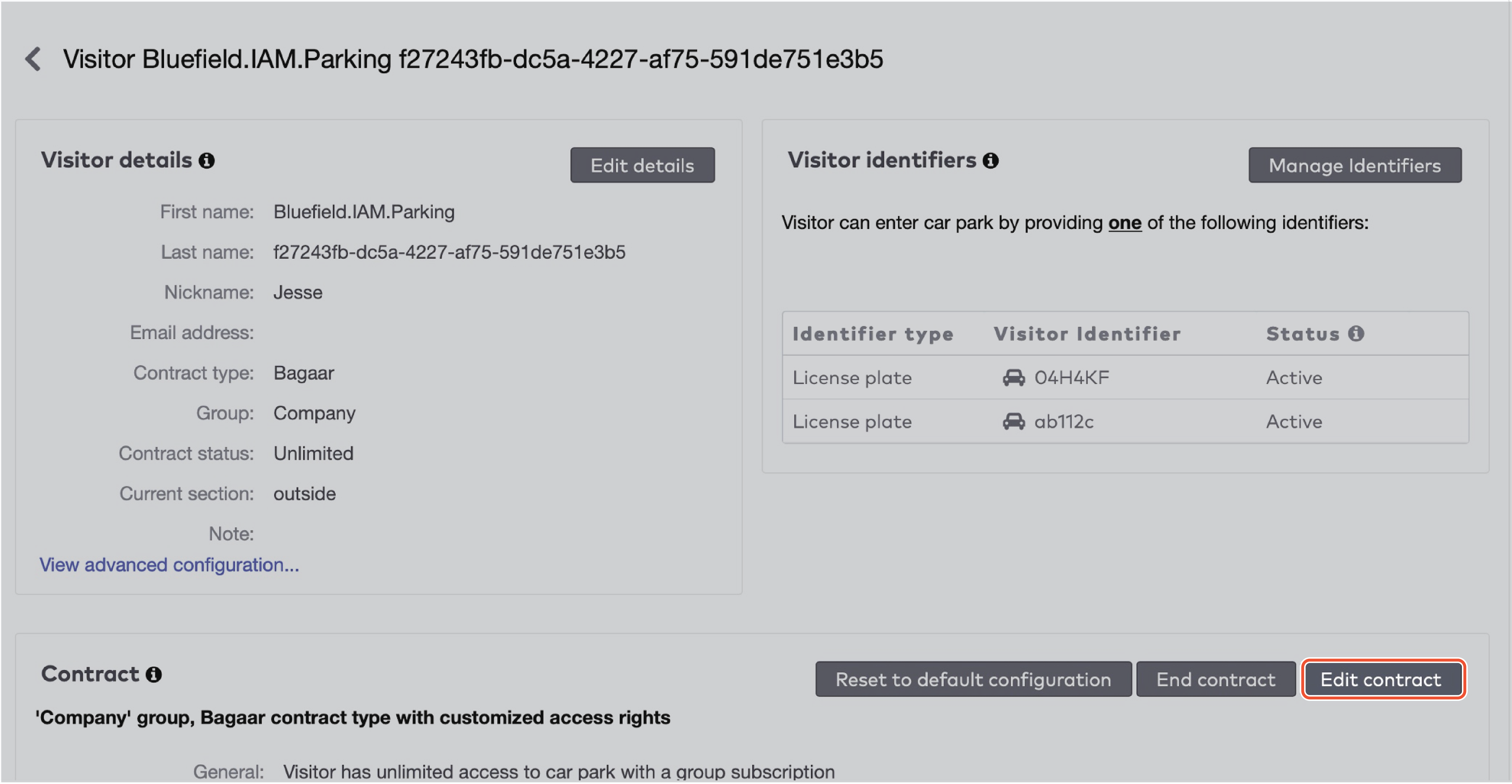
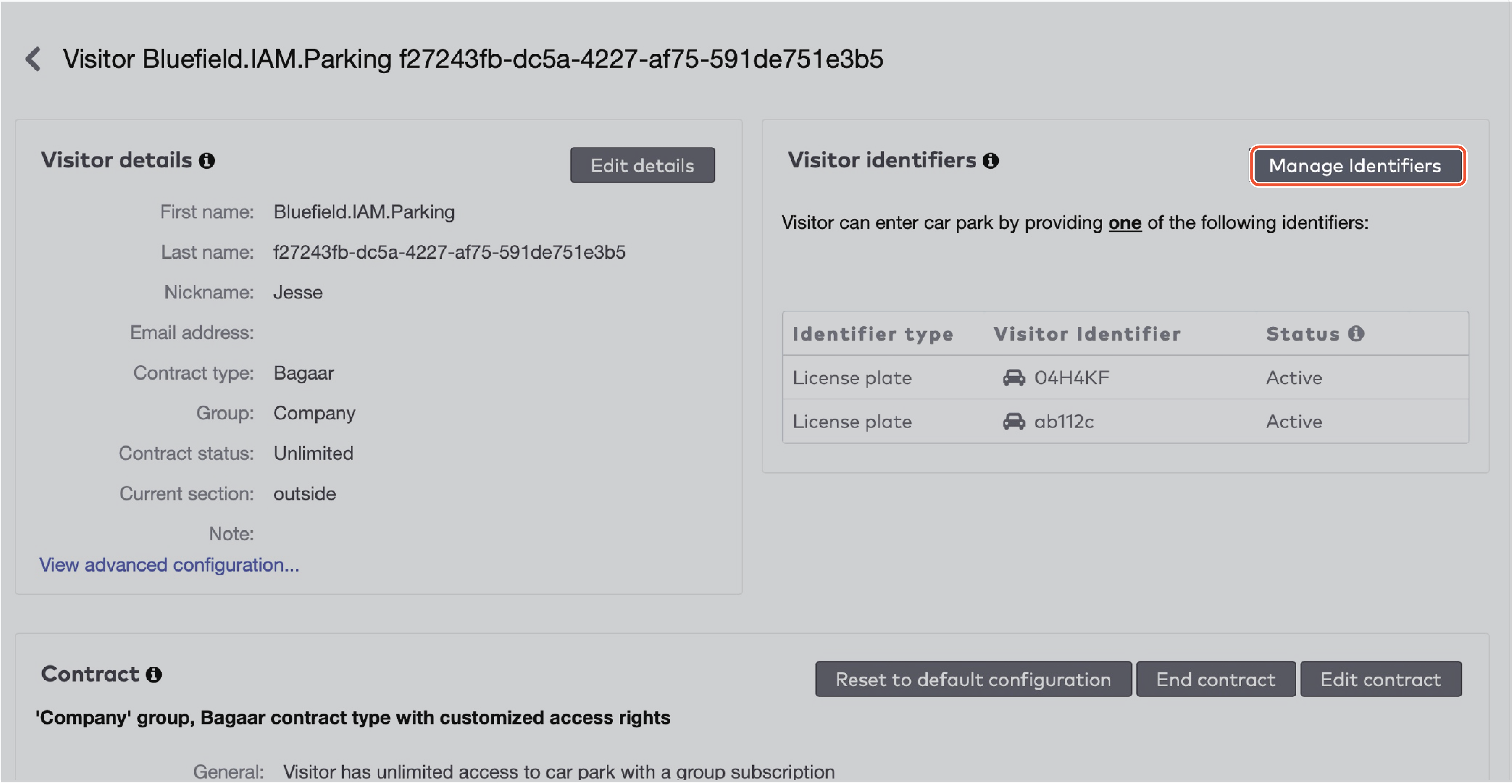
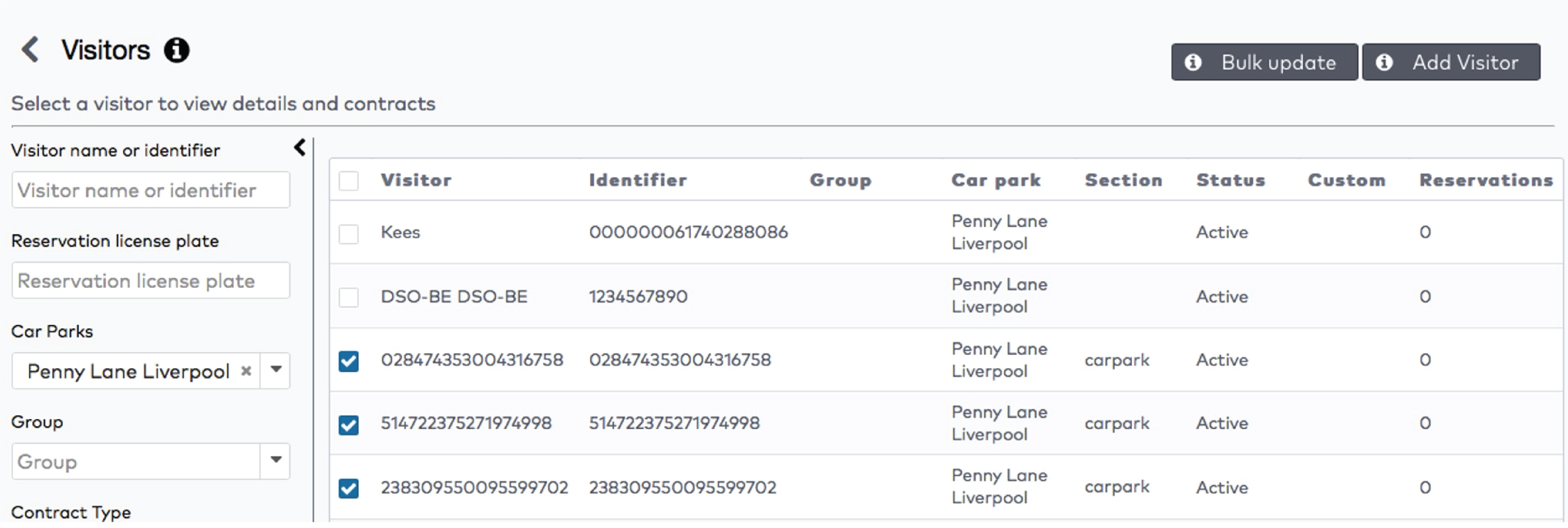
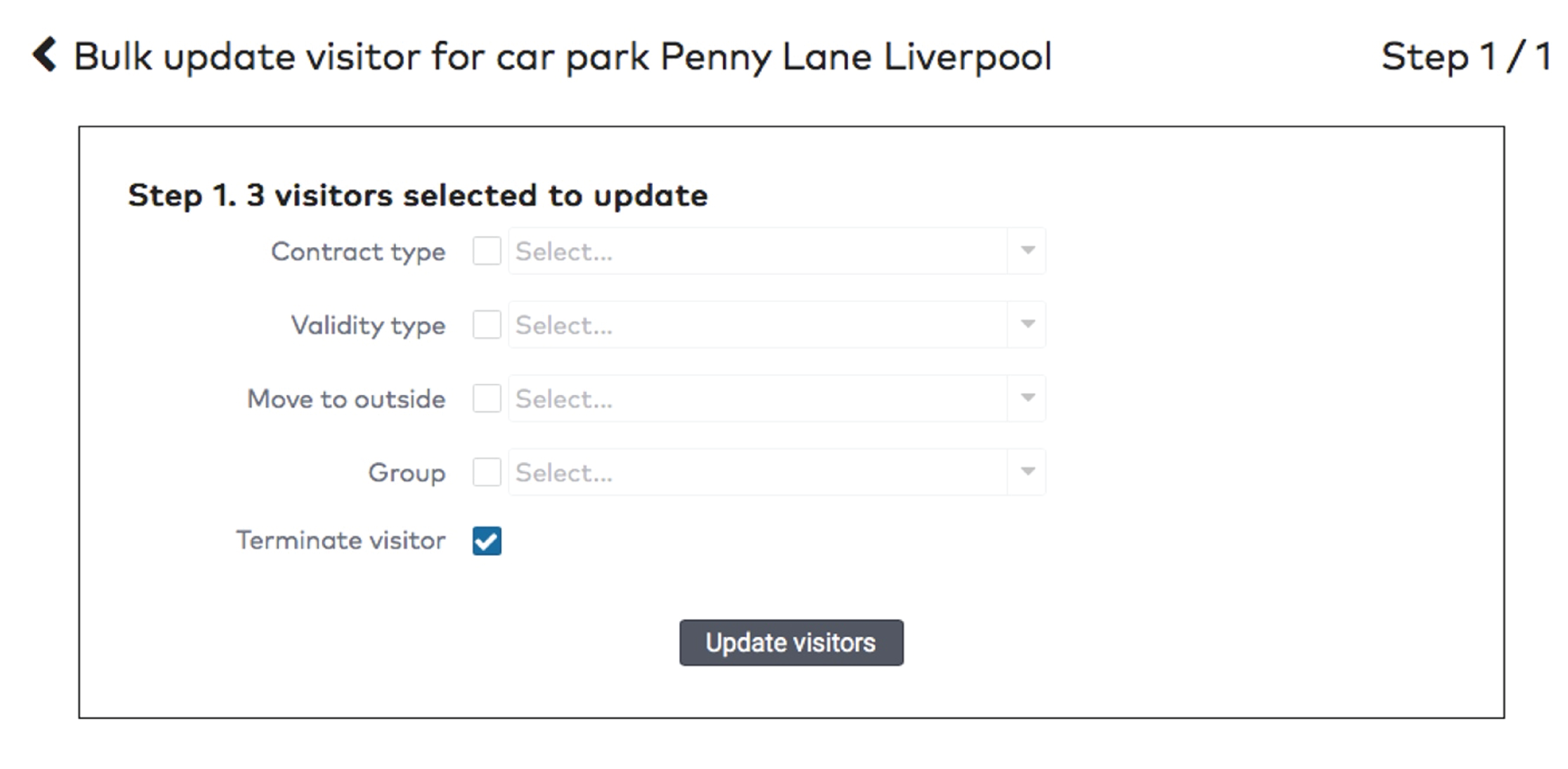
 in the Group dropdown menu.
in the Group dropdown menu.

|
|
|
|
|
|
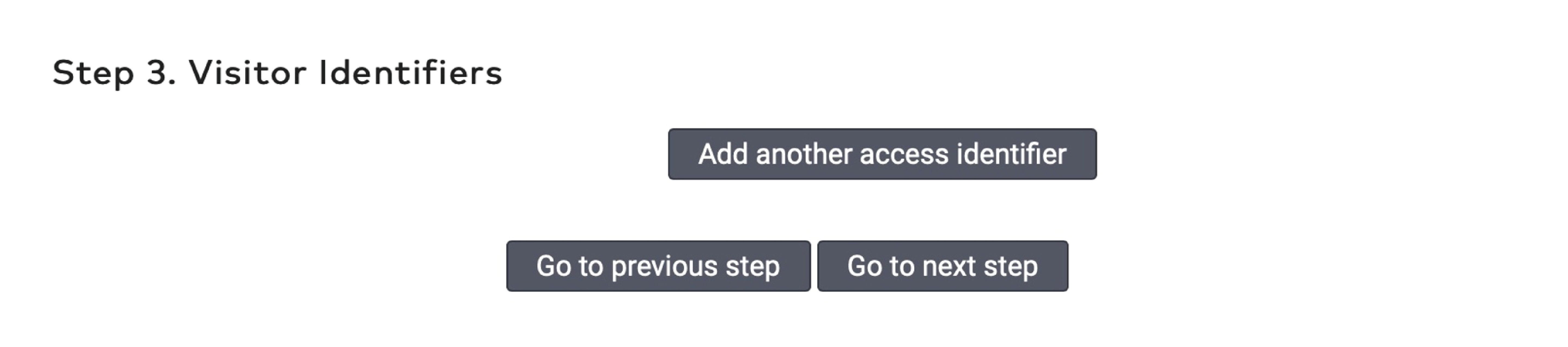
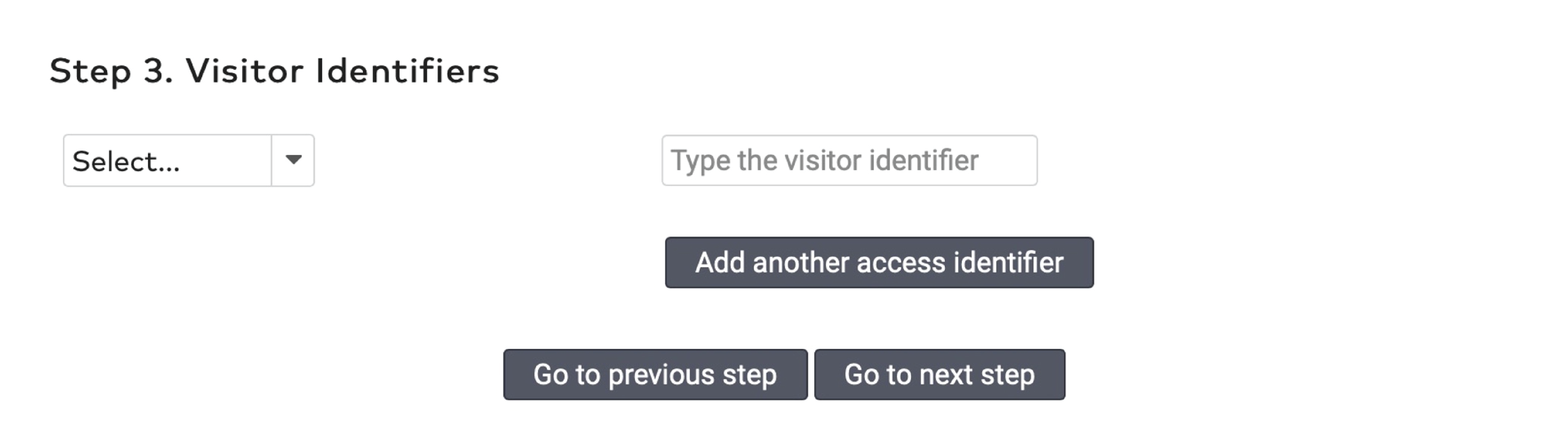
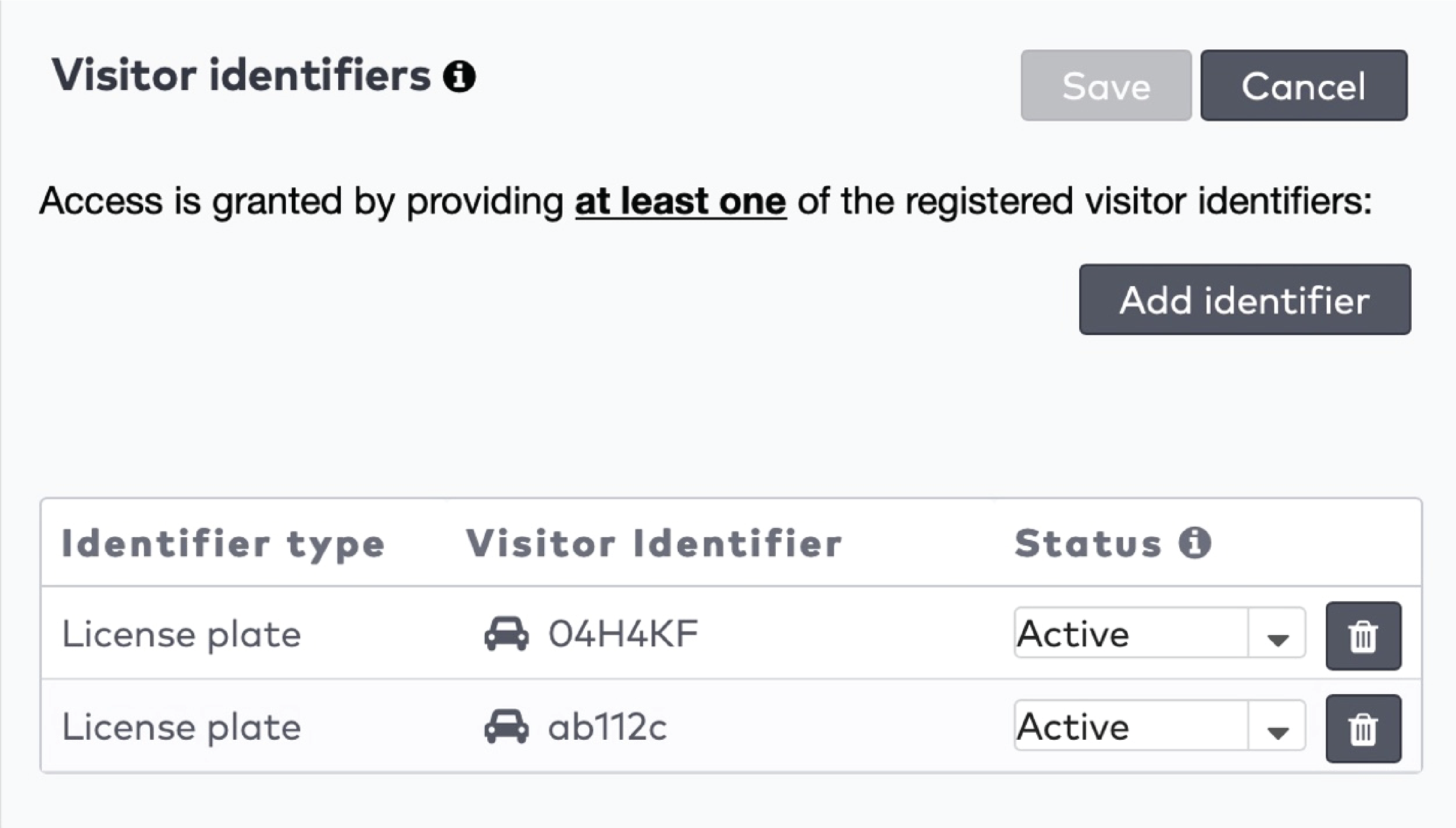
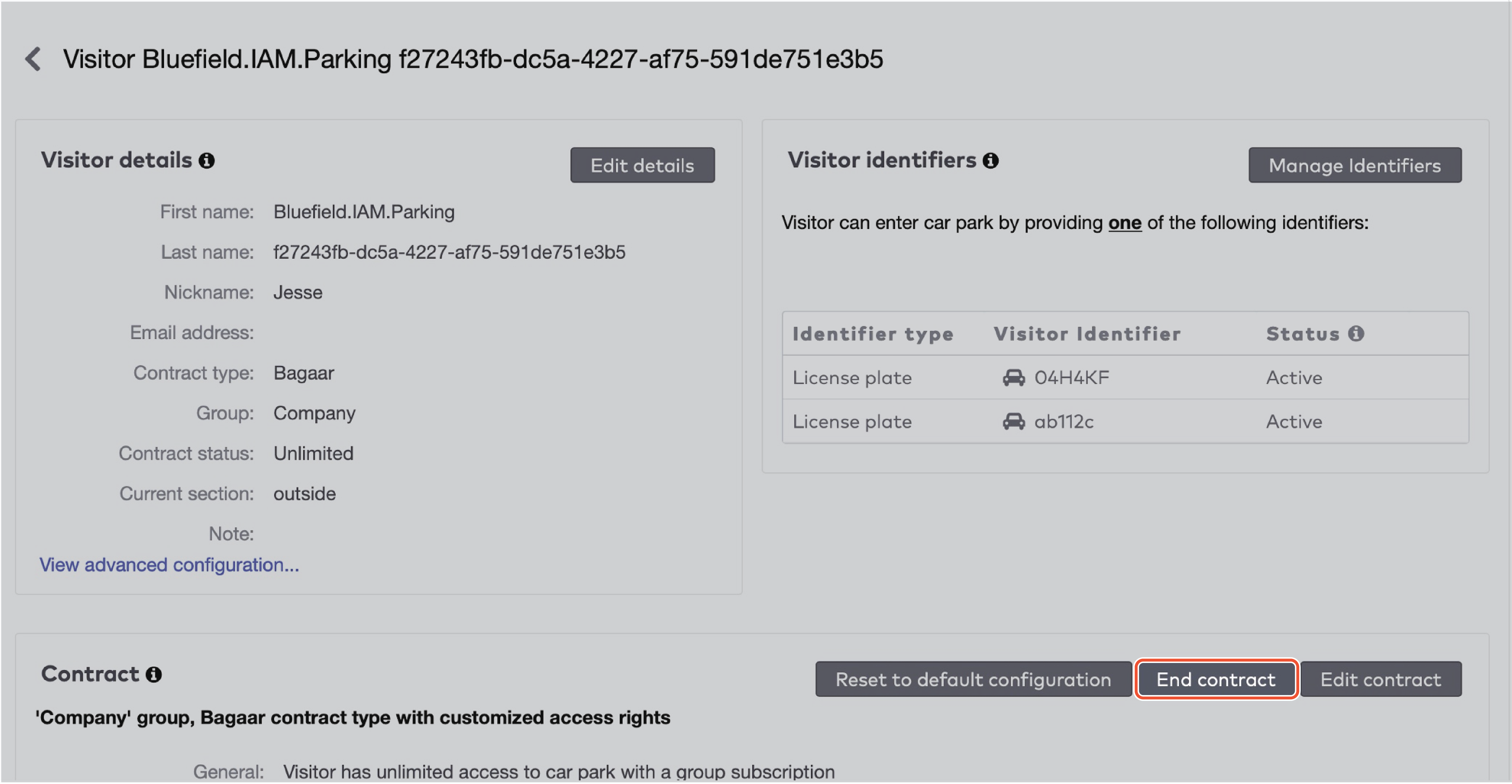
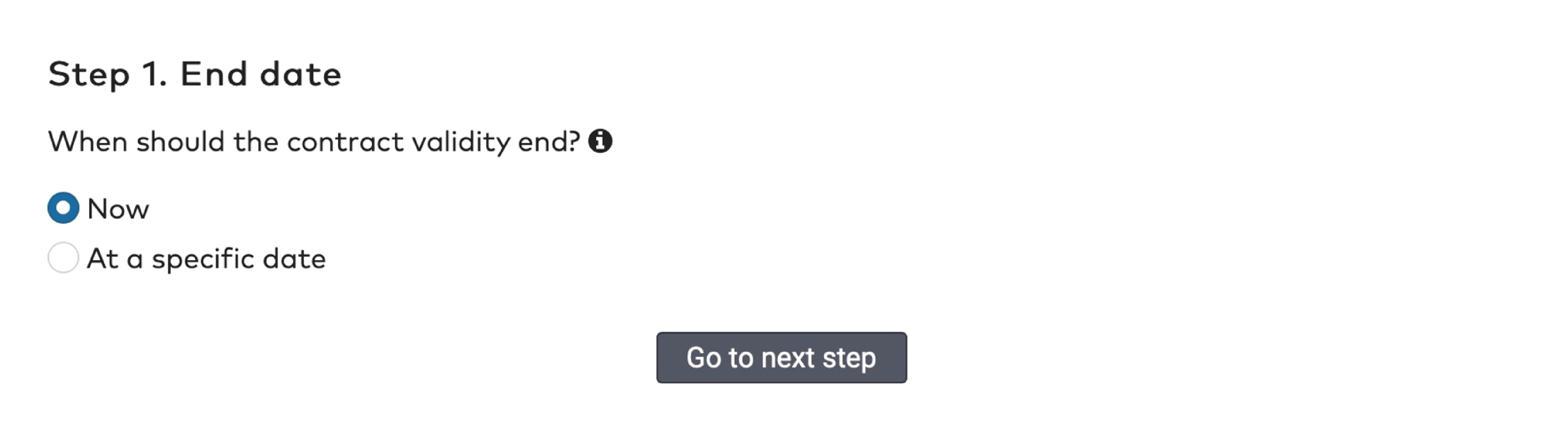
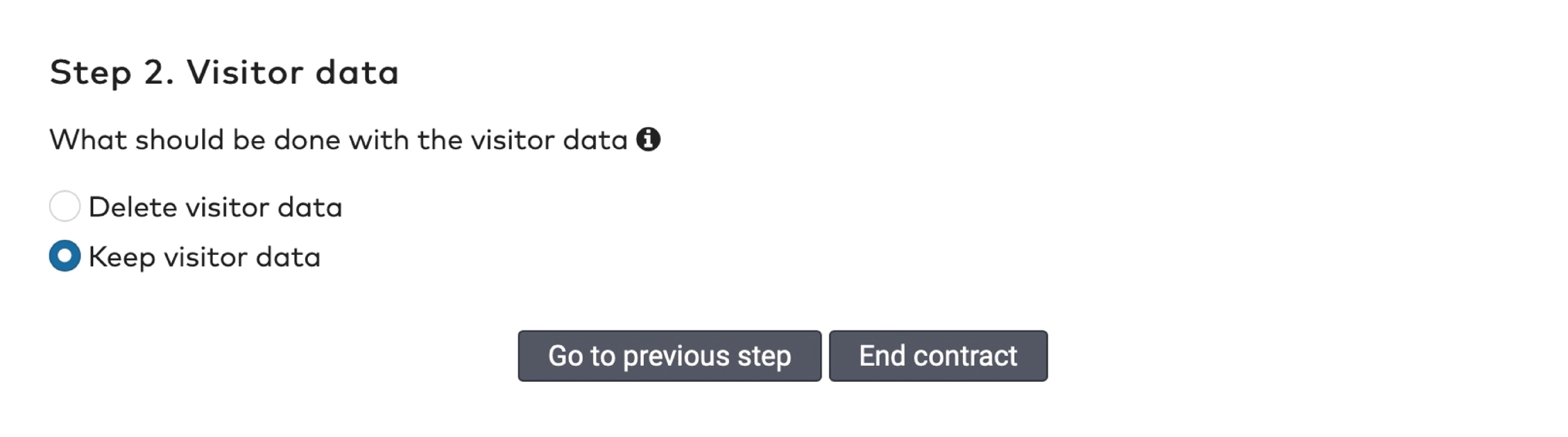
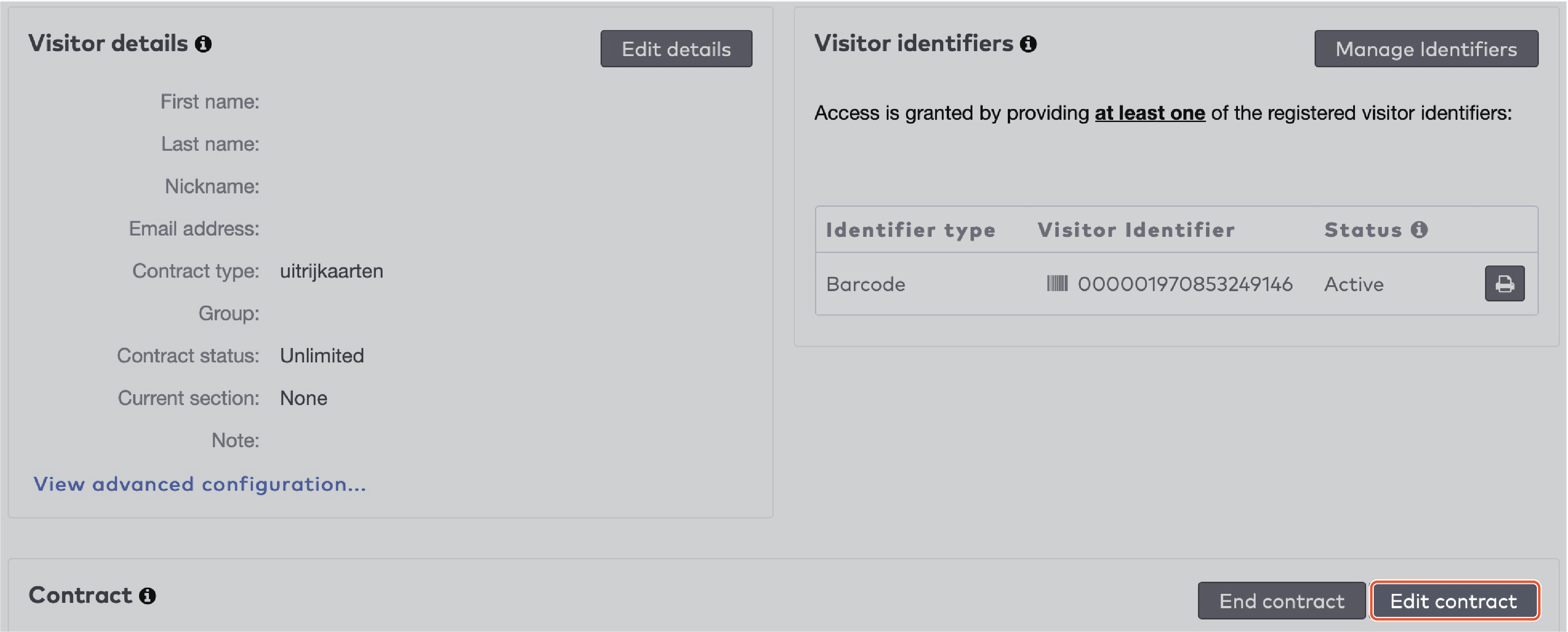
 to delete an identifier.
to delete an identifier.
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
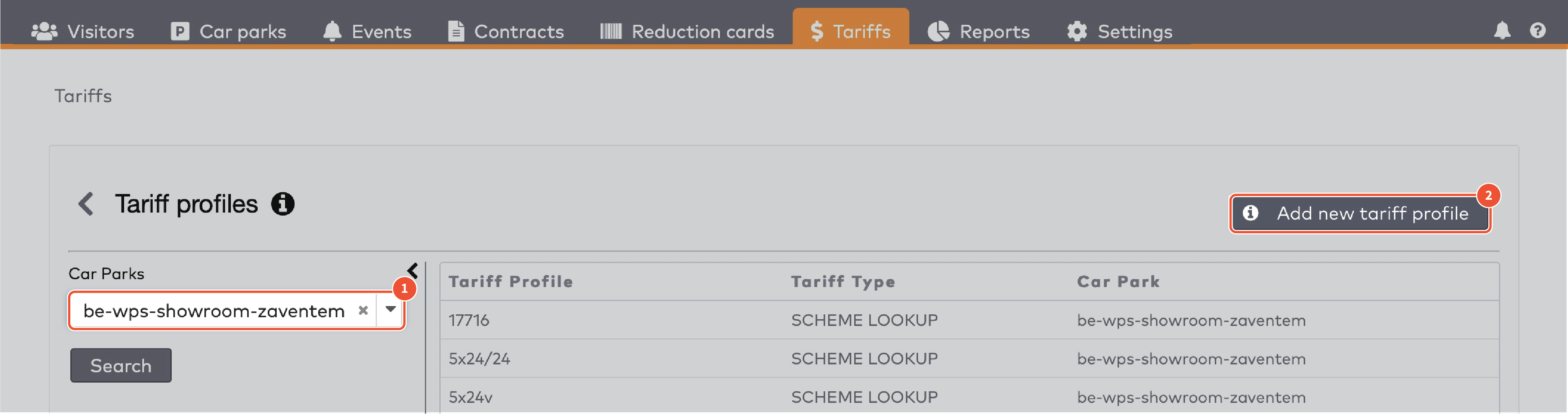
|
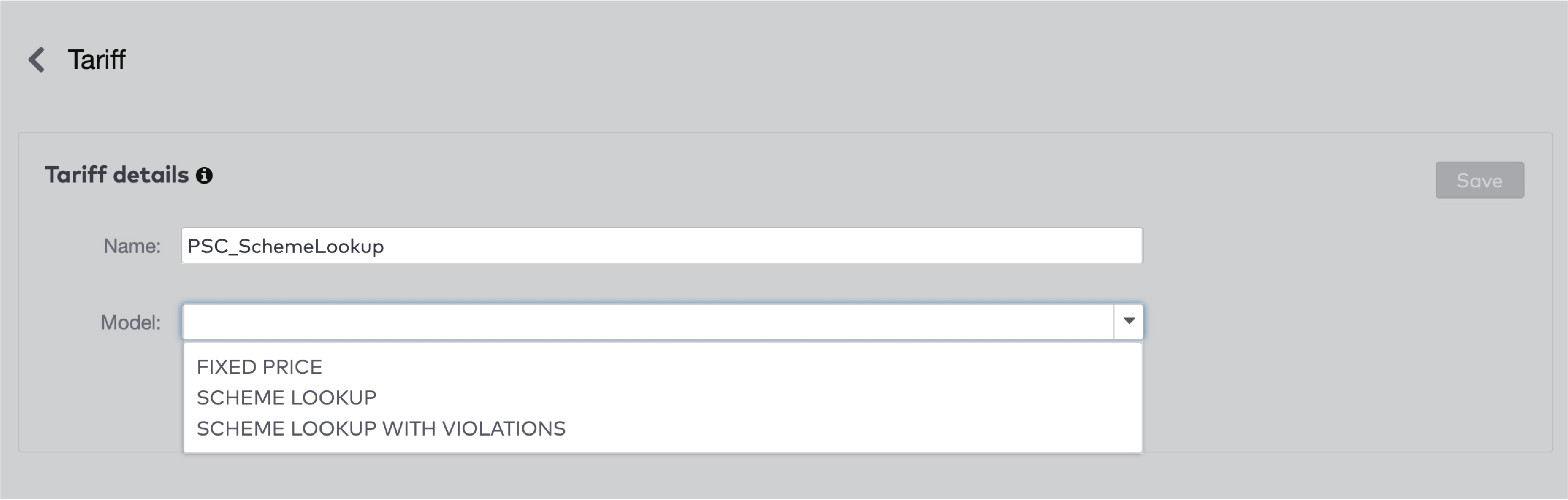
|

|
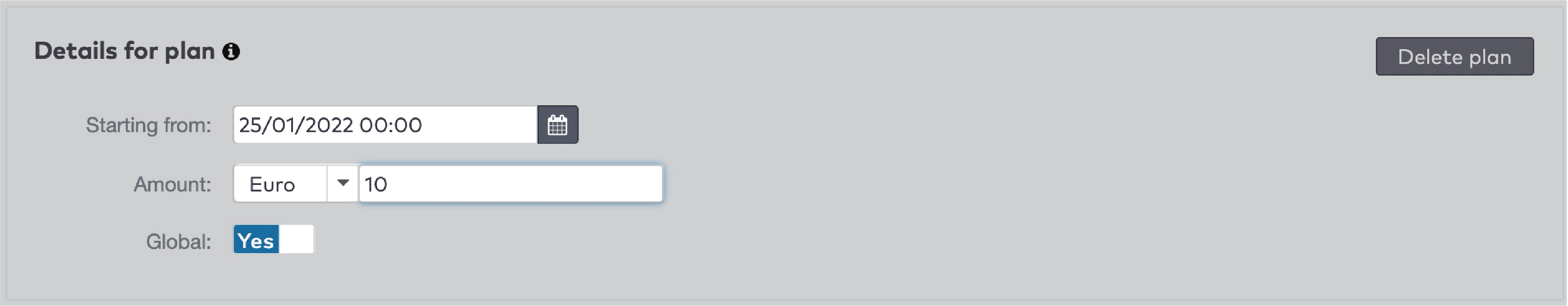
|
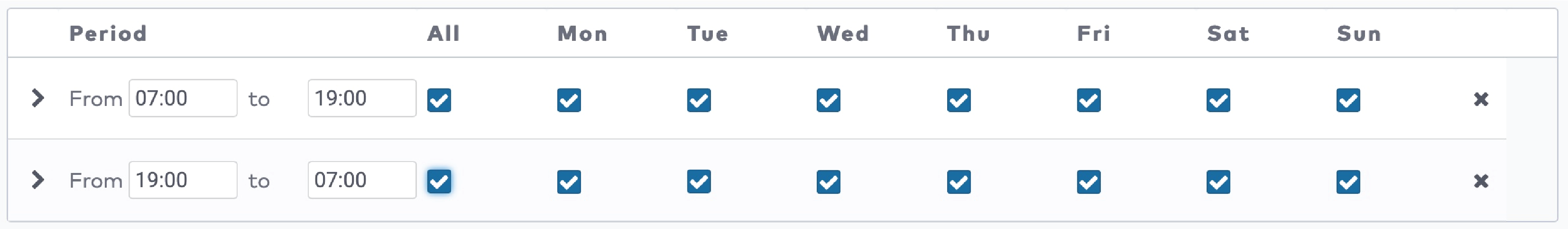
|
|
|
|
|
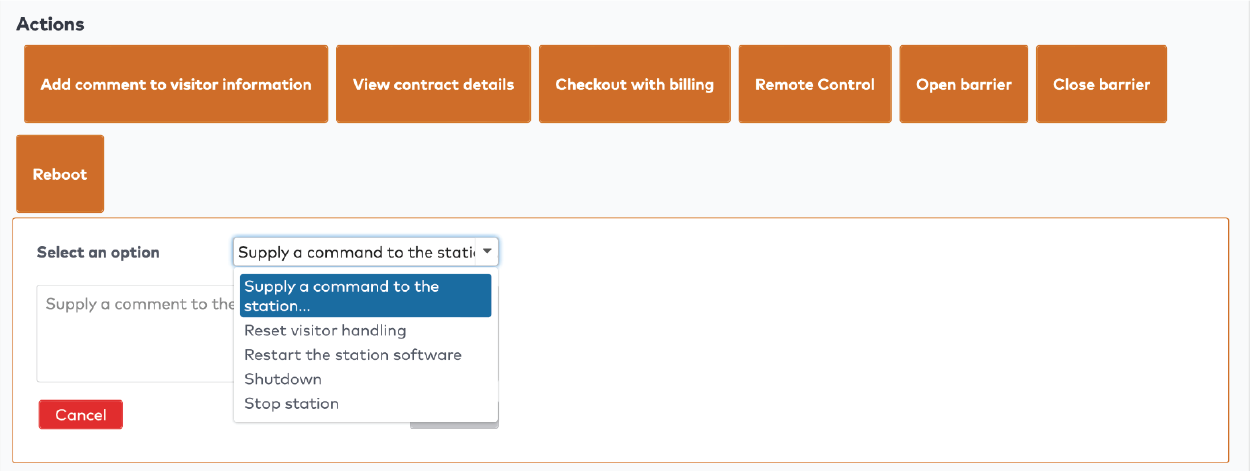
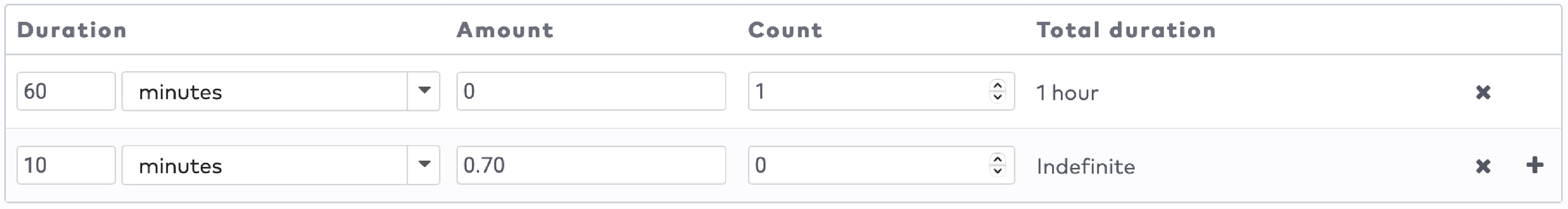
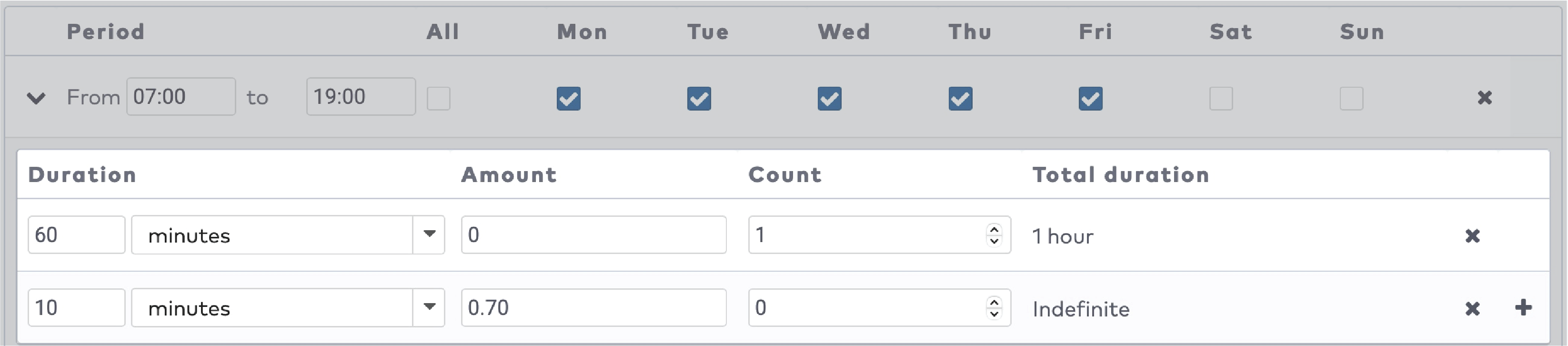
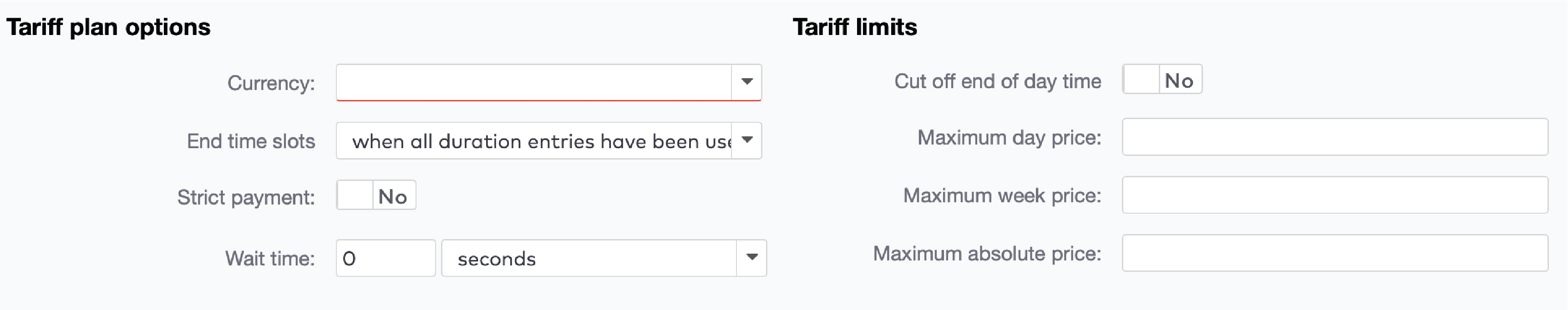
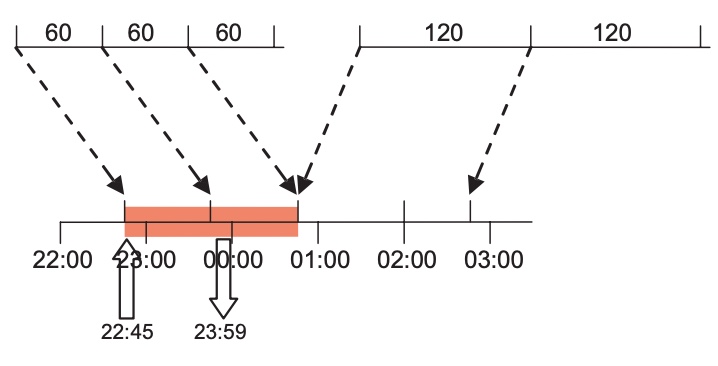
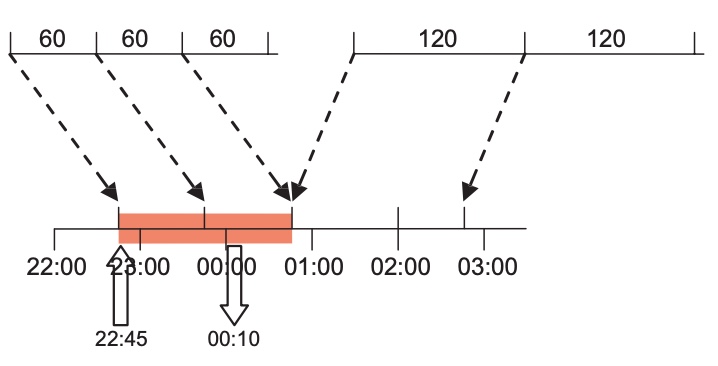
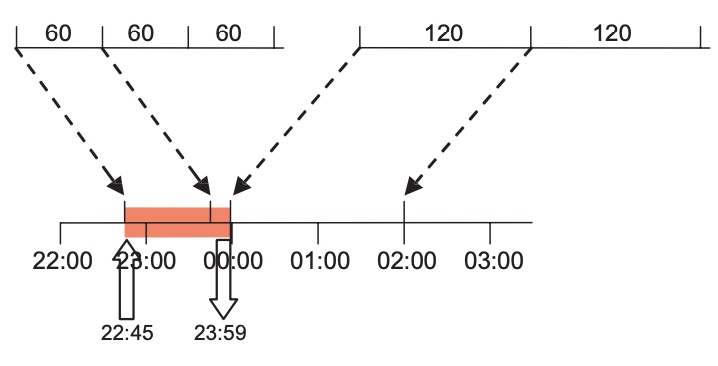
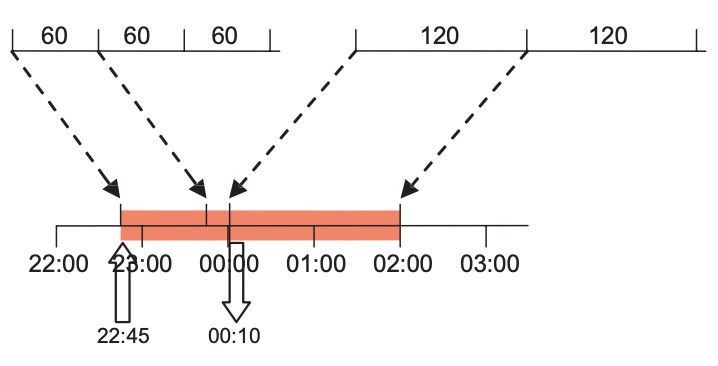
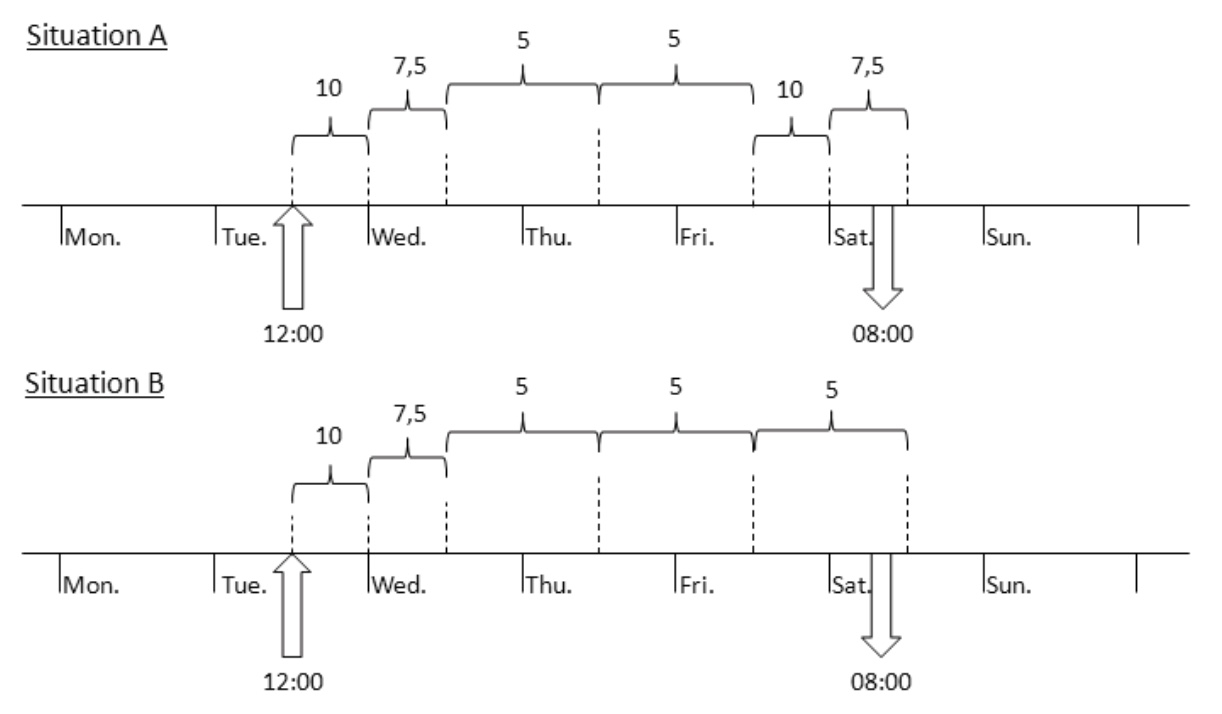
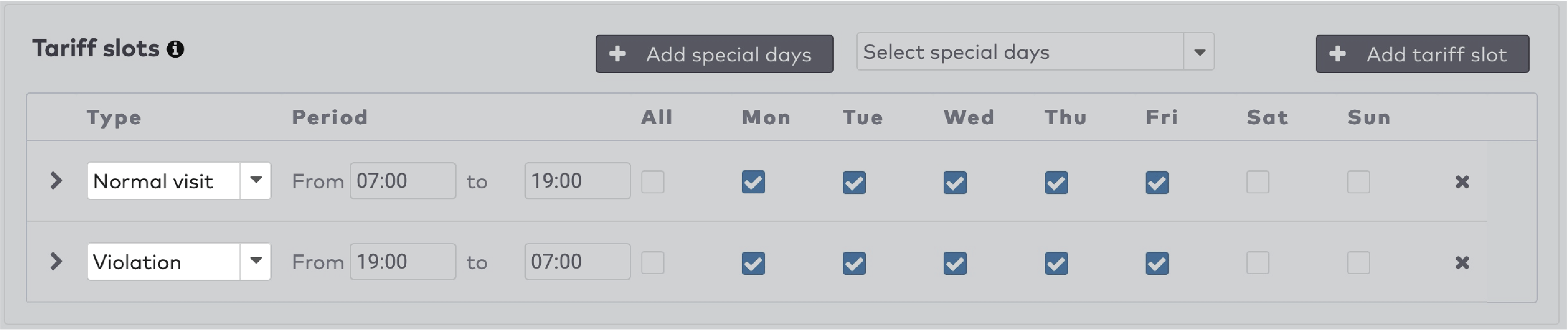
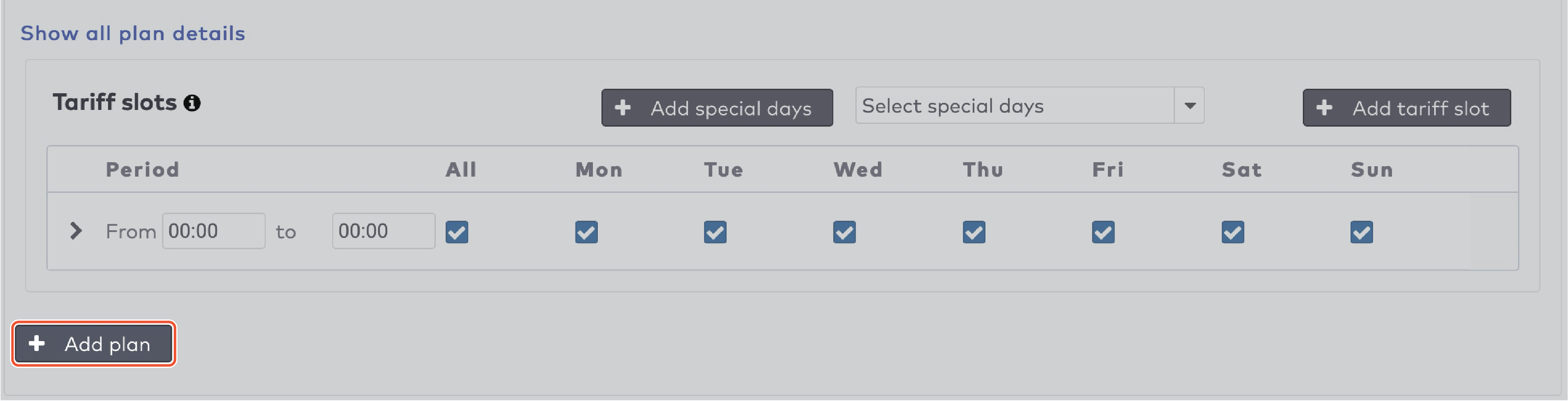
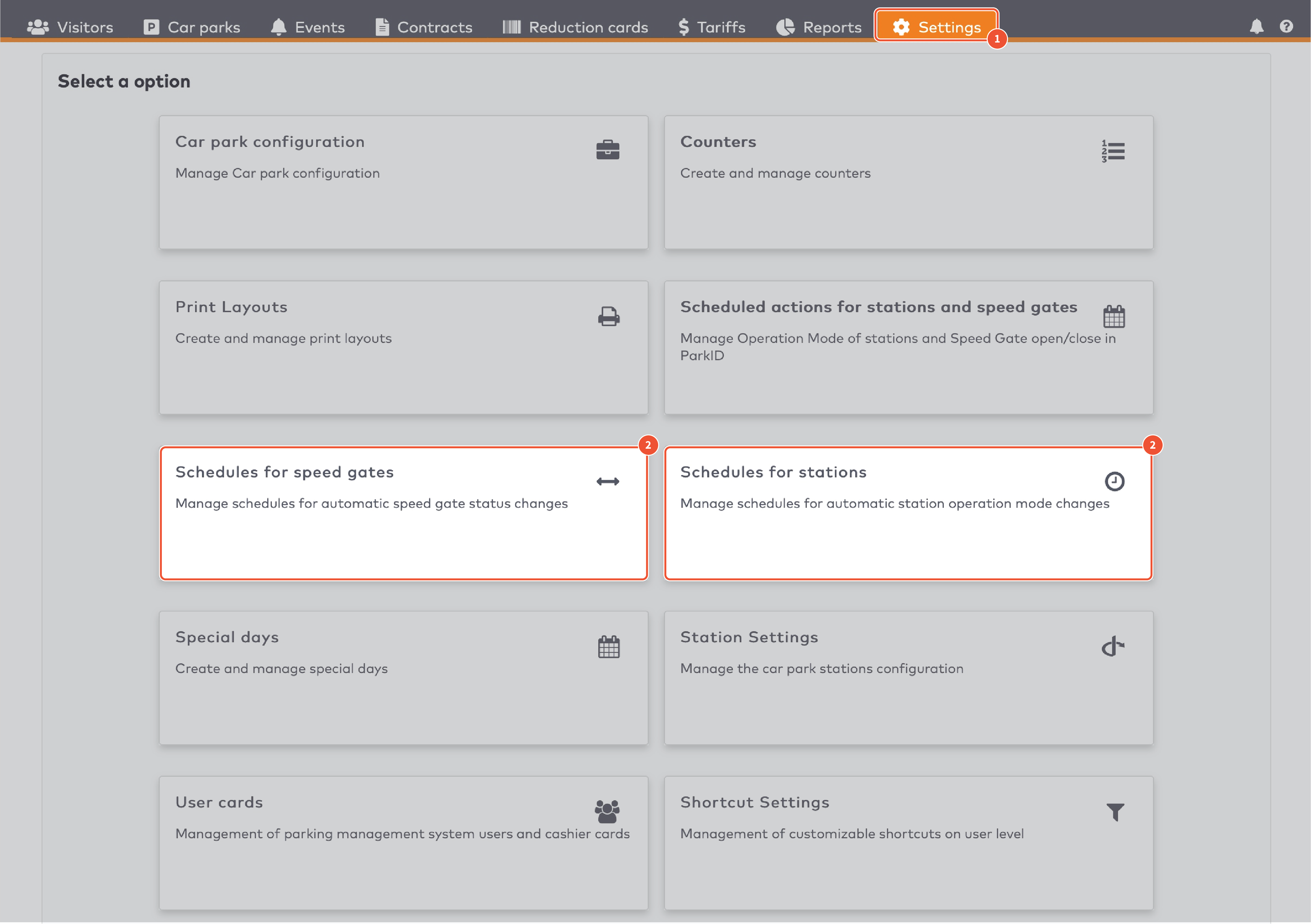
 to create the duration entries for this tariff slot. Press
to create the duration entries for this tariff slot. Press  to add a new duration entry.
to add a new duration entry.
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
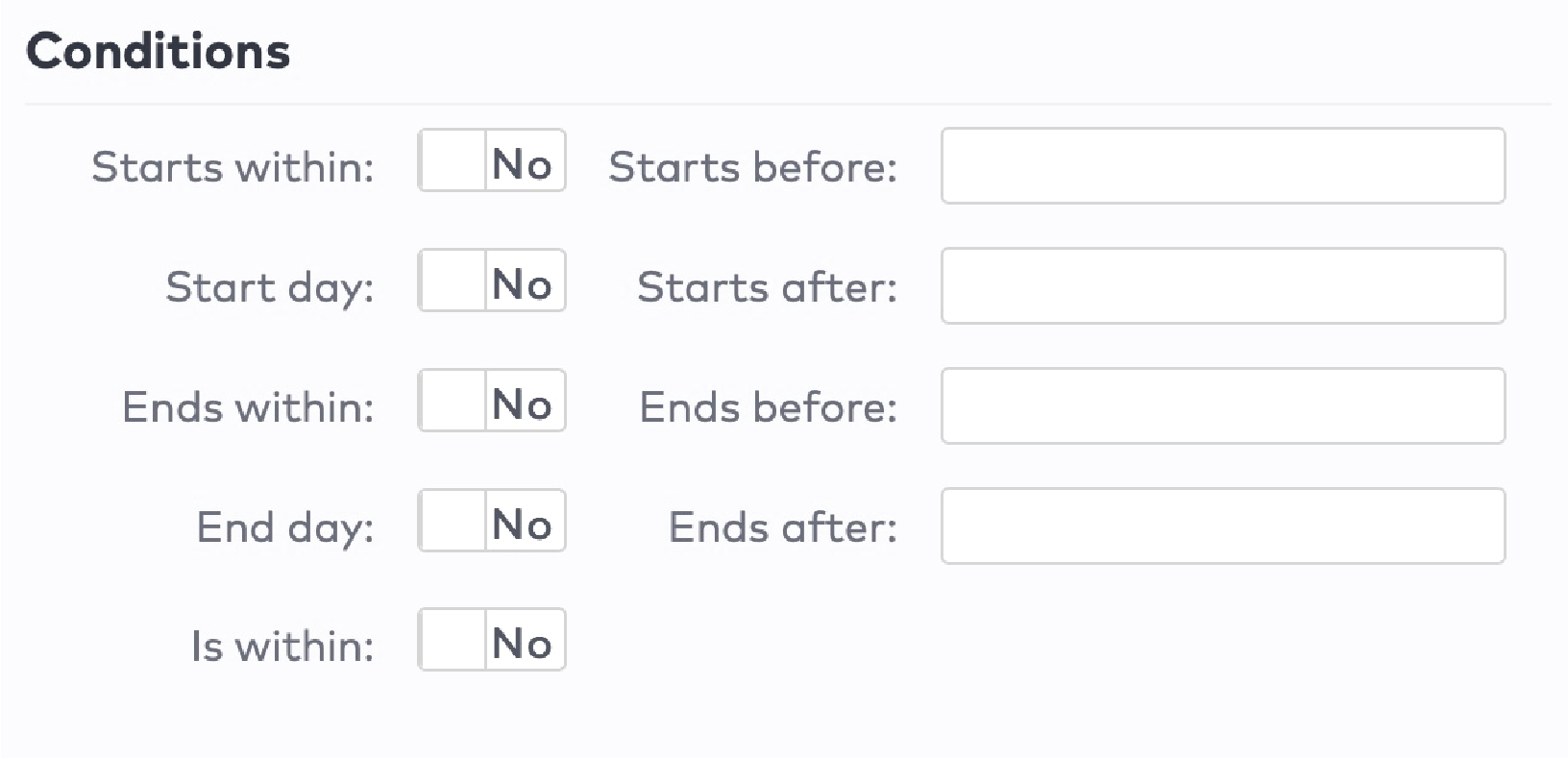
|
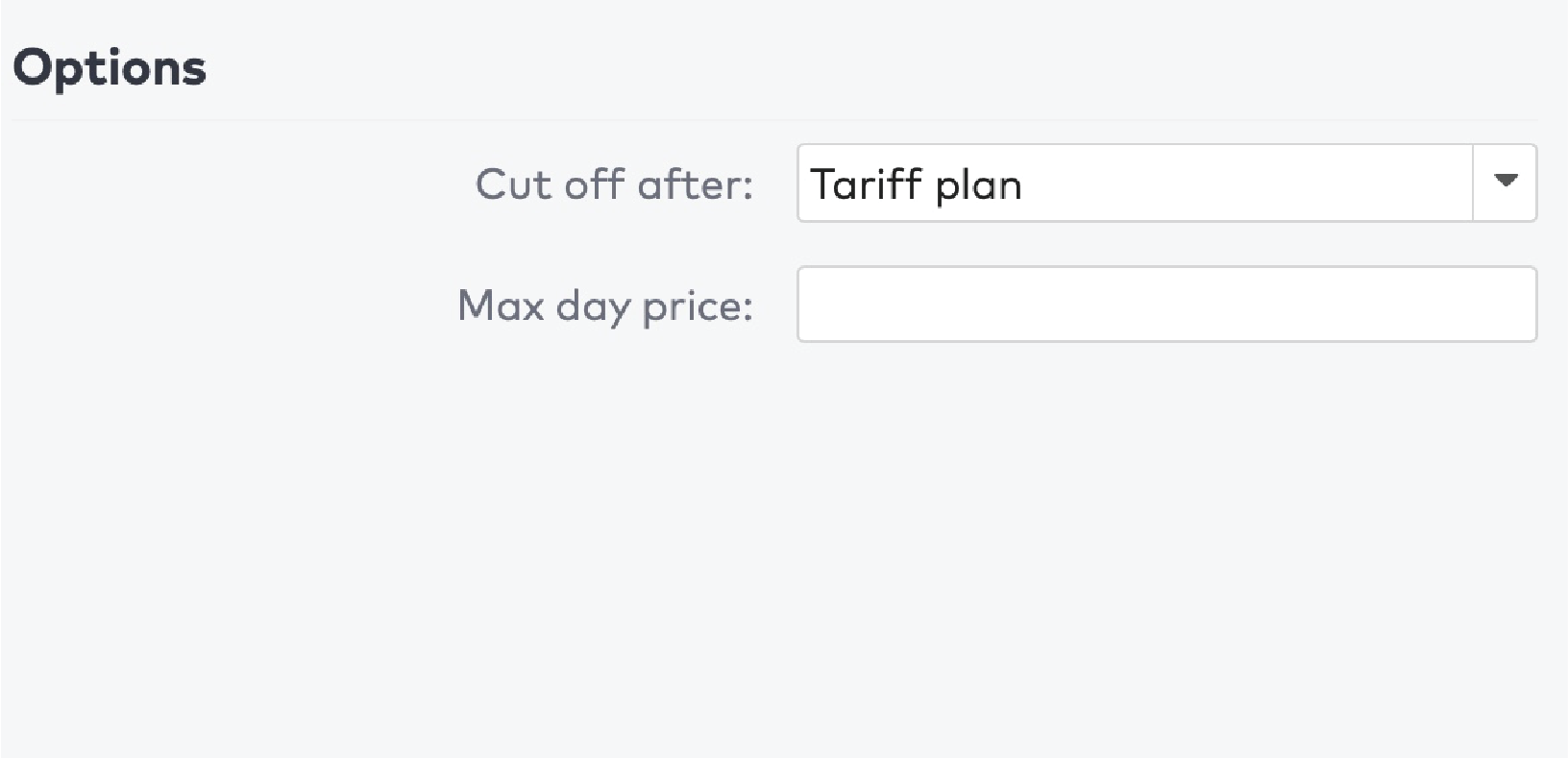
|

|
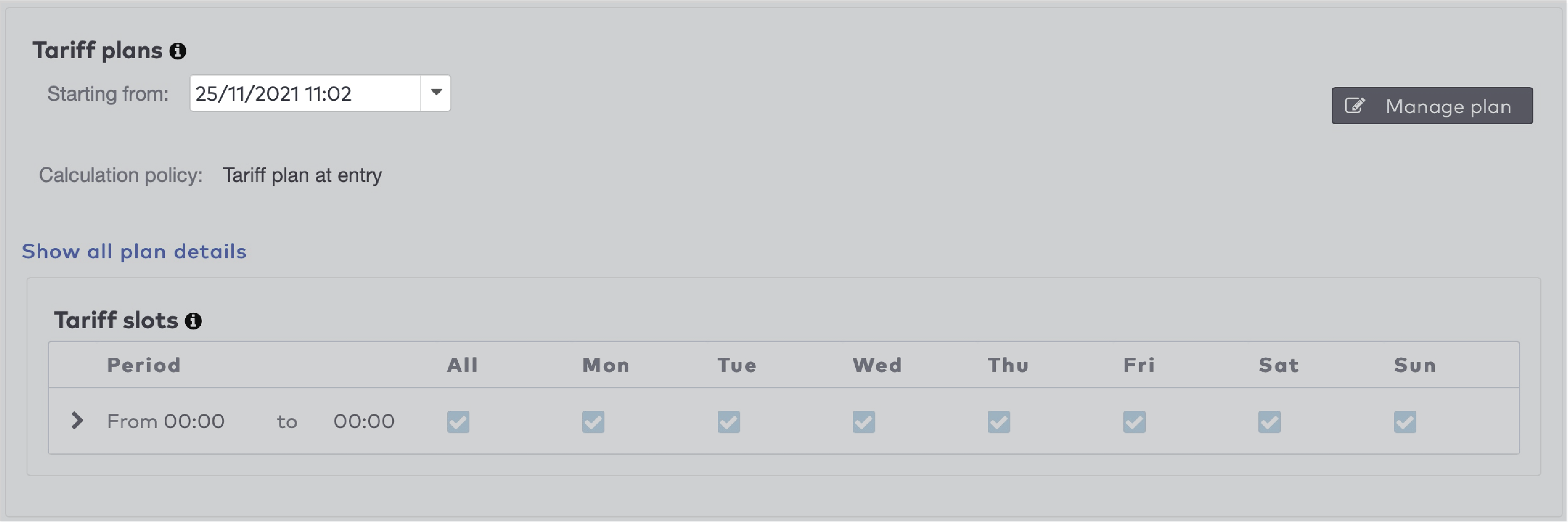
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
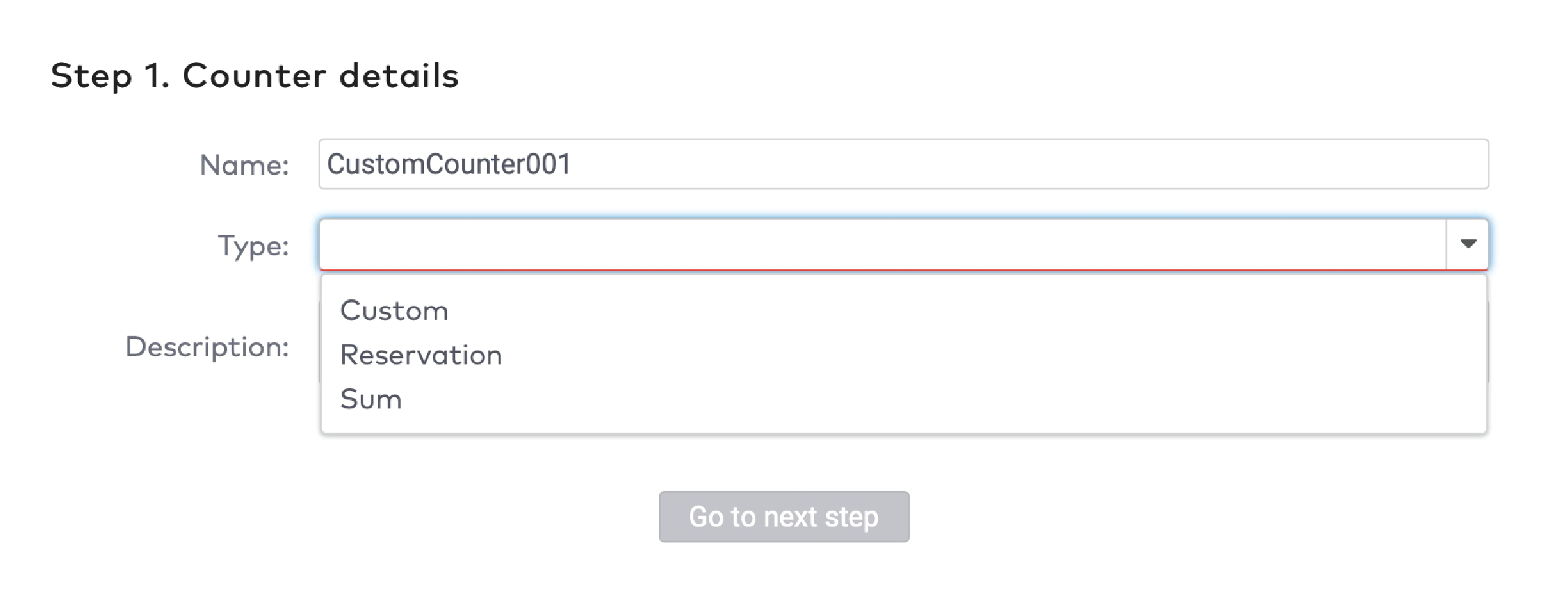
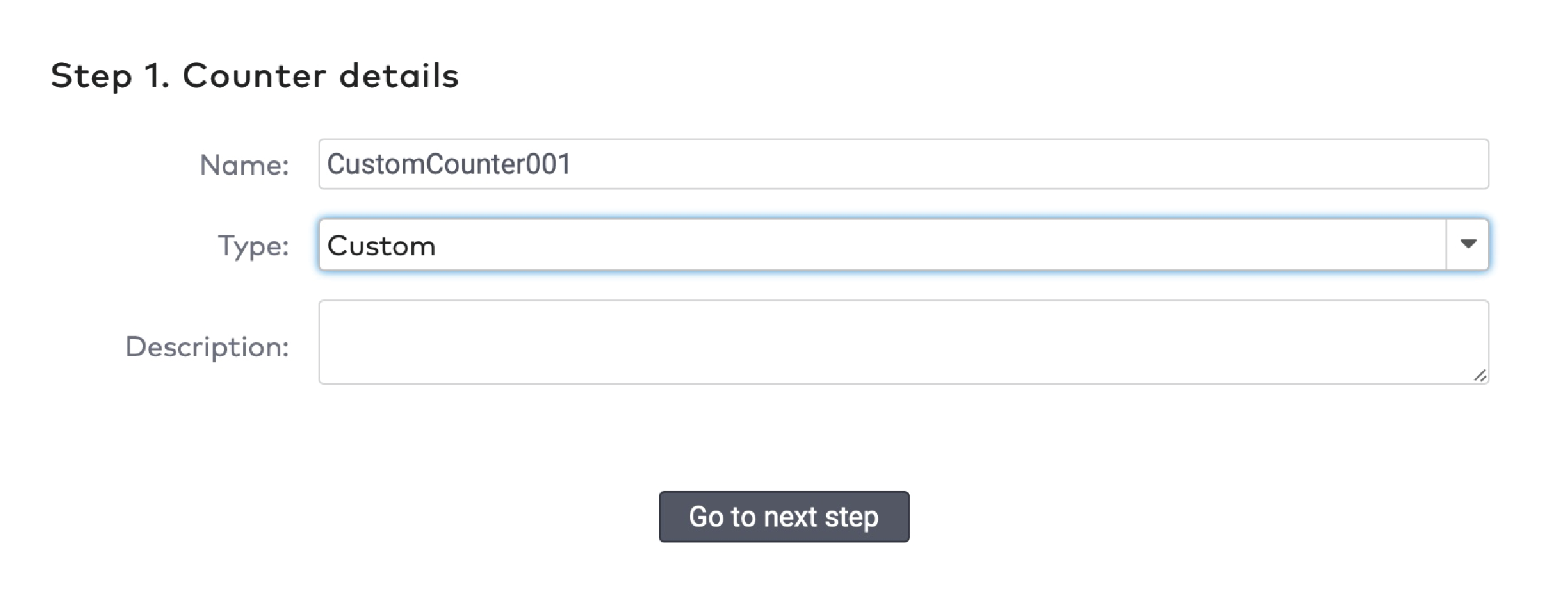
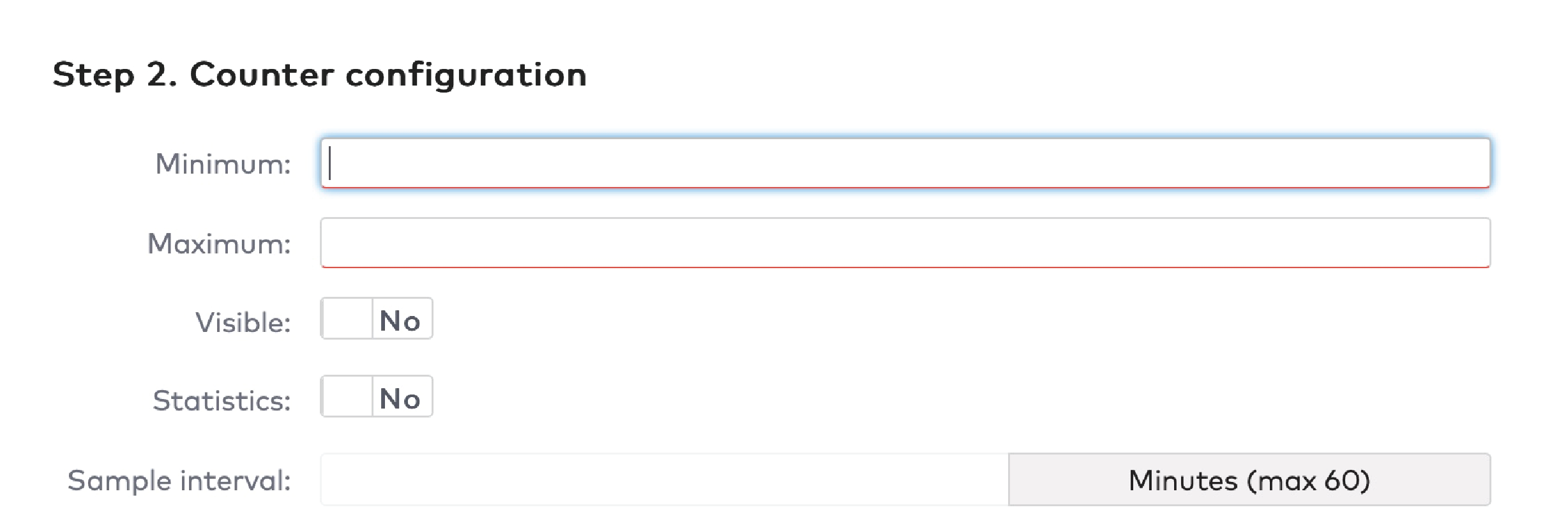
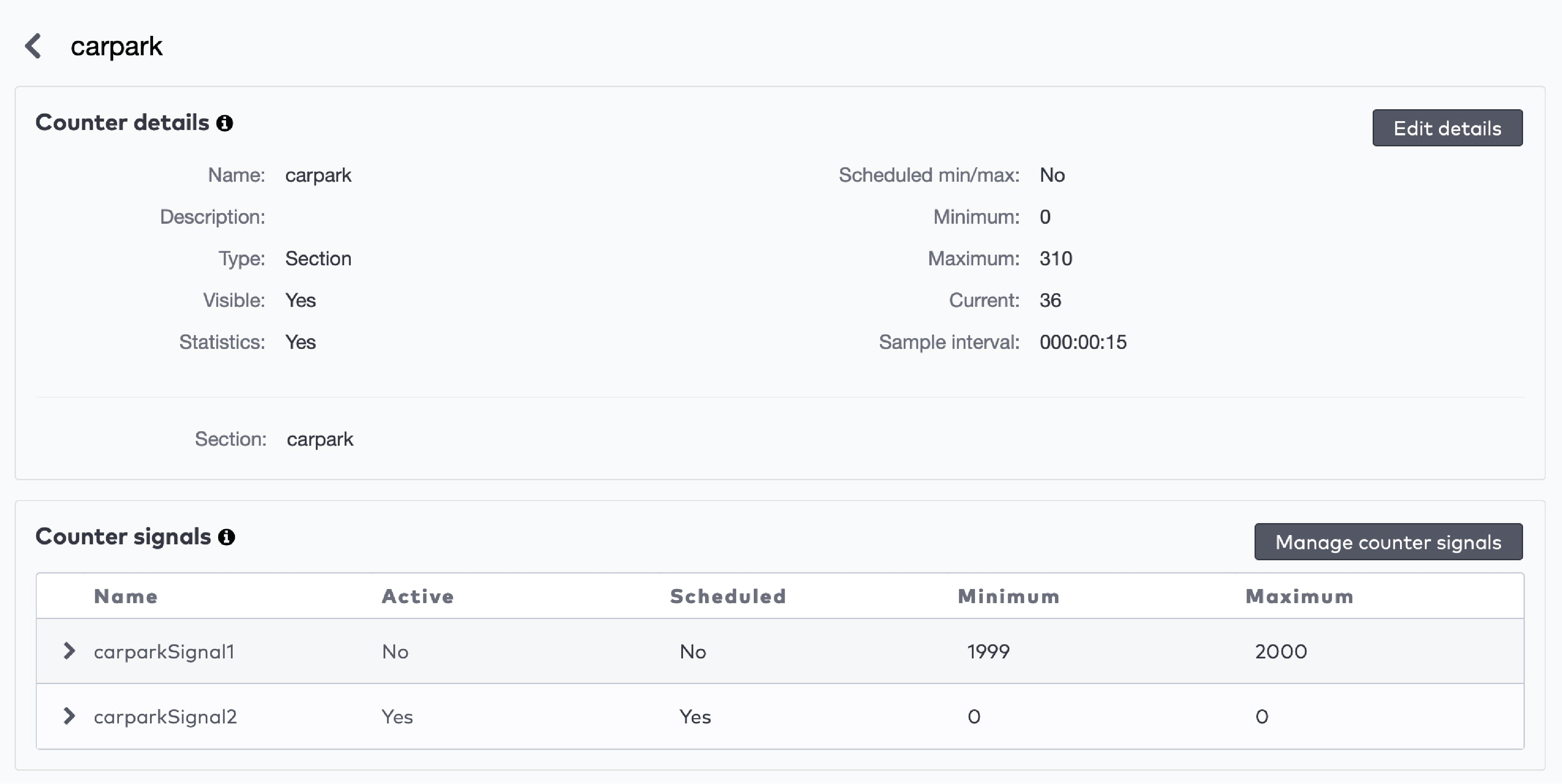
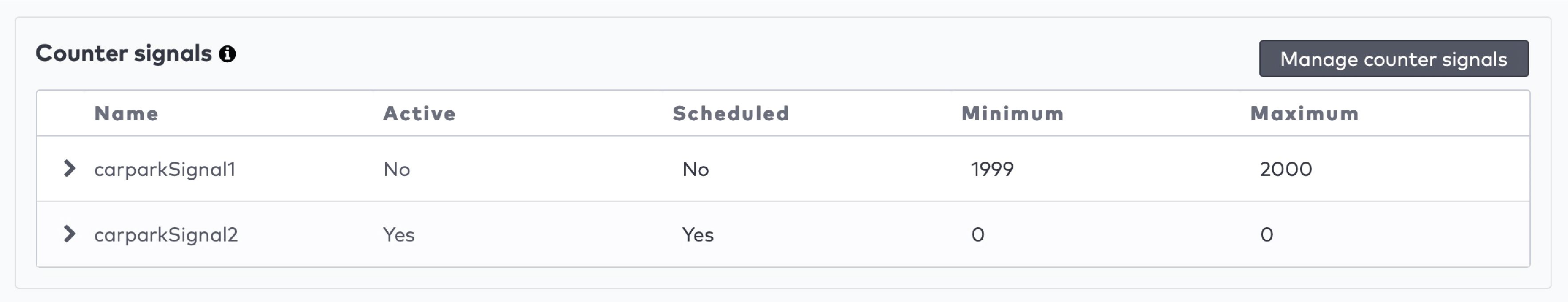
Example
You use a counter to count the number of visitors in a car park. The maximum capacity of your car park is 100 visitors. You configure a signal to be flagged when the car park reaches 100 visitors. The car park is closed and a message “Full” is displayed. You have configured the minimum value for the signal to be unflagged to be 98. When at least two visitors leave, the car park is opened again, and the message “Full” disappears.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
 next to the signal.
next to the signal.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
 to remove the orange bar.
to remove the orange bar.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
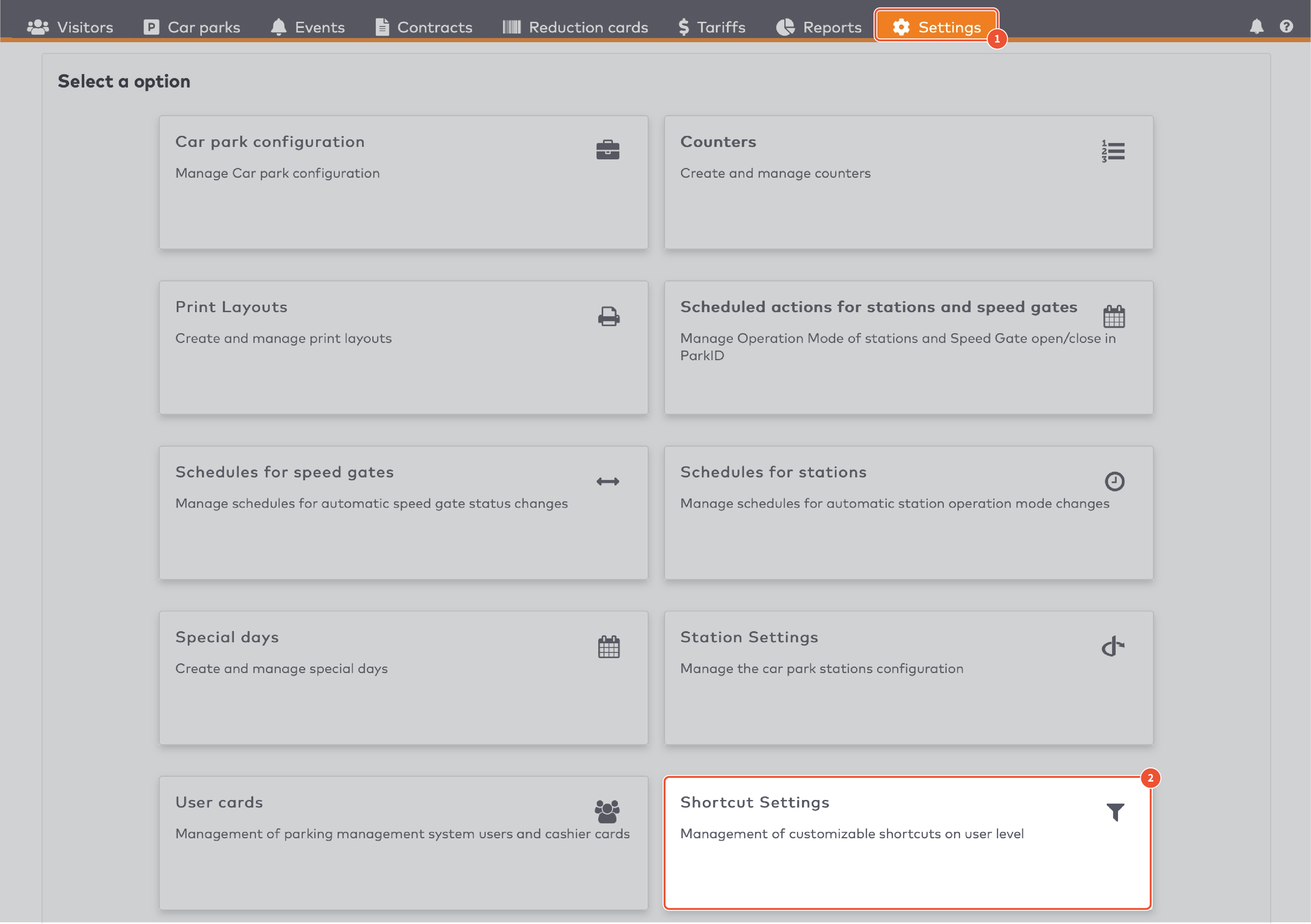
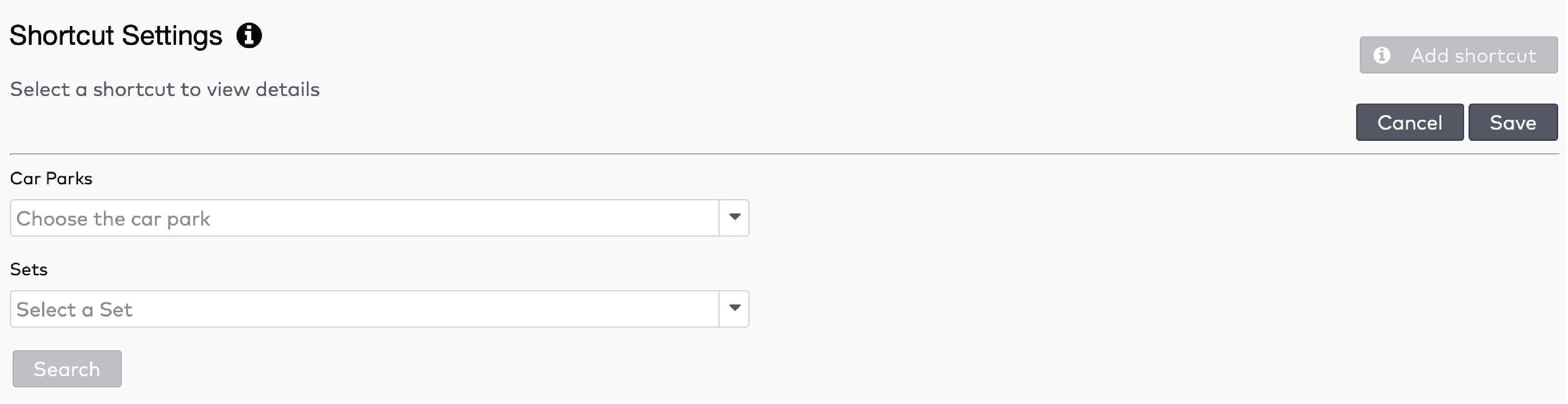
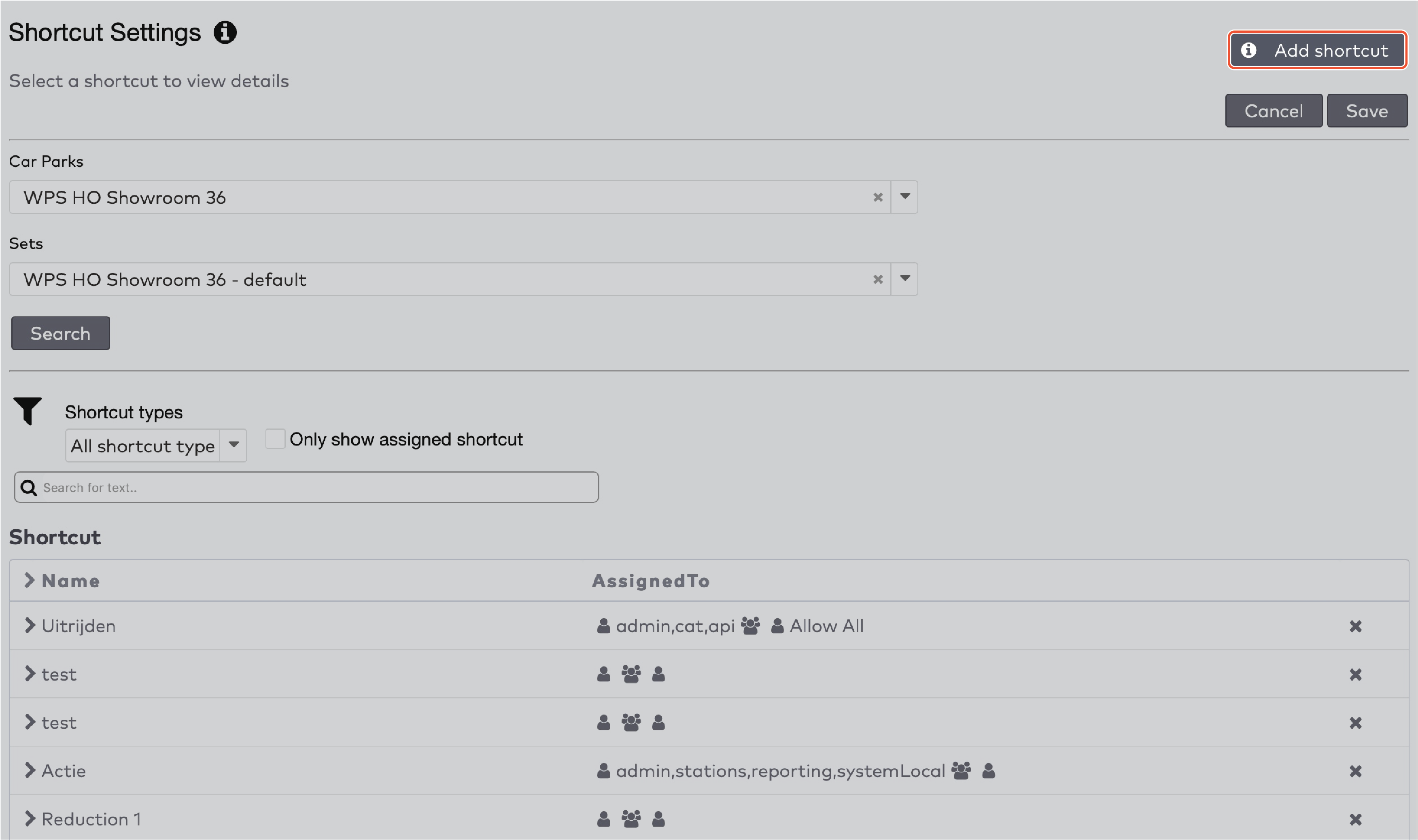
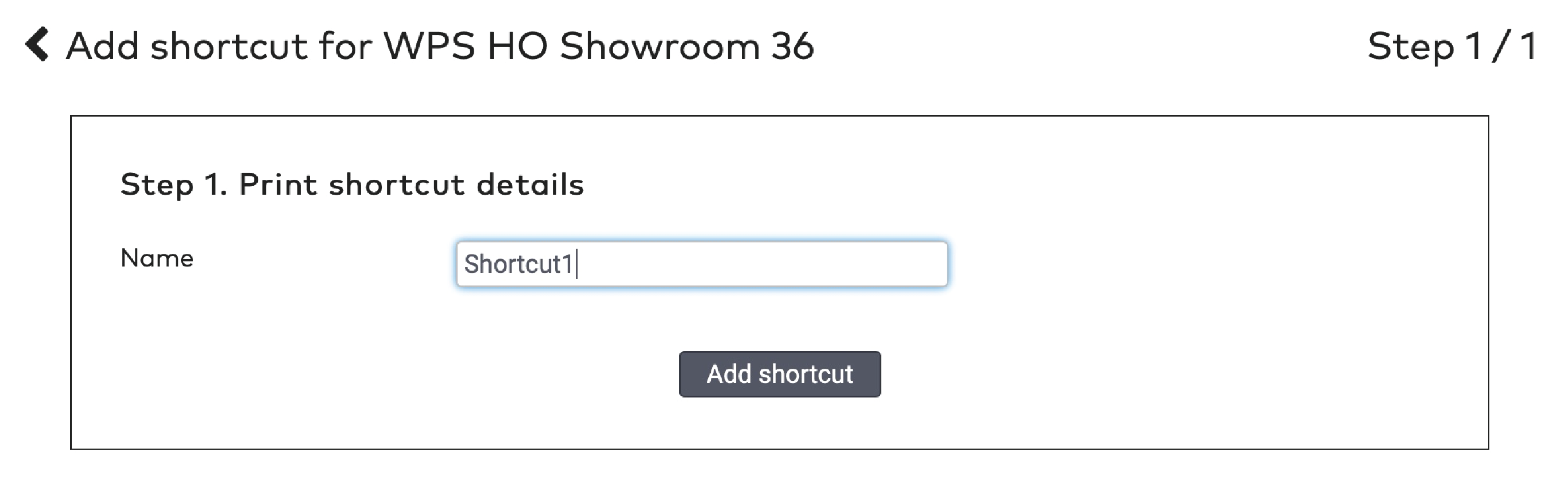
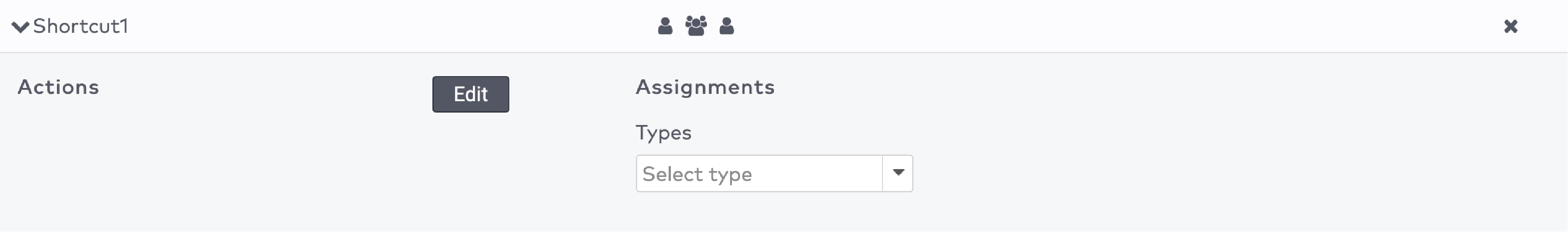
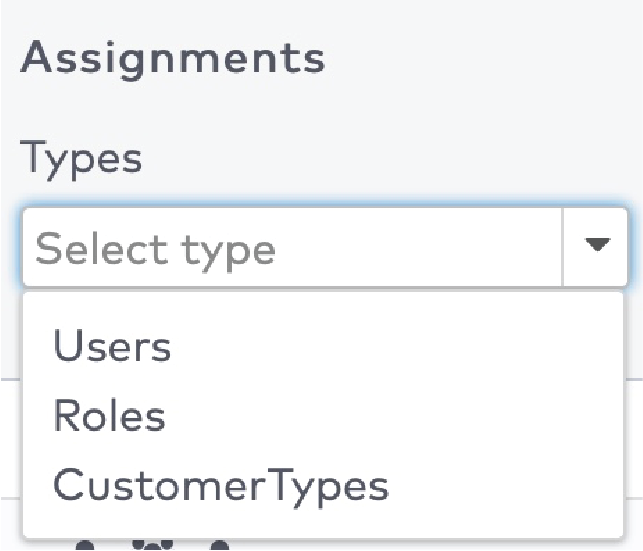
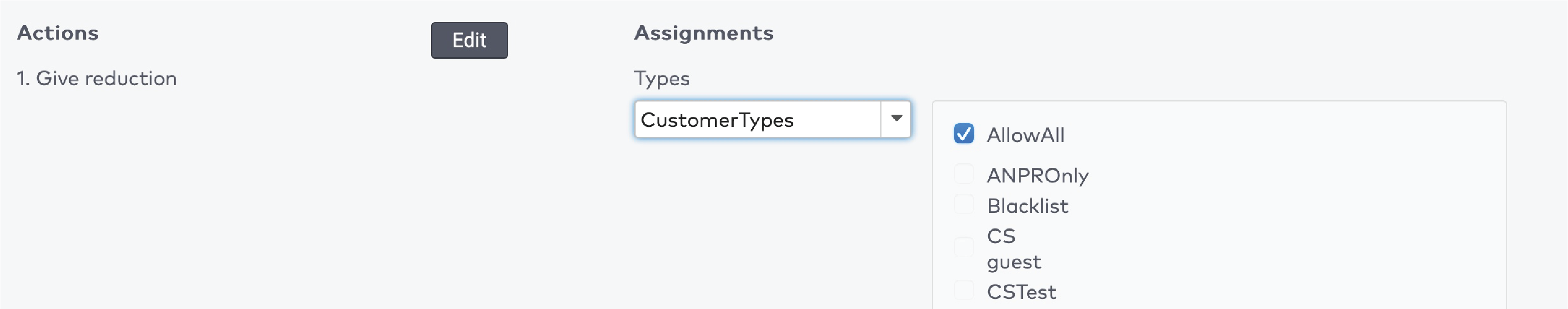
 next to the shortcut’s name.
next to the shortcut’s name.
|
|
|
|
 in the menu bar.
in the menu bar.

|
|
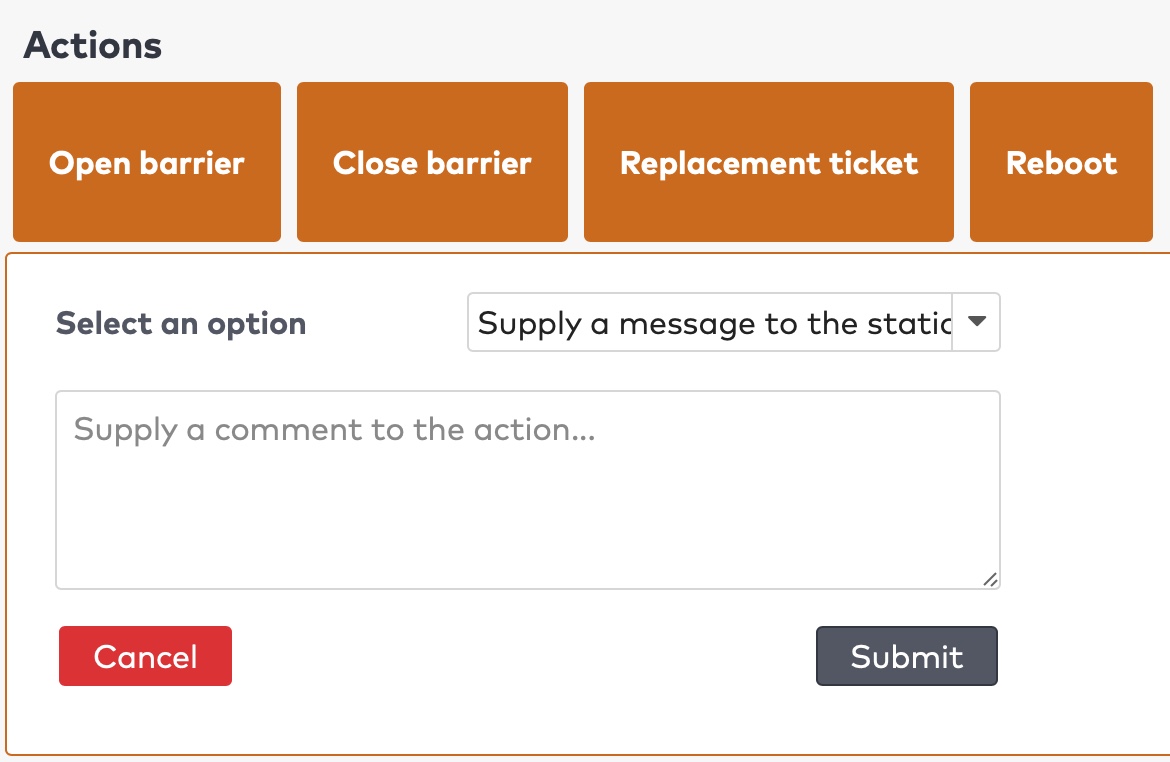
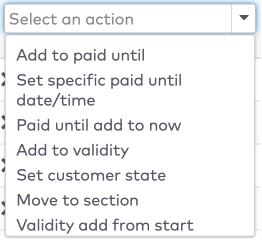
 next to the action
next to the action
|
|

|
|
|
Spring naar:
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
In dit artikel:
Individuele automaten bedienen. De automaten worden gegroepeerd per zone in de parkeerplaats (5)
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
De automaat is actief en werkt normaal.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Blijf gesloten. Bezoekers hebben geen doorgang.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Blijf open. Bezoekers kunnen inrijden en uitrijden.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Onderhoud. De automaat staat in de onderhoudsmodus. De automaat accepteert geen bezoekers.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Vol. De barrière gaat alleen open voor bezoekers met toegang tot parkeerplaatsen die vol zijn. Dit zijn bijvoorbeeld medewerkers, onderhoudspersoneel of andere personen die te allen tijde toegang tot de parkeerplaats moeten hebben.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Vrije doorgang. Accepteert bezoekers zonder te controleren op hun geldigheid, toestemming of schema.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat is ingesteld op Buiten werking. Deze automaat is buiten werking en de barrière is gesloten.
|

|
De automaat is offline en de status is onbekend.
|

|
De bedrijfsmodus van deze automaat wordt afgedwongen. Alle schema's voor deze automaat worden overschreven.
|

|

|

|
|
Bedrijfsmodus
|
Inrij-automaat
|
Uitrij-automaat
|
Betaalautomaat
|
Deur
|
|
Actief. Deze automaat werkt normaal.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Blijf gesloten. De automaat is continu gesloten. Bezoekers hebben geen doorgang.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Blijf open. De automaat is continu open. Bezoekers kunnen inrijden en uitrijden.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Onderhoud. De automaat staat in de onderhoudsmodus. De automaat accepteert geen bezoekers.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Vol. De barrière gaat alleen open voor bezoekers met toegang tot parkeerplaatsen die vol zijn. Dit zijn bijvoorbeeld medewerkers, onderhoudspersoneel of andere personen die te allen tijde toegang tot de parkeerplaats moeten hebben.
|
X
|
|||
|
Vrije doorgang Accepteert bezoekers zonder te controleren op hun geldigheid, toestemming of schema.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Buiten werking Deze automaat is buiten werking en de barrière is gesloten.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om een datum en tijd in te voeren.
om een datum en tijd in te voeren.

|

|

|
 naast de teller die u wilt aanpassen.
naast de teller die u wilt aanpassen.
 om de wijzigingen te annuleren.
om de wijzigingen te annuleren.

|
 naast de teller die u wilt aanpassen.
naast de teller die u wilt aanpassen.

|

|
|
De vijf meest recente systeemmeldingen (2)
|

|

|

|
 in de menubalk.
in de menubalk.

|

|

|
Kritieke melding
Een zeer belangrijk bericht aan de gebruiker over een onverwachte gedraging of status van het systeem die grote gevolgen kan hebben voor de systeemprestatie, gebruikerservaring of bezoekerservaring.
|

|
Melding
Een belangrijk bericht aan de gebruiker over een onverwachte gedraging of status van het systeem
|

|
Verzoek tot gebruikersactie
Een bericht om de gebruiker aan te zetten tot actie
|

|

|
 voor een gedetailleerde beschrijving ervan.
voor een gedetailleerde beschrijving ervan.

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Voorbeeld kortingskaart met barcode.
|
Voorbeeld kortingskaart met QR-code.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Type korting
|
|
Er zijn vijf typen korting:
Kortingsbedrag
Bepaalde tijd
Percentage
Verkoopbedrag
Tariefwisseling
Kortingsbedrag
Een bepaald bedrag wordt in mindering gebracht van het verschuldigde bedrag.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker die €10 moet betalen en een kortingskaart heeft met een bepaald bedrag van €6, betaalt €4.
Vul het Kortingsbedrag in.
Kies de toepasbare valuta uit het dropdown-menu.

Bepaalde tijd
Een bepaalde tijdsperiode wordt afgetrokken van de totale parkeertijd.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker die 1,5 uur heeft geparkeerd en een kortingskaart heeft met een bepaalde tijd van twee uur mag gratis uitrijden.
Vul het aantal Dagen, Uren en Minuten in in de bijbehorende velden.

Percentage
Het verschuldigde bedrag wordt verlaagd met een bepaald percentage van het oorspronkelijke bedrag.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker die €10 moet betalen en een kortingskaart heeft van 50%, betaalt €5.
Vul het Percentage in in hele getallen, zonder decimalen.
Vul een maximaal kortingsbedrag in, indien van toepassing.
Bijvoorbeeld: het maximale kortingsbedrag is €10 en een bezoeker moet €50 euro betalen. Hij heeft een kortingskaart van 50%, ontvangt de maximale korting van €10 en betaalt €40.

Verkoopbedrag
Het verschuldigde bedrag wordt vervangen met een bepaald bedrag.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker die €10 moet betalen en een kortingskaart heeft met verkoopbedrag van €3, betaalt €3.
Vul het Verkoopbedrag in in hele getallen, zonder decimalen.

Tariefwisseling
Het tarief dat wordt toegepast op de parkeertijd wordt gewijzigd.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker die 4 uur overdag heeft geparkeerd voor €2,50/uur en een kortingskaart met tariefwisseling heeft voor het gunstigere nachttarief van €2/uur, betaalt €8.
Kies een Tarief uit het dropdown-menu.

|
|
Type afrekening
|
|
Kortingskaarten worden betaald door de verstrekkende groep. U kunt de kosten bij de groep in rekening brengen:
Wanneer de kaarten worden aangemaakt (in rekening brengen bij uitgifte). Alle kaarten worden betaald, ongeacht of ze gebruikt worden.
Wanneer de kaarten daadwerkelijk worden gebruikt (in rekening brengen bij transactie). Ongebruikte kaarten worden niet in rekening gebracht.
Als u de kosten bij de groep in rekening brengt wanneer de kaarten daadwerkelijk worden gebruikt, kunt u:
Een bepaalde prijs per kaart bepalen (bepaalde prijs bij transactie), ongeacht de daadwerkelijke waarde van de korting. Bijvoorbeeld: u kunt een set kortingskaarten aanmaken met een percentagekorting van 50% en ze verkopen voor €2,50 per stuk.
Het exacte kortingsbedrag in rekening brengen (exacte prijs bij transactie).
Wanneer u uw keuze heeft gemaakt:
Kies het Type afrekening uit het dropdown-menu.

Vul het In rekening gebrachte bedrag in, indien van toepassing.

Kies een valuta uit het dropdown-menu.
Klik op Volgende stap.
|
|
Geldigheid
|
|
Kortingskaarten zijn beperkt geldig. U moet een datumbereik invoeren waarbinnen de kortingskaarten geldig zijn. U kan ook een tijdvak instellen waarbinnen ze geldig zijn. Bijvoorbeeld tussen 09:00 en 18:00.

Kies een Geldigheidstype uit het dropdown-menu. Dit kan een periode zijn in dagen vanaf de aanmaakdatum of een specifiek datumbereik.
Indien u kiest voor Periode, vul dan de Periode in dagen in.

Indien u kiest voor Specifiek, kies dan een startdatum en een einddatum.

Een tijdvak instellen waarbinnen de korting kan worden toegepast:
Vul een start- en eindtijd in bij het veld Toegestaan gebruik.

U kunt kortingskaarten geldig maken voor één of meerdere keren of voor een ongelimiteerd aantal keren. Onder Aantal gebruiken
Zet Onbeperkt op Ja als u kaarten wilt zonder gebruiksbeperking.
Zet Onbeperkt op Nee als u het gebruik van de kaarten wilt beperken. Vul het maximaal Aantal gebruiken in.

Klik op Volgende stap.
|

|

|

|
|
Afdrukopties
|
|
Stel het Aantal kortingskaarten in om aan te maken. Het maximale aantal kaarten is 9.999.
Kies de gewenste Papierinstellingen.
Vink Exporteer als CSV aan als u de volgnummers en barcodenummers in een apart bestand wilt bewaren.
|

|

|

|
|
Afdrukopties
|
|
Stel het Aantal kortingskaarten in om aan te maken. Het maximale aantal kaarten is 9.999.
Kies de gewenste Papierinstellingen.
Vink Exporteer als CSV aan als u de volgnummers en barcodenummers in een apart bestand wilt bewaren.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
ParkID detecteert misbruik van bezoekersidentificatoren. Dit staat bekend als anti-passback. Bijvoorbeeld wanneer dezelfde bezoekersidentificator tegelijkertijd wordt gebruikt door twee of meer bezoekers.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om de oranje balk te verwijderen.
om de oranje balk te verwijderen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Met Poelen kunt u het aantal bezoekers van een groep beperken. Er zijn drie soorten poelen:
1.
Bezoekers wordt de toegang geweigerd wanneer het maximaal aantal bezoekers is bereikt.
2.
Als poelschending wordt de gehele parkeertijd in rekening gebracht bij de bezoekers.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker (bezoek 1) rijdt de parkeerplaats in en maakt gebruik van de poel. Bezoek 1 wordt in rekening gebracht volgens het standaardtarief dat is ingesteld voor de groep. Wanneer bezoek 2 aankomt, is de poel vol. Voor bezoek 2 wordt voor de gehele parkeertijd een ander tarief in rekening gebracht.

3.
Alleen de parkeertijd gedurende de poelschending wordt in rekening gebracht bij de bezoekers.
Bijvoorbeeld: een bezoeker (bezoek 1) rijdt de parkeerplaats in en maakt gebruik van de poel. Bezoek 1 wordt in rekening gebracht volgens het standaardtarief dat is ingesteld voor de groep. Wanneer bezoek 2 aankomt, is de poel vol. Voor bezoek 2 wordt een ander tarief in rekening gebracht. Wanneer bezoek 1 uitrijdt, komt er een plek beschikbaar in de poel. Voor bezoek 2 wordt vanaf dat moment het standaardtarief in rekening gebracht.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om de barcode te printen.
om de barcode te printen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om de barcode te printen.
om de barcode te printen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om de barcode te printen.
om de barcode te printen.

|

|

|
 in het dropdown-menu Groep.
in het dropdown-menu Groep.

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om een identificator te verwijderen.
om een identificator te verwijderen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
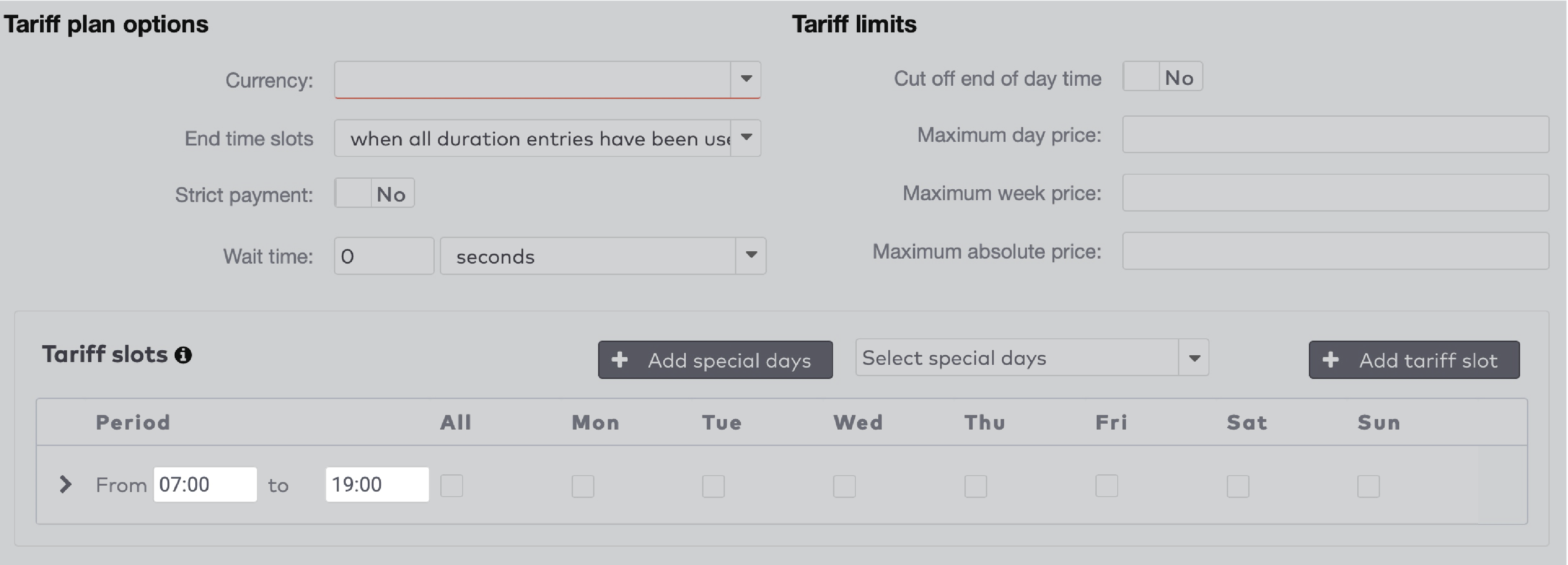
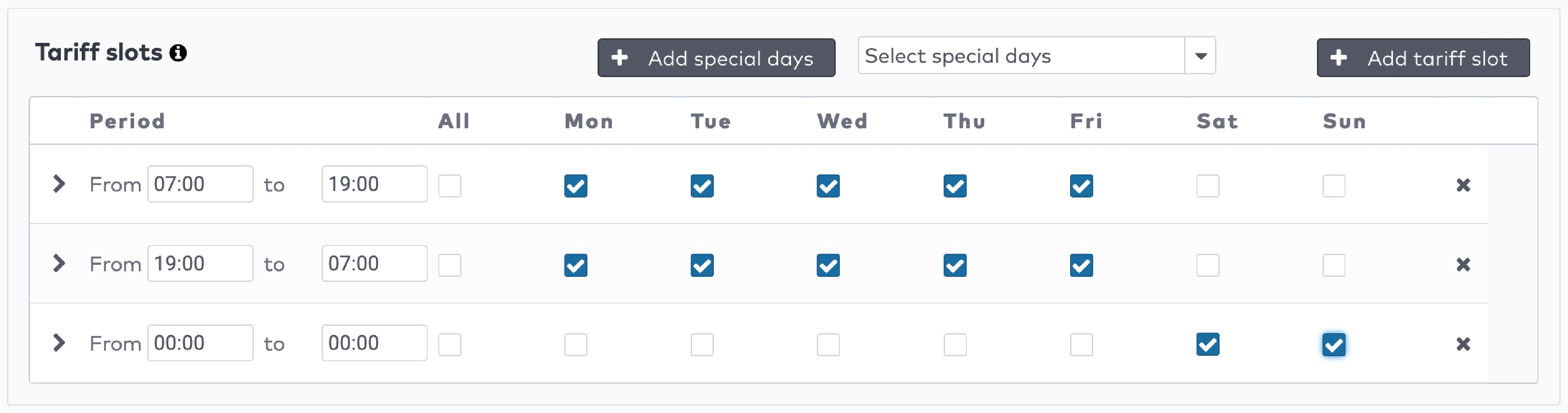
 om de tijdvakken voor dit tariefvenster in te stellen. Klik op
om de tijdvakken voor dit tariefvenster in te stellen. Klik op  om een nieuw tijdvak toe te voegen.
om een nieuw tijdvak toe te voegen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Voorbeeld
U kunt een teller gebruiken om het aantal bezoekers op een parkeerplaats te tellen. Uw parkeerplaats heeft plaats voor maximaal 100 bezoekers. U configureert een signaal dat wordt geactiveerd wanneer er 100 bezoekers op de parkeerplaats zijn. De parkeerplaats wordt gesloten en het bericht ‘Vol’ wordt getoond. U hebt als minimumwaarde voor opheffing van het signaal ‘98’ ingesteld. Wanneer minimaal twee bezoekers uitrijden, wordt de parkeerplaats weer geopend en verdwijnt het bericht ‘Vol’.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 om de oranje balk te verwijderen.
om de oranje balk te verwijderen.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 in de menubalk.
in de menubalk.

|

|


|

|

|

|
|
Allez rapidement à :
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Allez rapidement à :
|

|
|
Dans cet article :
Gérez les stations individuelles. Les stations sont groupées par section dans le parking (5)
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
La station est active et fonctionne normalement.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Rester fermé » (Stay closed). Les visiteurs ne peuvent pas passer.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Rester ouvert » (Stay closed). Les visiteurs peuvent entrer et sortir librement.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Service » (Service). La station est en mode de maintenance. La station n’accepte pas les visiteurs.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Complet » (Full). La barrière ne s’ouvre que pour les visiteurs autorisés à accéder aux parkings lorsqu’ils sont pleins. Par exemple, les employés, le personnel de maintenance ou toute autre personne qui doit pouvoir accéder au parking à tout moment.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Accès libre » (Free to pass). Les visiteurs sont admis sans contrôler leur validité, leur autorisation ou leur planning.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de cette station est réglé sur « Hors service » (Out of order). La station est hors service et la barrière est fermée.
|

|
La station est hors ligne et le statut est inconnu.
|

|
Le mode de fonctionnement de la station est imposé. Tous les plannings de cette station sont outrepassés.
|
|
Dans cet article :
|

|

|

|
|
Mode de fonctionnement
|
Station d’entrée
|
Station de sortie
|
Station de paiement
|
Porte
|
|
Active (Actif). La station fonctionne normalement.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Stay closed (Rester fermé). La station est toujours fermée. Les visiteurs ne peuvent pas passer.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Stay open (Rester ouvert). La station est toujours ouverte. Les visiteurs peuvent entrer et sortir librement.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Service. (Maintenance) La station est en mode de maintenance. La station n’accepte pas les visiteurs.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Full (Complet). La barrière ne s’ouvre que pour les visiteurs autorisés à accéder aux parkings lorsqu’ils sont pleins. Par exemple, les employés, le personnel de maintenance ou toute autre personne qui doit pouvoir accéder au parking à tout moment.
|
X
|
|||
|
Free to pass (Accès libre). Les visiteurs sont admis sans contrôler leur validité, leur autorisation ou leur planning.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
Out of order (Hors service). La station est hors service et la barrière est fermée.
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour saisir la date et l’heure d’entrée.
pour saisir la date et l’heure d’entrée.

|

|

|
 près du compteur que vous souhaitez régler.
près du compteur que vous souhaitez régler.
 pour supprimer les modifications.
pour supprimer les modifications.

|
 près du compteur que vous souhaitez régler.
près du compteur que vous souhaitez régler.

|

|
|
Les cinq avertissements système les plus récents (2)
|

|

|

|
 dans la barre de menu.
dans la barre de menu.

|

|

|
« Avertissement critique » (Critical warning)
Un message très important envoyé à l’utilisateur concernant un comportement inattendu du système ou un statut qui peut avoir des répercussions importantes sur la performance du système, l’expérience de l’utilisateur ou celle du visiteur.
|

|
« Avertissement » (Warning)
Un message important envoyé à l’utilisateur concernant un comportement ou un statut inattendu du système.
|

|
« Demandes d’actions de la part de l’utilisateur » (User action requests)
Un message destiné à inciter l’utilisateur à prendre des mesures.
|

|

|
 près de celui-ci :
près de celui-ci :

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Exemple de carte de réduction avec code-barres.
|
Exemple de carte de réduction avec code QR.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Type de réduction
|
|
Il existe cinq types de réduction :
Réduction du montant
Durée fixe
Pourcentage
Montant des ventes
Changement de tarif
Réduction du montant
Un montant fixe est soustrait du montant dû.
Par exemple : un visiteur qui doit payer une somme de 10 € et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction d’un montant fixe de 6 € paiera 4 €.
Complétez la « réduction du montant » (Amount reduction.)
Sélectionnez la « Devise applicable » (currency) dans le menu déroulant.

Durée fixe
Une durée fixe est soustraite du temps de stationnement total.
Par exemple, un visiteur qui aura stationné une heure et demie et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction d’un montant fixe de deux heures bénéficiera de la sortie gratuite.
Indiquez le nombre de « Jours » (Days), « Heures » (Hours ) et « Minutes » (Minutes) dans les champs respectifs.

Pourcentage
Le montant dû sera réduit d’un pourcentage défini de la somme d’origine.
Par exemple : un visiteur qui doit payer une somme de 10 € et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction de 50 % paiera 5 €.
Complétez le « Pourcentage » (Percentile) en nombres entiers, sans décimales.
Indiquez le cas échéant un « Montant de réduction maximal » maximum reduction.
Par exemple, si le montant maximal de réduction est de 10 €, un visiteur qui doit payer la somme de 50 € et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction de 50 % bénéficiera de la réduction maximale de 10 € et ne paiera que 40 €.

Montant des ventes
Le montant dû est remplacé par un montant défini.
Par exemple : un visiteur qui doit payer une somme de 10 € et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction avec un montant de ventes de 3 € paiera 3 €.
Complétez le champ « Montant des ventes » (Sales Amount) en nombres entiers, sans décimales.

Changement de tarif
Le tarif appliqué à la durée de stationnement est modifié.
Par exemple : un visiteur qui aura stationné 4 heures au cours de la journée à 2,50 €/heure et qui dispose d’une carte de réduction avec changement de tarif et offrant le tarif de nuit plus avantageux de 2 €/heure paiera 8 €.
Sélectionnez un « Tarif » Tariff dans le menu déroulant.

|
|
Type de facturation
|
|
Les cartes de réduction sont payées par le groupe émetteur. Vous pouvez faire payer le groupe
Lorsque les cartes sont créées (paiement à l’émission). Toutes les cartes sont payées, qu’elles soient utilisées ou non.
Lorsque les cartes sont réellement utilisées (paiement à la transaction). Les cartes non utilisées ne seront pas facturées.
Si vous facturez le groupe lorsque les cartes sont réellement utilisées, vous pouvez soit
Définir un montant fixe par carte (facturation fixe par transaction) quelle que soit la valeur réelle de la réduction. Par exemple, vous pourriez créer un groupe de cartes de réduction avec un pourcentage de réduction de 50 % et les vendre 2,50€ chacune.
Facturer le montant de réduction exact (facturation exacte par transaction).
Lorsque vous avez fait votre choix :
Sélectionnez le « Type de facturation » (Charge Type) dans le menu déroulant.

Indiquez le « Montant de facturation » (Charge amount), le cas échéant.

« Sélectionnez une devise » (Select a currency) depuis le menu déroulant.
Cliquez sur « Aller à l’étape suivante » (Go to next step).
|
|
Validité
|
|
Les cartes de réduction ont une validité limitée. Vous devez spécifier une plage de dates pendant laquelle la carte de réduction peut être utilisée. En outre, vous pouvez définir une fenêtre horaire pendant laquelle elle peut aussi être utilisée. Par exemple entre 9 h et 18 h.

Sélectionnez un « Type de validité » (Validity type) dans le menu déroulant. Il peut s’agir d’une « durée » (duration) en jours à compter de la date de création, ou d’une plage de dates spécifiques (specific).
Si vous avez sélectionné « Durée » (Duration), complétez le champ « Durée en jours » (Duration in days).

Si vous avez sélectionné « Plage de dates spécifique » (Specific), choisissez une « date de début » (start ) et une « date de fin » (end).

Pour définir la plage de temps dans laquelle la réduction peut être appliquée :
Indiquez une « heure de début » (start ) et une « heure de fin » (end) dans le champ « Utilisation autorisée » (Allowed usage).

Vous pouvez définir des cartes de réduction à usage unique, à usages multiples ou à usage illimité. Dans « Nombre d’utilisations » (Usage count)
Placez « Illimité » (Unlimited) sur « Oui » (Yes) si vous voulez des cartes sans limite d’utilisation.
Placez « Illimité » (Unlimited) sur « Non » (No) si vous voulez limiter l’utilisation des cartes. Indiquez le « nombre d’utilisations » maximal (Number of uses).

Cliquez sur « Aller à l’étape suivante » (Go to next step).
|

|

|

|
|
Options d’impression
|
|
Définissez le « nombre de cartes de réduction » (Number of reduction cards) à générer. Le nombre maximal de cartes est 9 999.
Sélectionnez la « configuration de papier » (Paper configuration) appropriée.
Cochez « Exporter en fichier csv » (Export to CSV) si vous voulez enregistrer les numéros de séquence et les numéros de code-barres dans un fichier séparé.
|

|

|

|
|
Options d’impression
|
|
Définissez le « nombre de cartes de réduction » (Number of reduction cards) à générer. Le nombre maximal de cartes est 9 999.
Sélectionnez la « configuration de papier » (Paper configuration) appropriée.
Cochez « Exporter en fichier csv » (Export to CSV) si vous voulez enregistrer les numéros de séquence et les numéros de code-barres dans un fichier séparé.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
ParkID détecte toute mauvaise utilisation des identifiants de visiteur. C’est ce qu’on appelle l’anti-pass back (ou anti-retour). Par exemple : lorsque le même identifiant de visiteur est utilisé par deux visiteurs ou plus en même temps.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour supprimer la barre orange.
pour supprimer la barre orange.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Avec « Regroupement » (Pooling), vous pouvez limiter le nombre de visiteurs d’un groupe. Il existe trois types de regroupement :
1.
Les visiteurs se voient refuser l’accès lorsque le nombre maximal de visiteurs est atteint.
2.
Les visiteurs sont facturés pour la durée entière de stationnement au titre de violation du regroupement.
Par exemple : un visiteur (visit 1) entre dans le parking tout en utilisant le regroupement. « Visit 1 » est facturé au tarif normal configuré pour le groupe. Lorsque « visit 2 » arrive, le regroupement est complet. « Visit 2 » sera facturé pour la durée entière à un tarif différent.

3.
Les visiteurs ne sont facturés que pour la durée de stationnement en statut de violation du regroupement.
Par exemple : un visiteur (visit 1) entre dans le parking tout en utilisant le regroupement. « Visit 1 » est facturé au tarif normal configuré pour le groupe. Lorsque « visit 2 » arrive, le regroupement est complet. « Visit 2 » est facturé à un tarif différent. Lorsque « visit 1 » part, un emplacement devient disponible dans le regroupement. « Visit 2 » est, à partir de ce moment-là, facturé au tarif normal.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour imprimer le code-barres.
pour imprimer le code-barres.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour imprimer le code-barres.
pour imprimer le code-barres.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour imprimer le code-barres.
pour imprimer le code-barres.

|

|

|
 dans le menu déroulant « Groupe ».
dans le menu déroulant « Groupe ».

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour supprimer un identifiant.
pour supprimer un identifiant.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour créer les enregistrements de durée pour ce créneau tarifaire. Appuyez sur
pour créer les enregistrements de durée pour ce créneau tarifaire. Appuyez sur  pour ajouter un nouvel enregistrement de durée.
pour ajouter un nouvel enregistrement de durée.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Exemple
Vous utilisez un compteur pour compter le nombre de visiteurs dans un parking. La capacité maximale de votre parking est de 100 visiteurs. Vous configurez un signal pour qu'il s’active lorsque le parking atteint 100 visiteurs. Le parking est fermé et un message « Complet » est affiché. Vous avez configuré la valeur minimale pour que le signal soit désactivé à 98. Lorsqu'au moins deux visiteurs partent, le parking est à nouveau ouvert et le message « Complet » disparaît.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 à côté du signal.
à côté du signal.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 pour supprimer la barre orange.
pour supprimer la barre orange.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 à côté du nom du raccourci.
à côté du nom du raccourci.

|

|

|

|
 dans la barre de menu.
dans la barre de menu.

|

|
 à côté de l’action.
à côté de l’action.

|

|

|

|